TRANSFAC 2.0
Explore TRANSFAC packages
Discover
TF binding sites in promoters
and enhancers of your genes
Reconstruct
signal transduction network
controlling your genes
Identify
drug targets
and disease biomarkers
TRANSFAC BASIC
Discover TF binding sites in promoters and enhancers of your genes
Introduction
TRANSFAC® is the database of eukaryotic transcription factors, their genomic binding sites and DNA-binding profiles. Dating back to a very early compilation 35 years ago, it has been carefully maintained and curated to become the gold standard in the field. Since then this biggest collection of transcription factors and their genomics binding sites has served the scientific community as the most reliable and comprehensive resource for gene regulation studies.
You can use TRANSFAC® as an encyclopedia of transcriptional regulation, or as a tool to identify potential TFBSs by applying its library of positional weight matrices, a unique collection of DNA-binding models. The latter can be done with the included MATCH (Suite) tools or with any of the respective modules in the geneXplain platform.
Database content
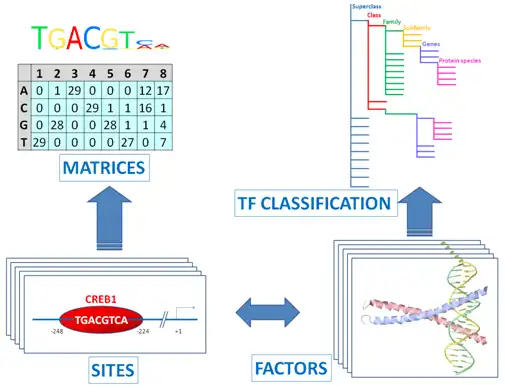
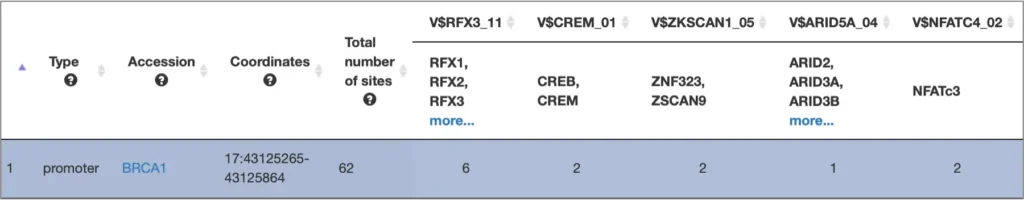
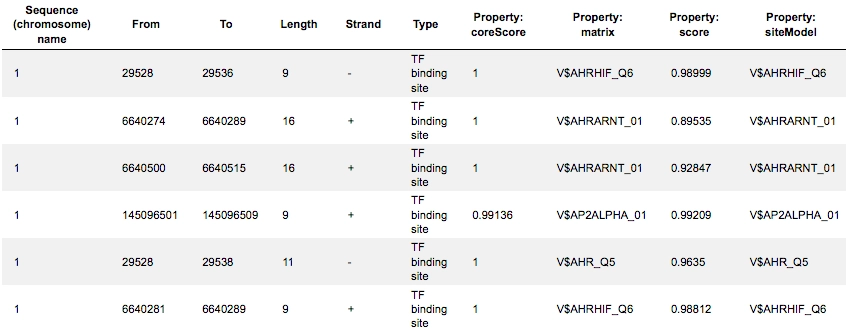
The core of TRANSFAC® comprises contents of two domains: One documents transcription factor-binding sites (TFBSs, SITES), usually in promoters or enhancers, and the derived DNA binding motifs in form of positional weight matrices (PWMs, MATRICES). The other describes the transcription factors (TFs, FACTORS) subsumed to classes, based on the general properties of their DNA-binding domains, which has been expanded to a comprehensive classification (TF CLASSIFICATION), the latest version of which can be found here.
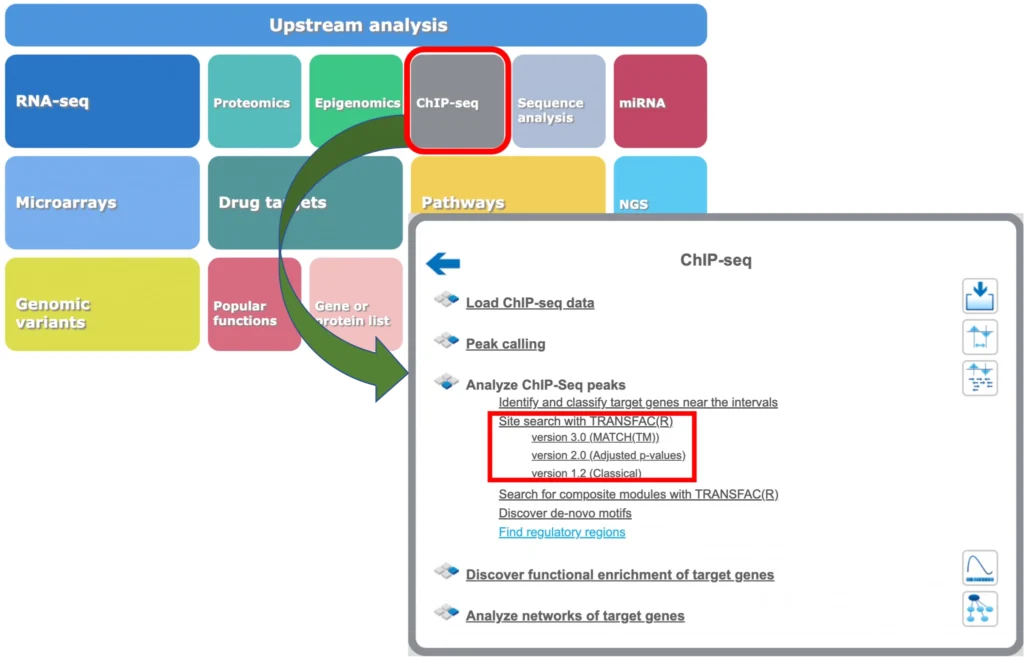
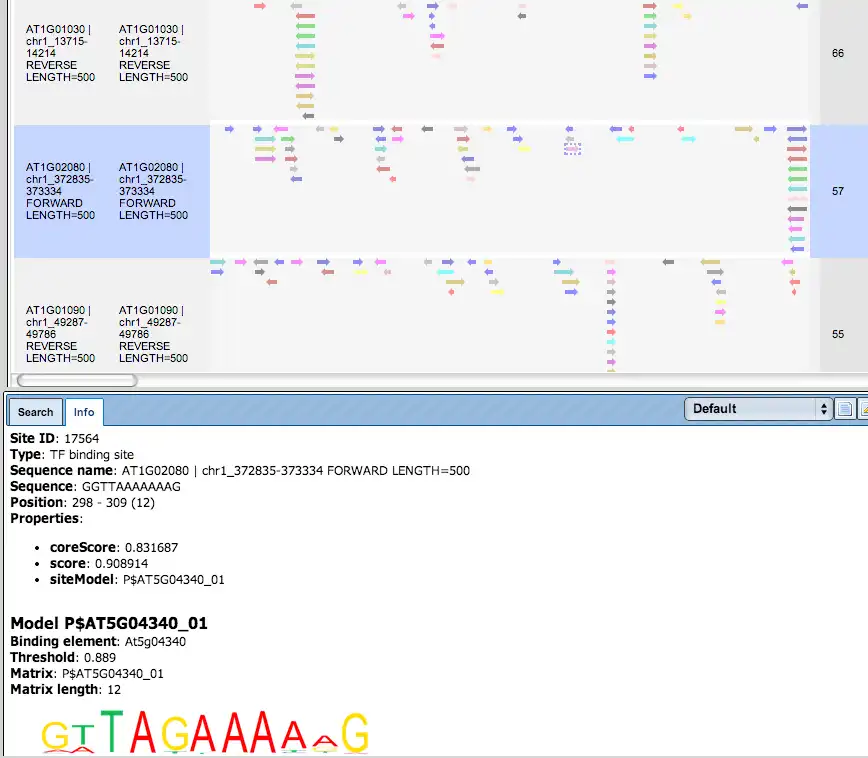
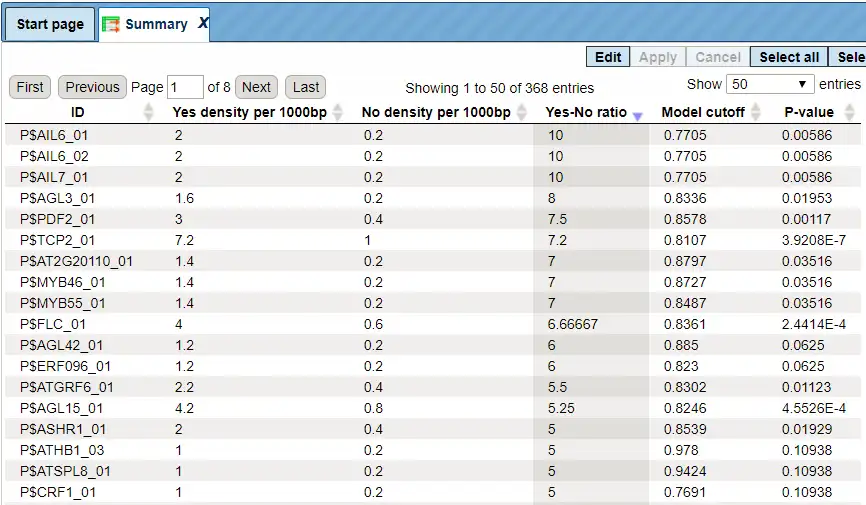
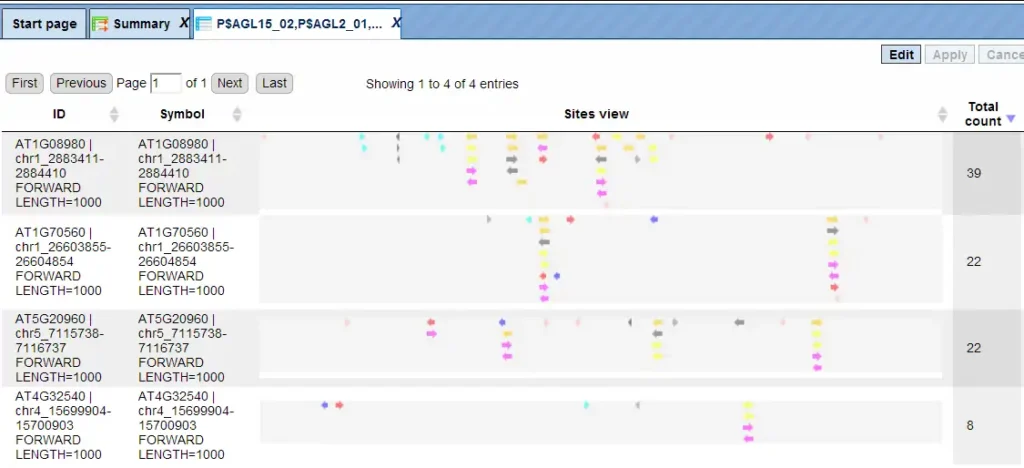
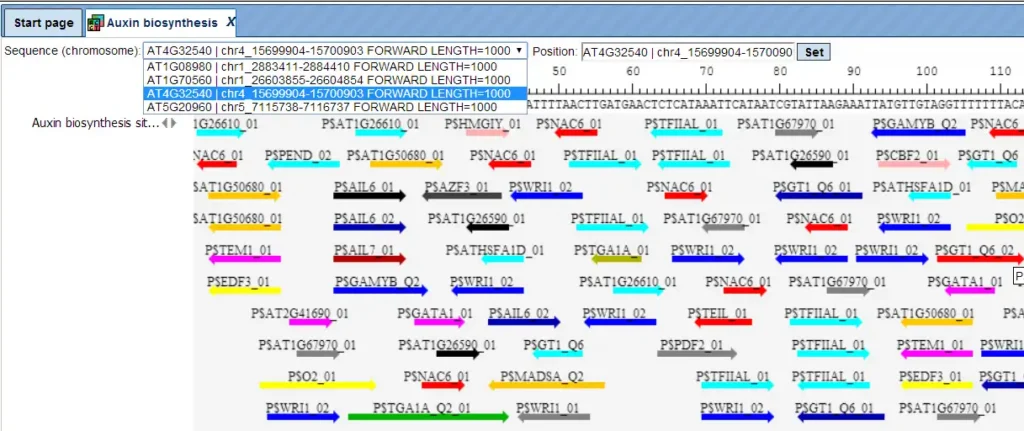
TRANSFAC search interface
The TRANSFAC® database search interface is provided in the web browser online.
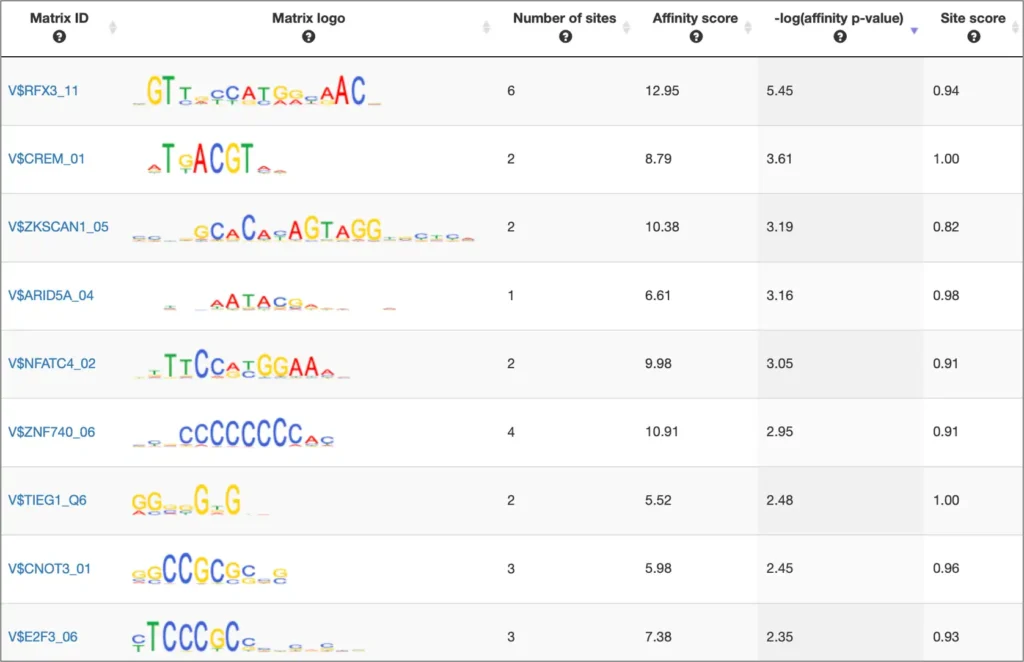
PWMs:
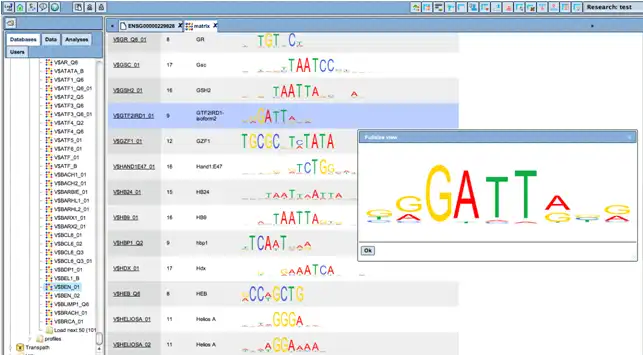
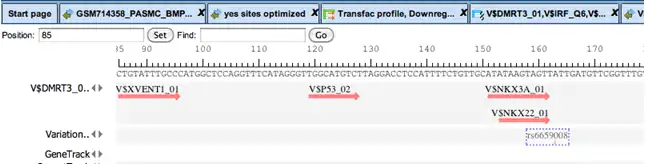
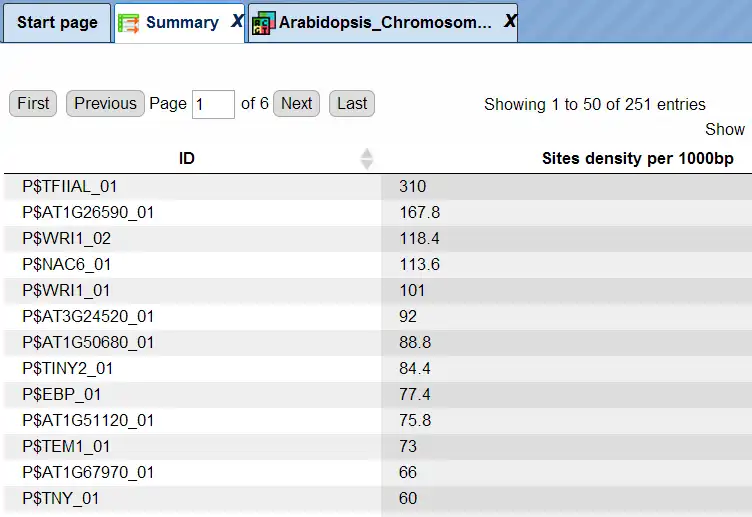
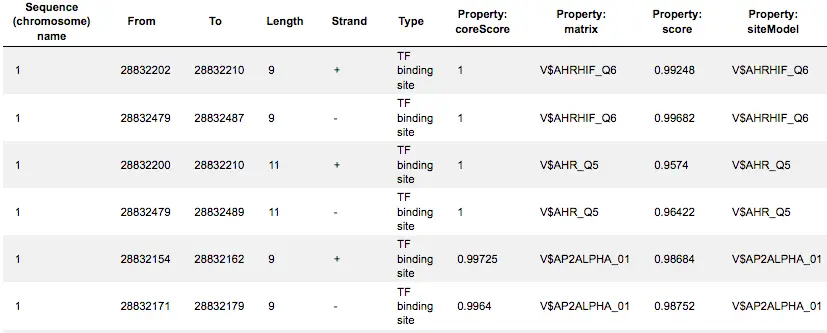
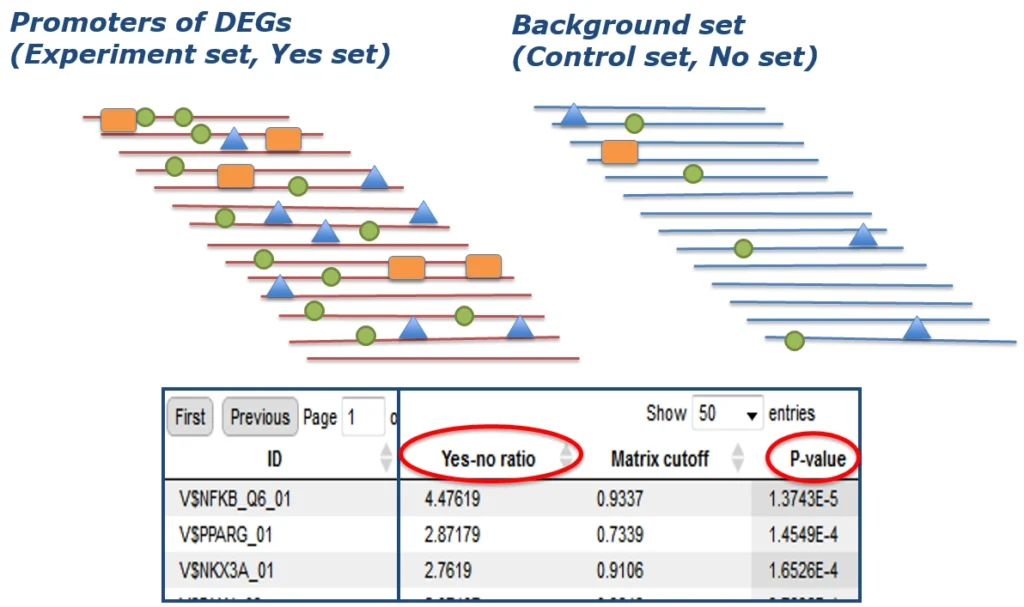
Binding sites referring to the same TF are merged into a positional weight matrix. Such a matrix reflects the frequency with which each nucleotide is found in each position of this TF’s binding sites and, thus, the base preference in each position.
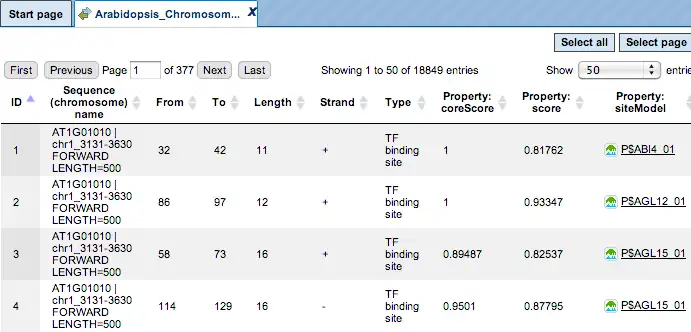
TF Sites:
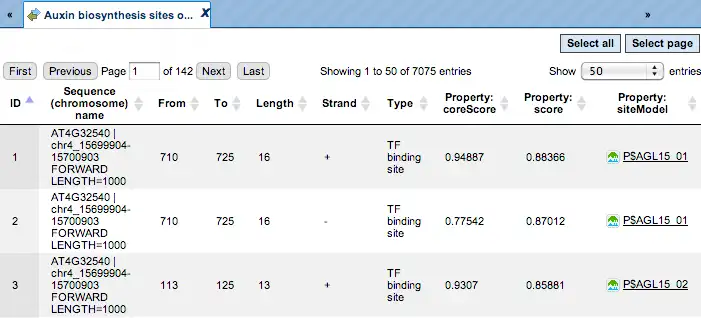
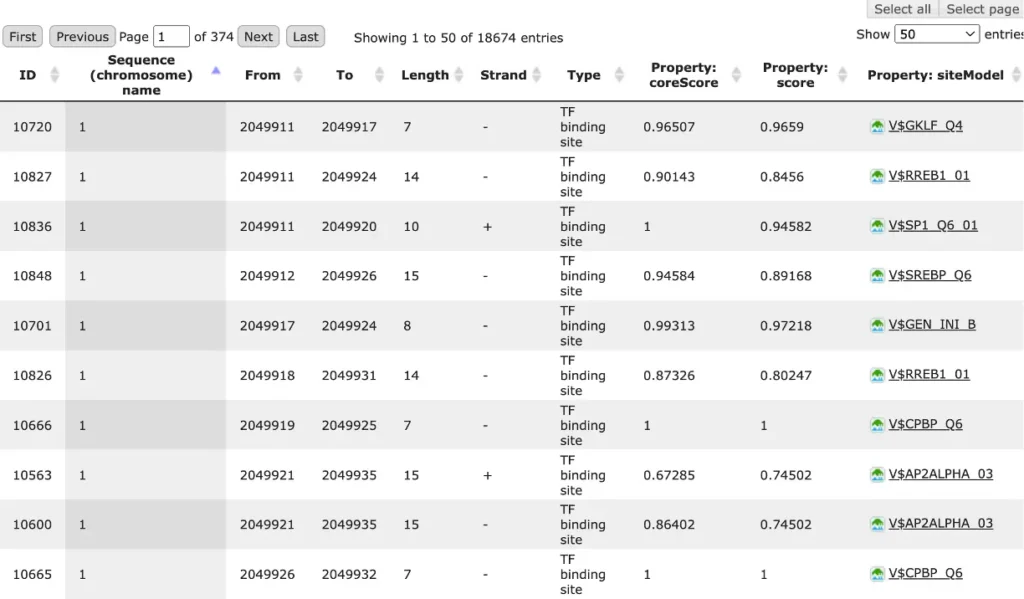
TRANSFAC® includes over 50,000 experimentally proven TF binding sites and about 100 million ChIP-seq TF binding regions.
ChIP-seq sites
TRANSFAC® includes 100 million ChIP-seq TF binding regions.
Promoters, Enhancers:
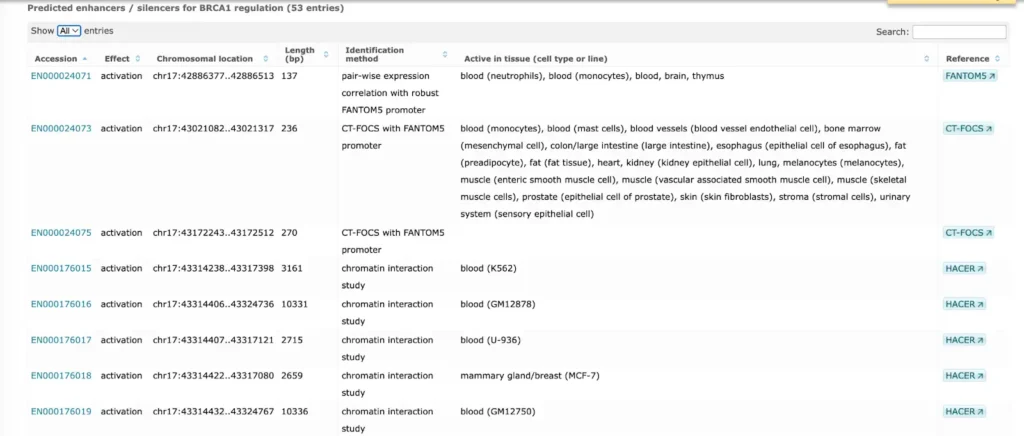
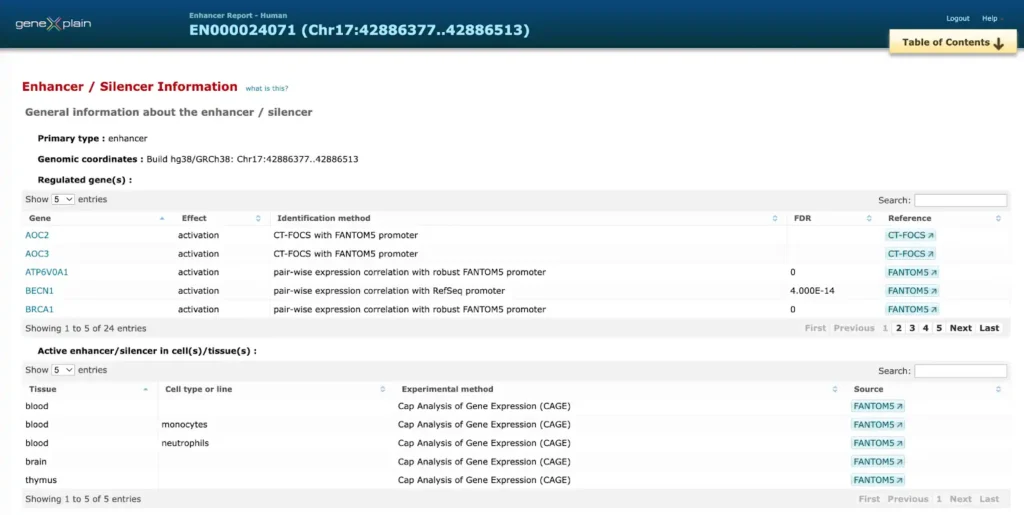
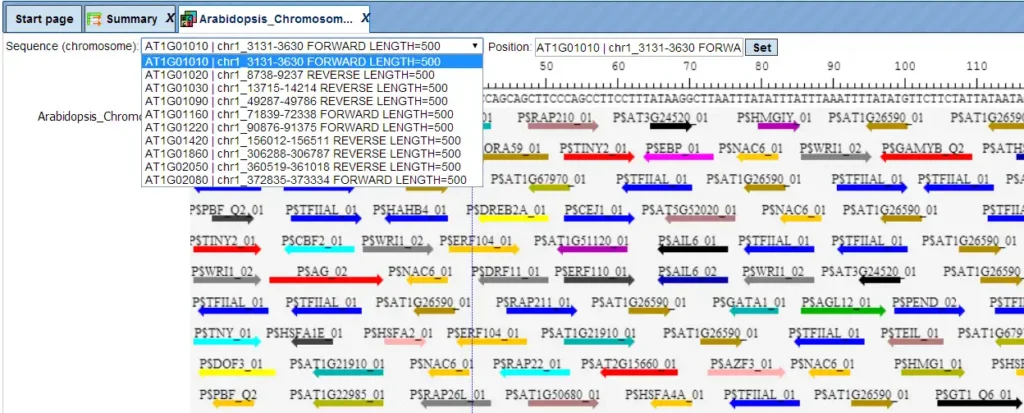
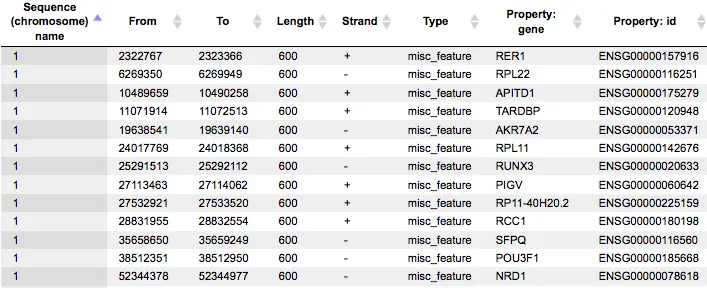
TRANSFAC® includes promoter genomic annotation for various vertebrate and invertebrate species as well as for plants and fungi. TRANSFAC® also includes genomic information for over 200,000 human enhancers and silences acting in different tissues and cell type-specific.
Tools
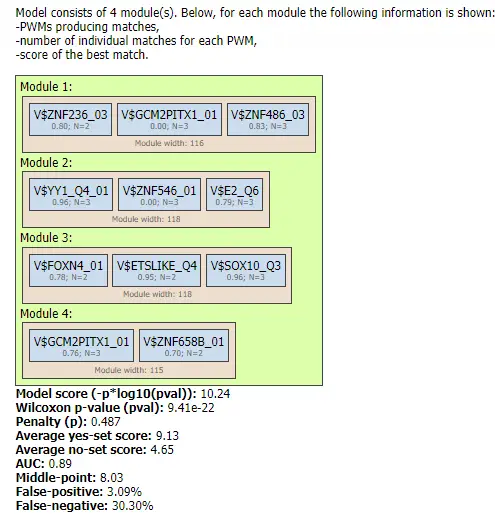
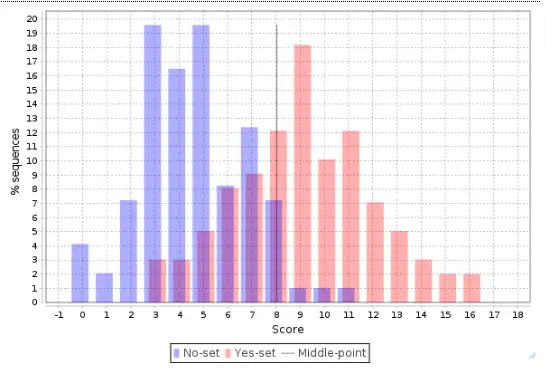
The PWMs in TRANSFAC are the basis for TFBS predictions with the included tools for analysis of DNA sequences of individual promoters, enhancers and other regulatory regions to the analysis of Omics data derived gene sets (DEGs).
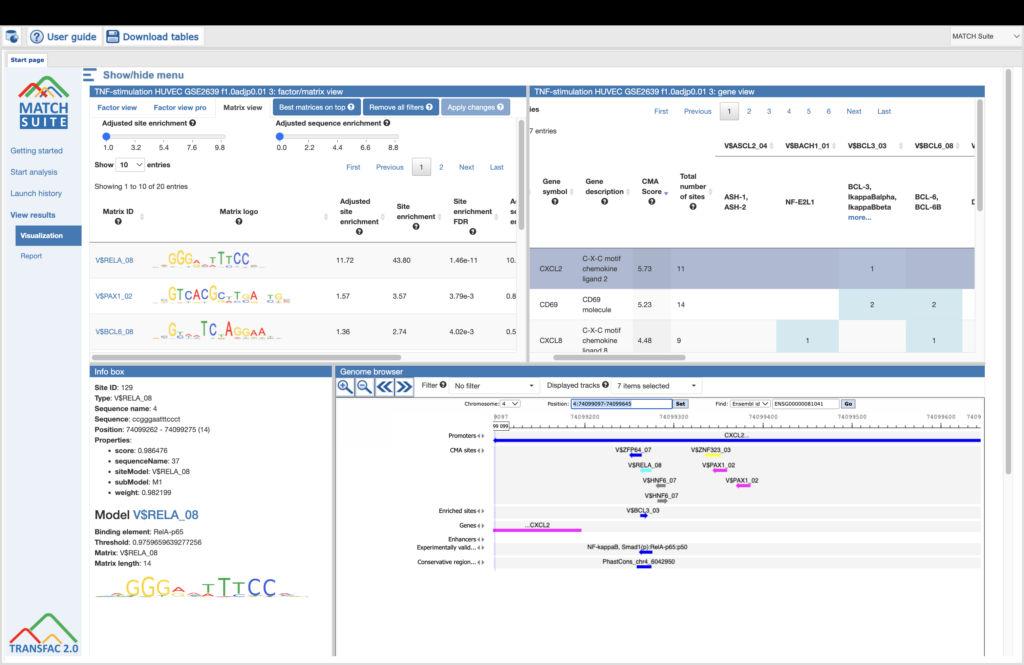
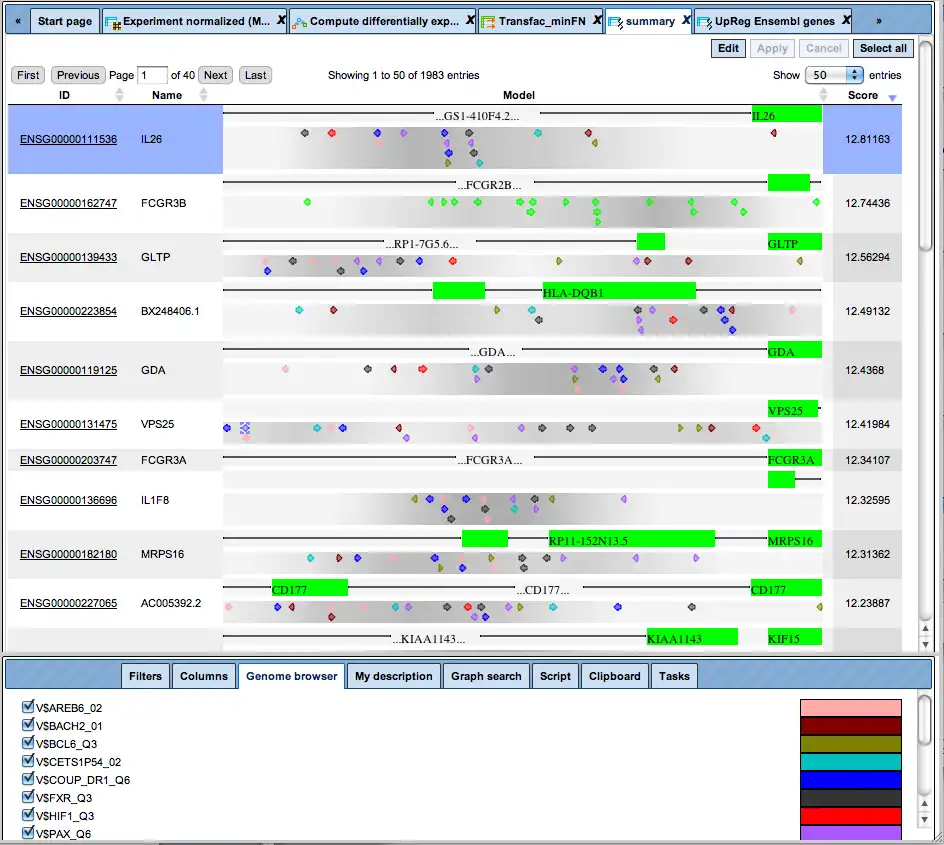
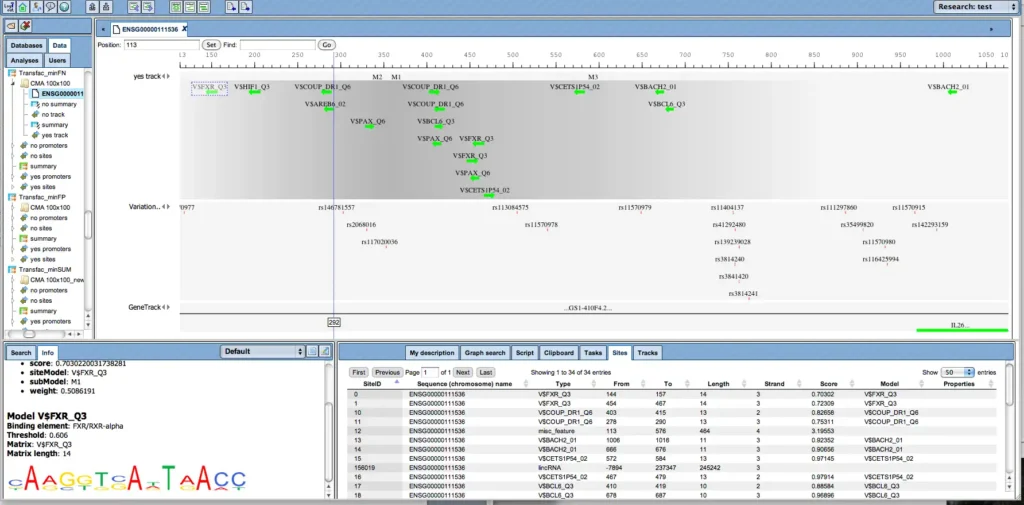
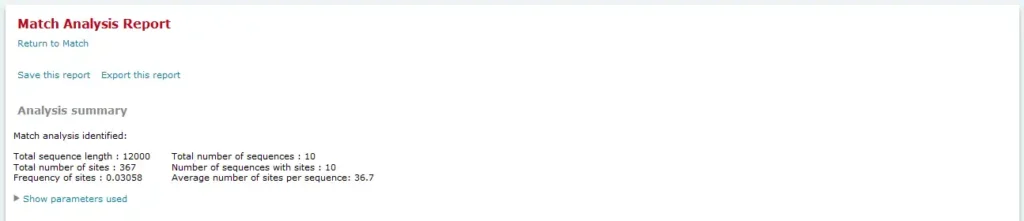
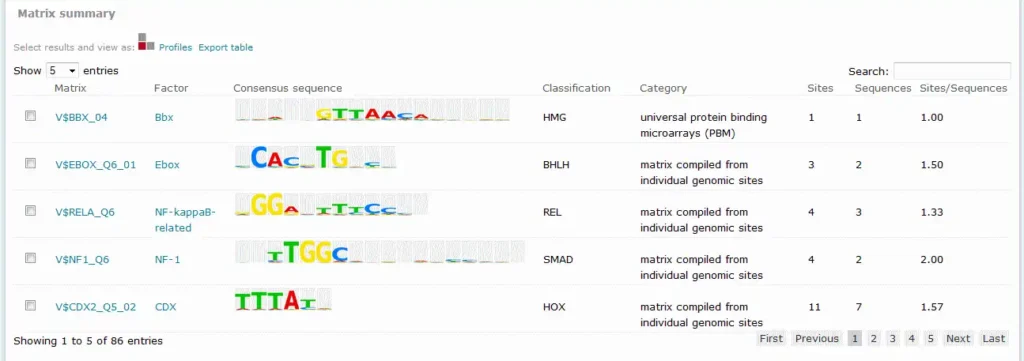
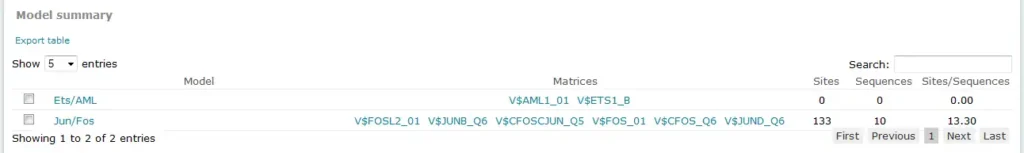
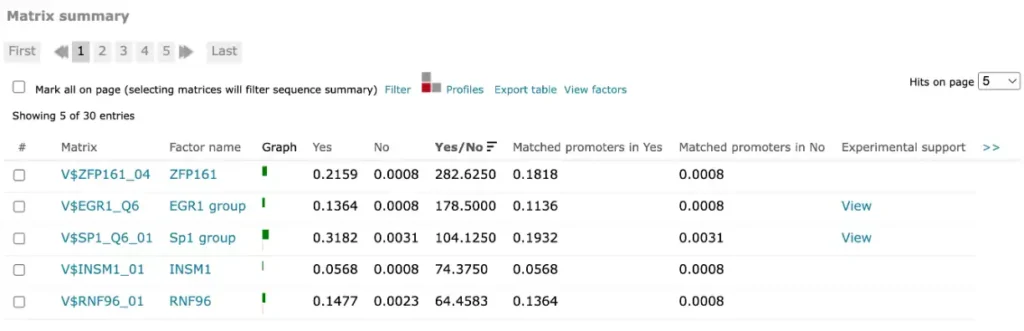
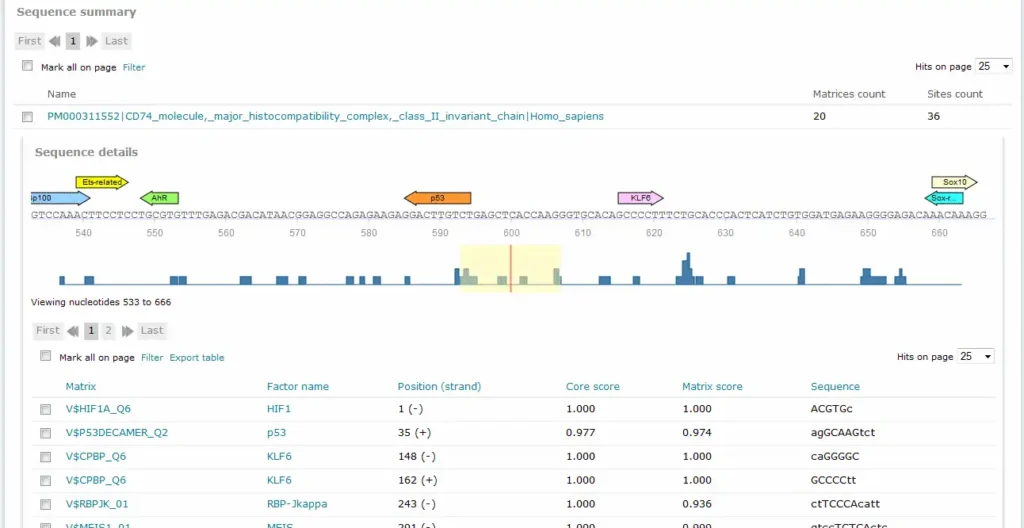
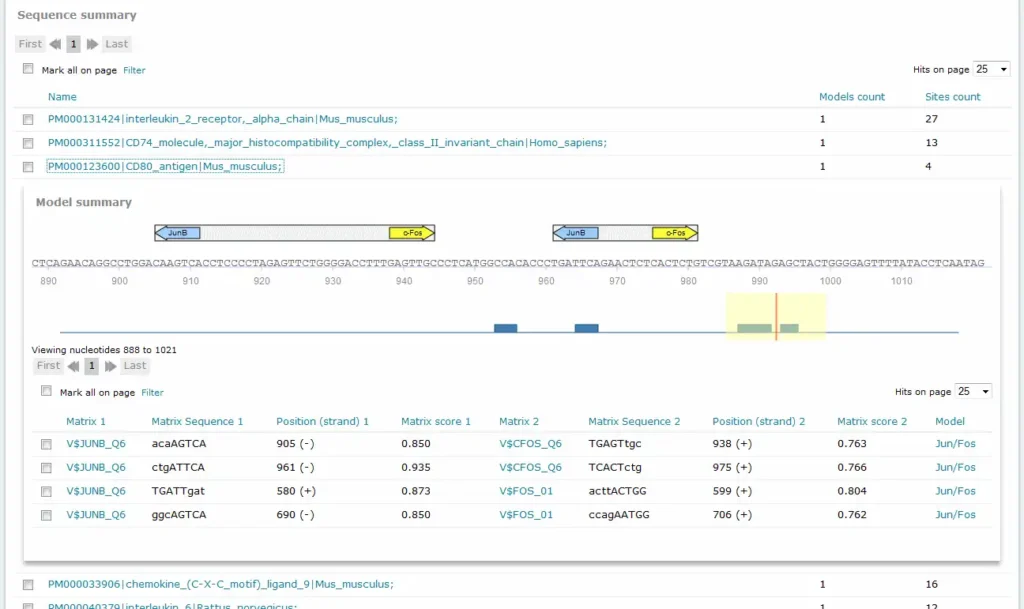
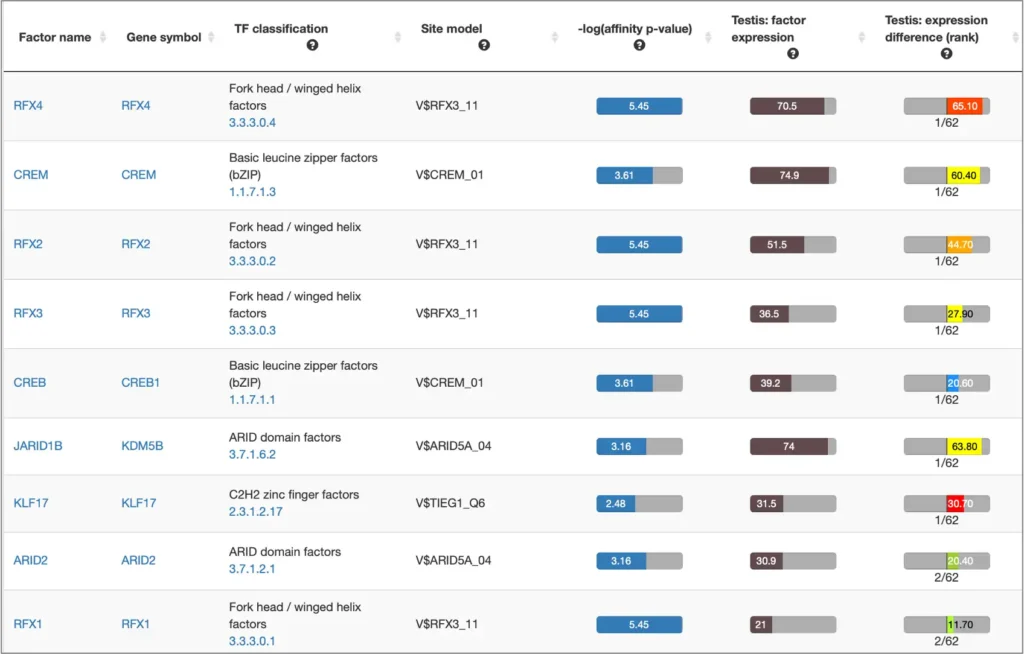
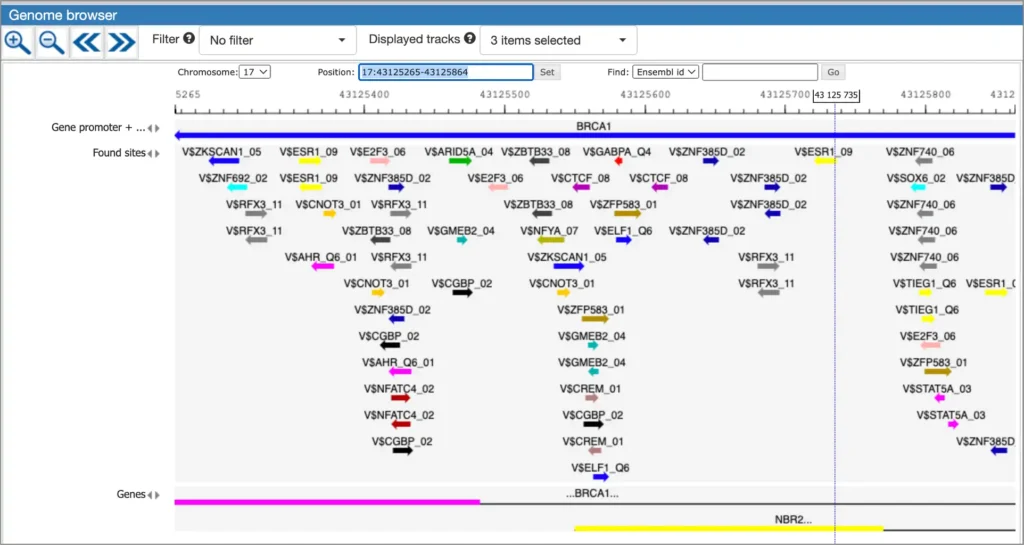
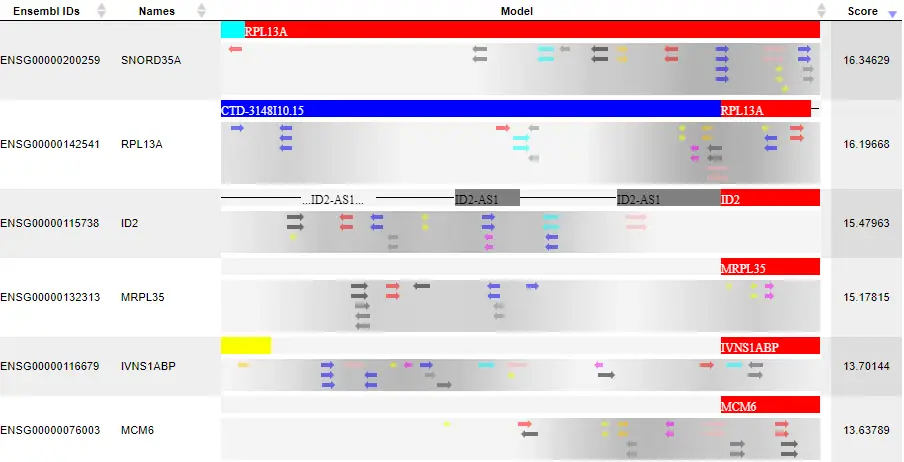
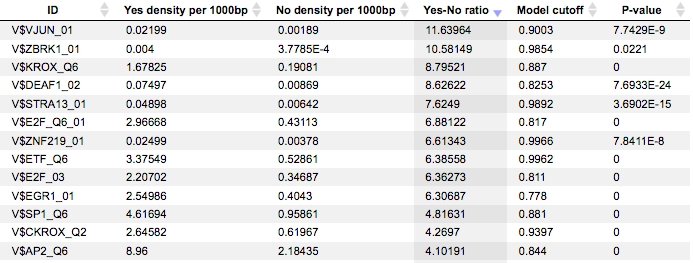
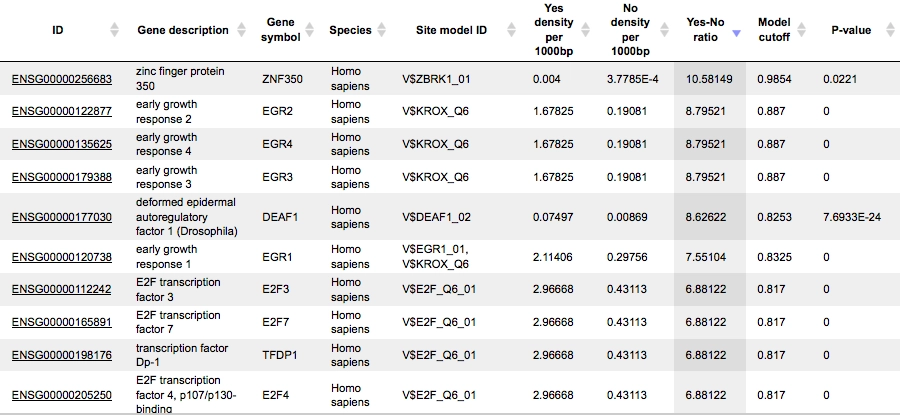
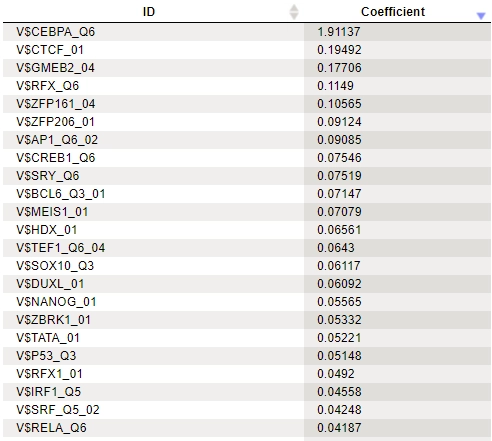
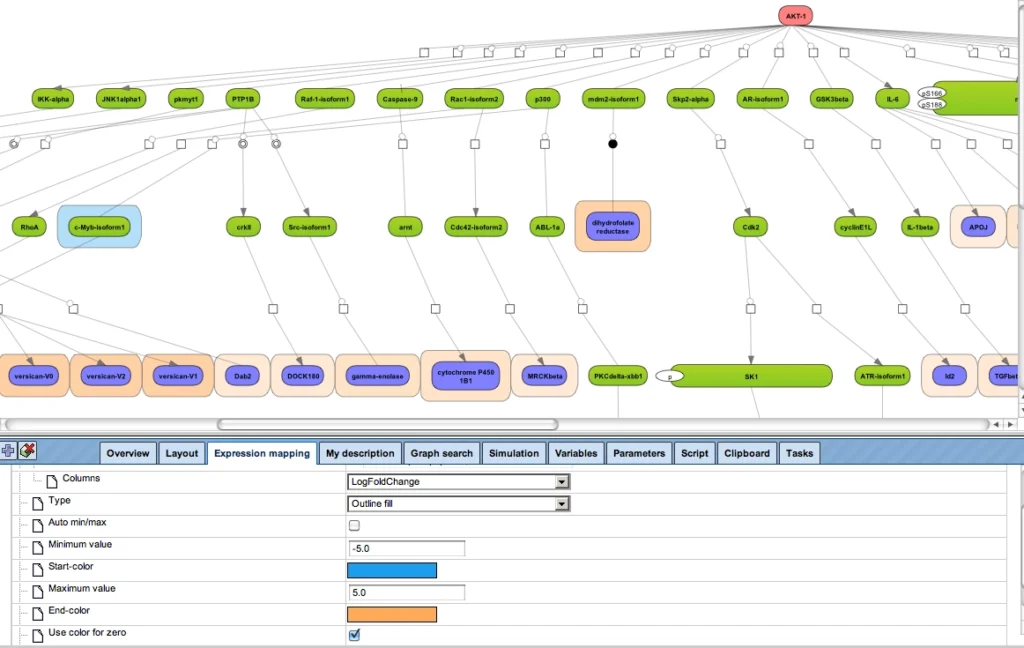
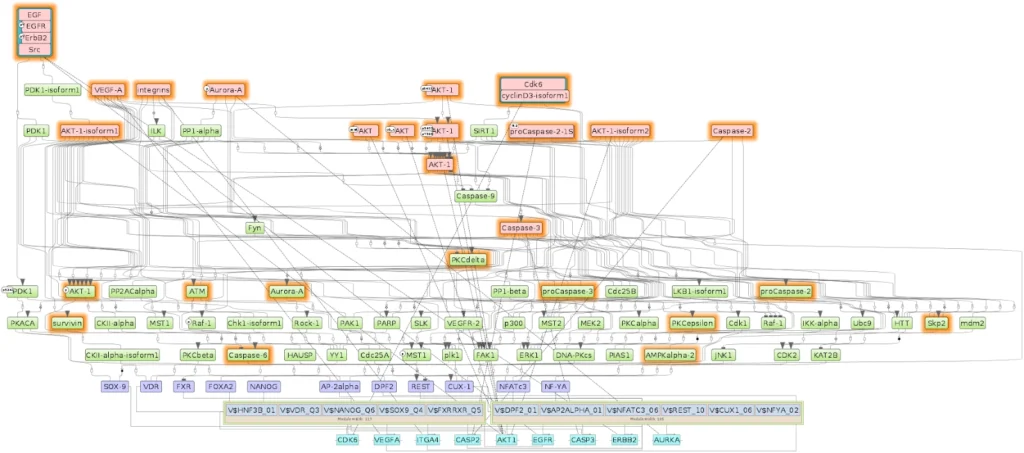
Example result of transcription factor analysis in MATCH Suite
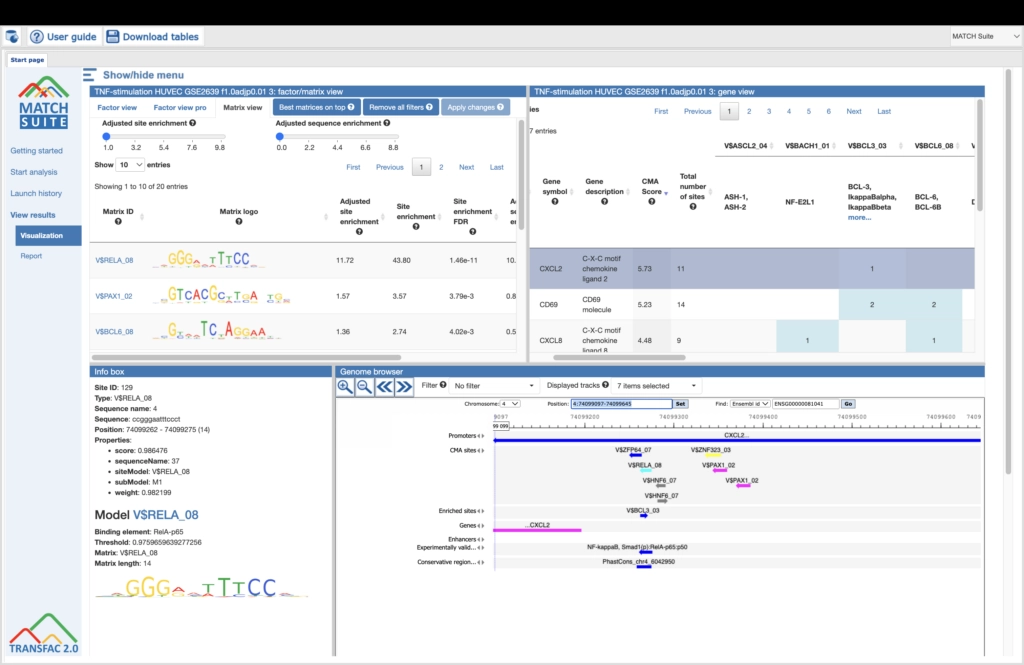
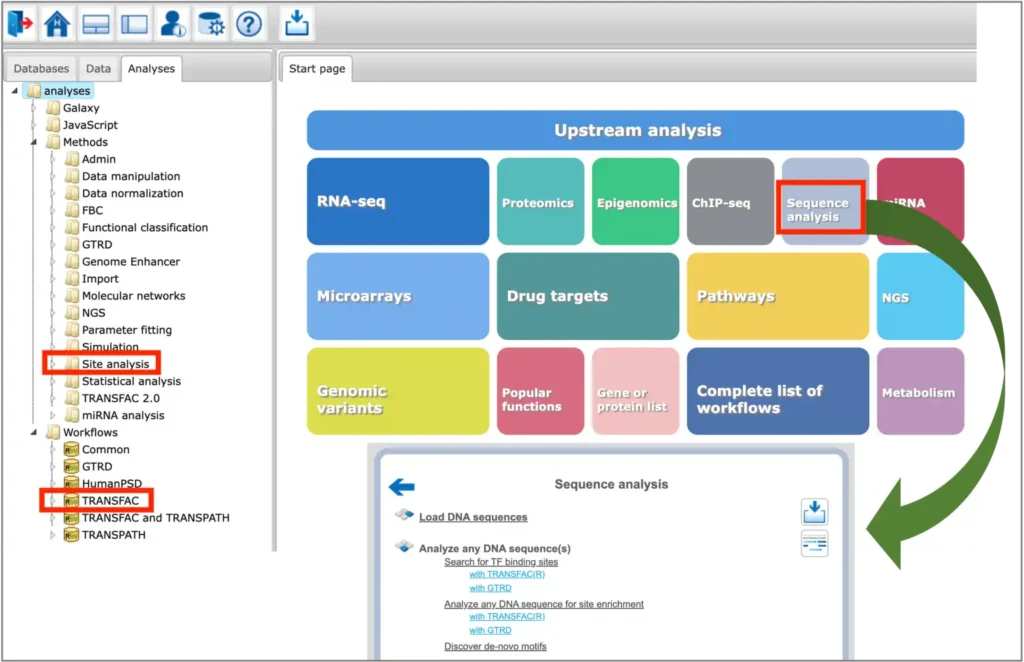
Site Analysis introduction
MATCH and FMatch:
TRANSFAC® includes one of the best site search and site enrichment tools equipped with powerful user interfaces for application in different analysis tasks.
MATCH Suite:
TRANSFAC® includes a powerful tool for analysis of TF binding sites in promoters and enhancers of genes for tissue- and function-specific transcription factors.
AI and ML:
TRANSFAC® includes Advanced tools for prediction of TFBS and their combinations on genomic scale using Machine Learning and AI methods.
geneXplain platform:
TRANSFAC® is equipped with the best in the field, flexible online software platform that provides:
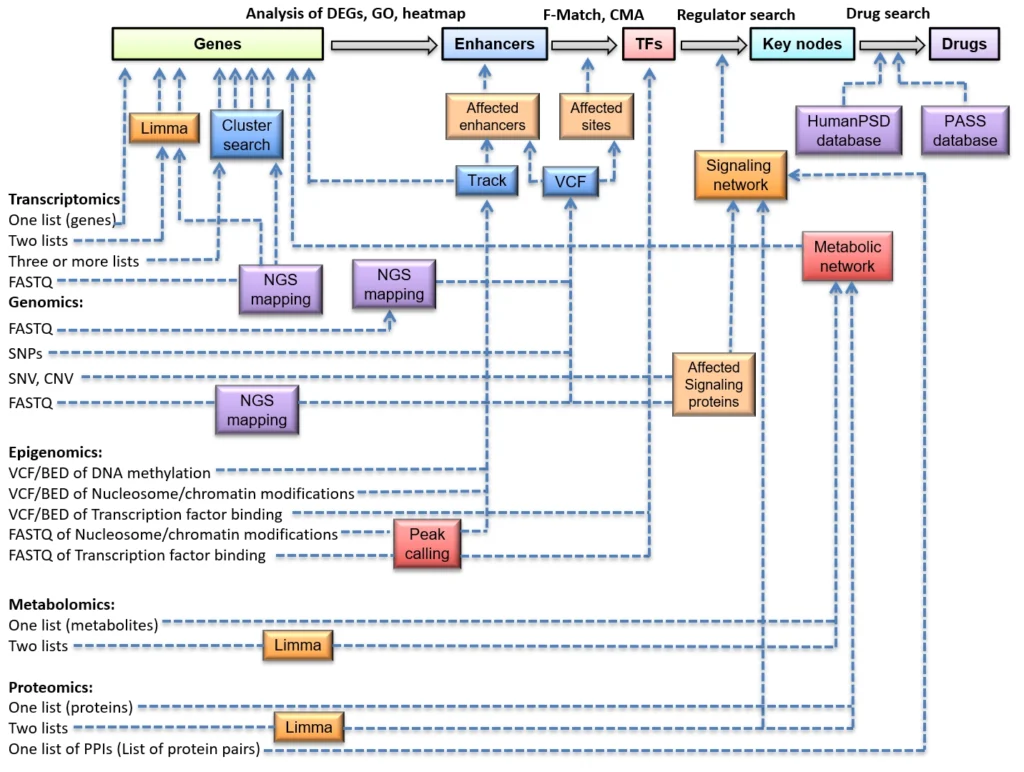
Omics analysis:
It has multiple tools for analysis of practically any omics data, including: RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, CUT&RUN, WGS, WES, and many others, also on the single cell level.
Over 200 tools and pipelines:
It integrates over 200 tools for analysis of gene lists and DEGs, as well as data in hundreds of input formats, such as FASTA, FASTQ, VCF, BED, ect. It is integrated with Galaxy platform and is equipped with a flexible workflow management system providing a variety of ready pipelines in all fields of bioinformatics.
Easy GUI:
The geneXplain platform provides a powerful and flexible graphical user interface (GUI) running in the web browser. User don’t need to do any installations and dont require to have any prior programming skills. The platform is the ready solution for no-coding bioinformatics.
API:
An elaborated Application Program Interface is freely available for geneXplain platform. It is provided for Python, R and Java and can be downloaded here:
https://github.com/genexplain
Cloud Storage:
100GB of working space is provided for the users of geneXplain platform in TRANSFAC Basic package. Users can use this space for uploading data and storing results in an unlimited number of projects.
TRANSFAC PATHWAYS
Reconstruct signal transduction network controlling your genes
Introduction
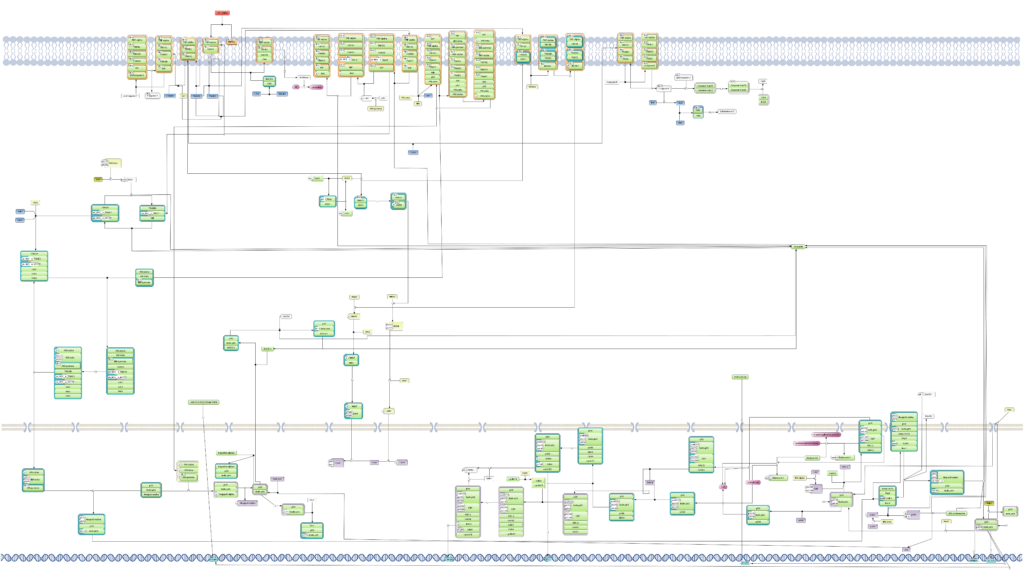
TRANSFAC PATHWAYS package comprises everything of TRANSFAC BASIC package plus TRANSPATH®, the database of mammalian signal transduction and metabolic pathways.
With more than 1,200,000 reactions, TRANSPATH has grown into one of the largest pathway databases and is used for pathway analysis, as well as for geneXplain’s proprietary Upstream Analysis, in connection with TRANSFAC promoter analysis.
Database content
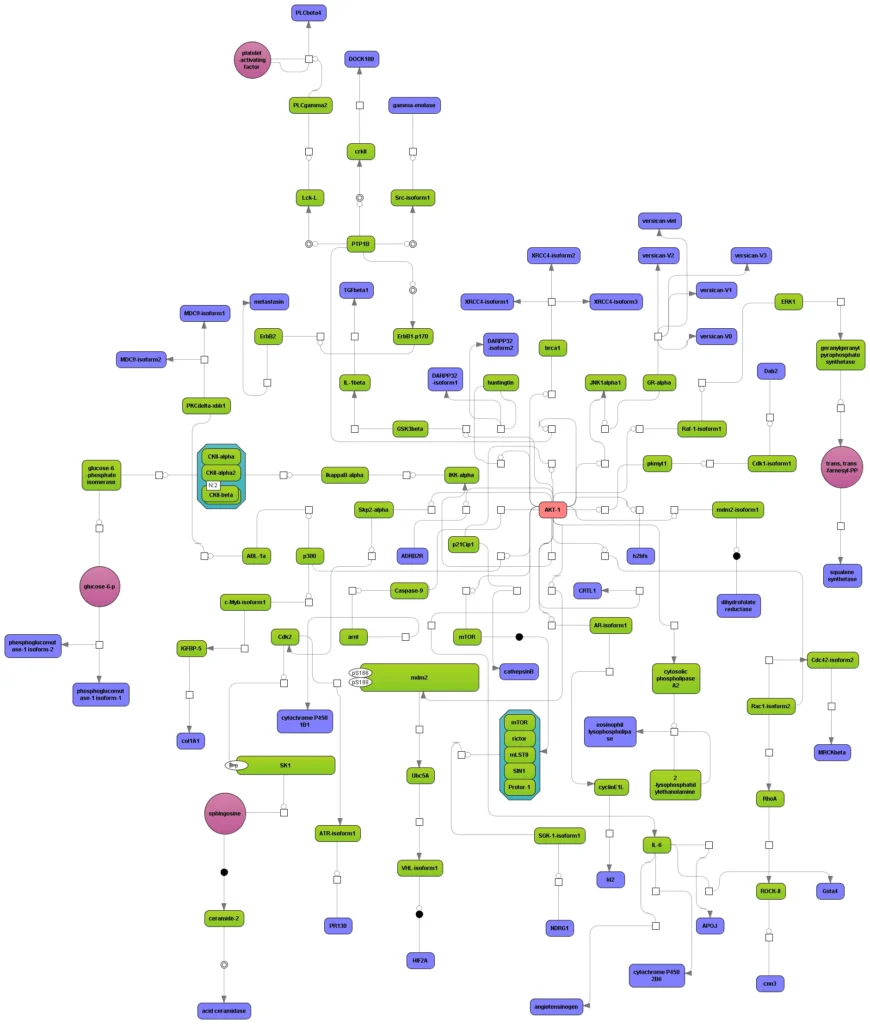
(incl. all data of TRANSFAC BASIC)TRANSPATH organizes the information about genes/molecules and reactions according to multiple hierarchies. Its sophisticated structure makes it one of the scientifically best conceptualized pathway resources, suitable for multi-purpose uses. It is complemented by one of the richest corpora of pathway data available manually curated by experts.
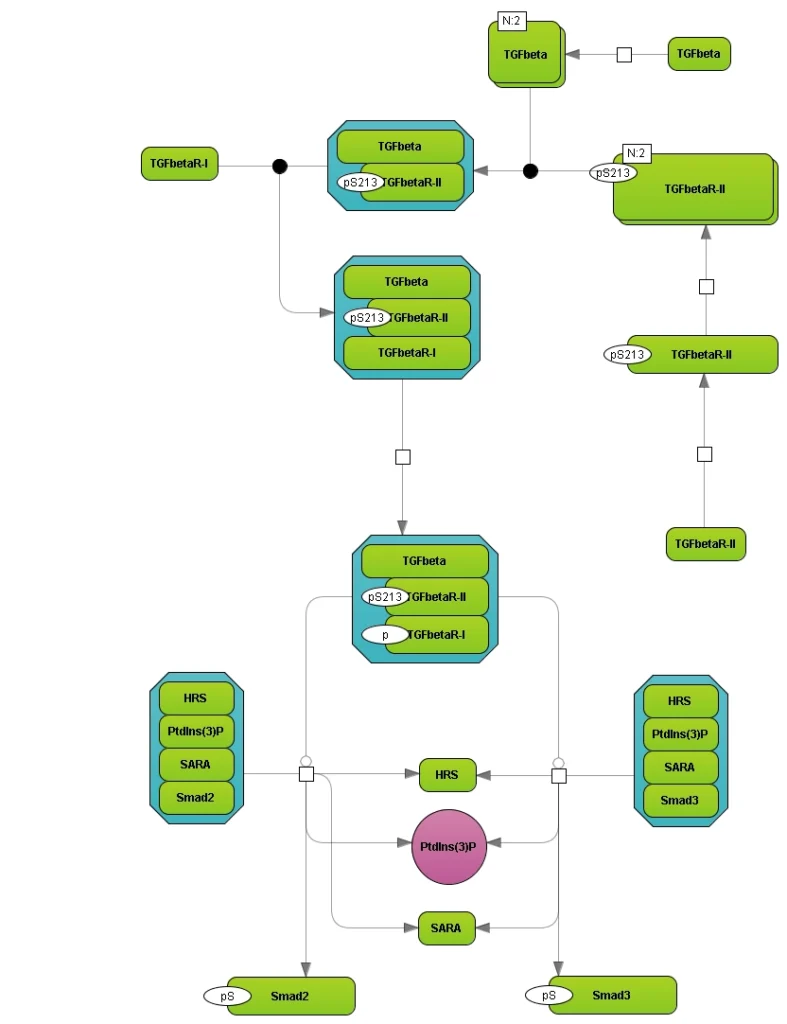
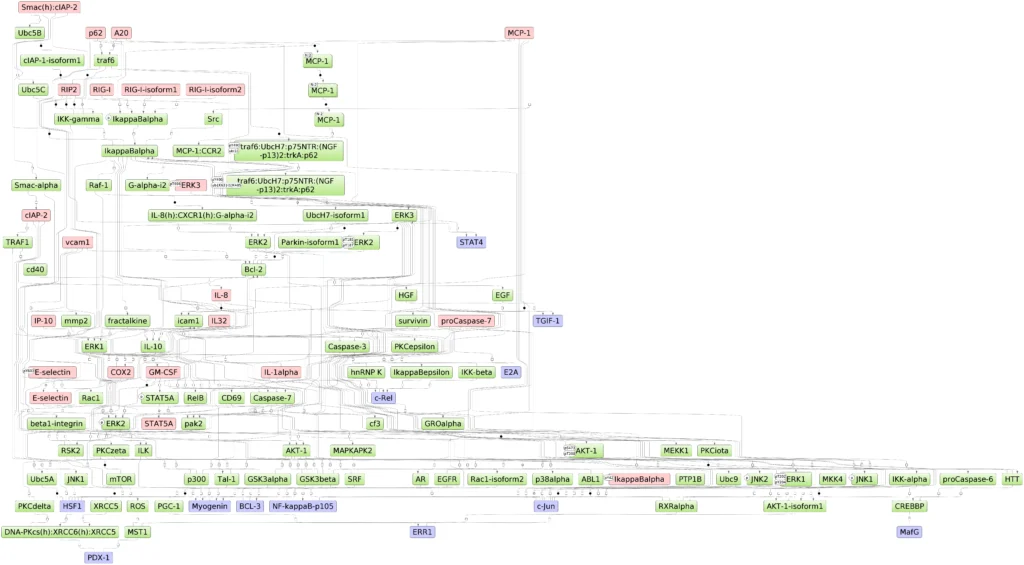
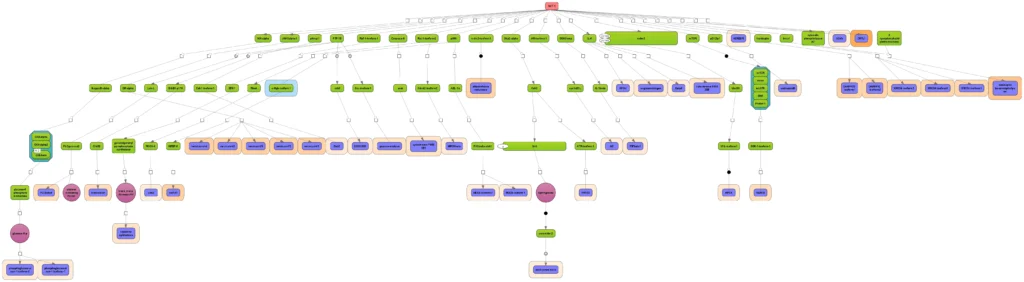
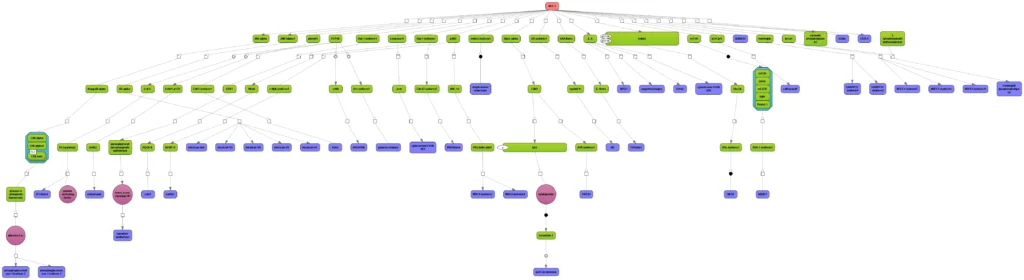
Reaction hierarchy in the TRANSPATH® database on molecular pathways:.
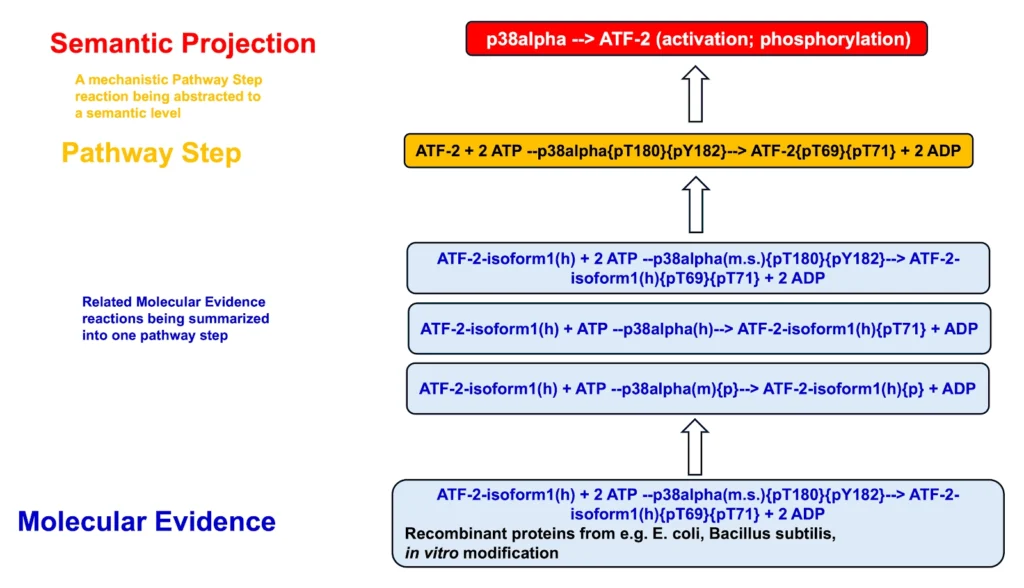
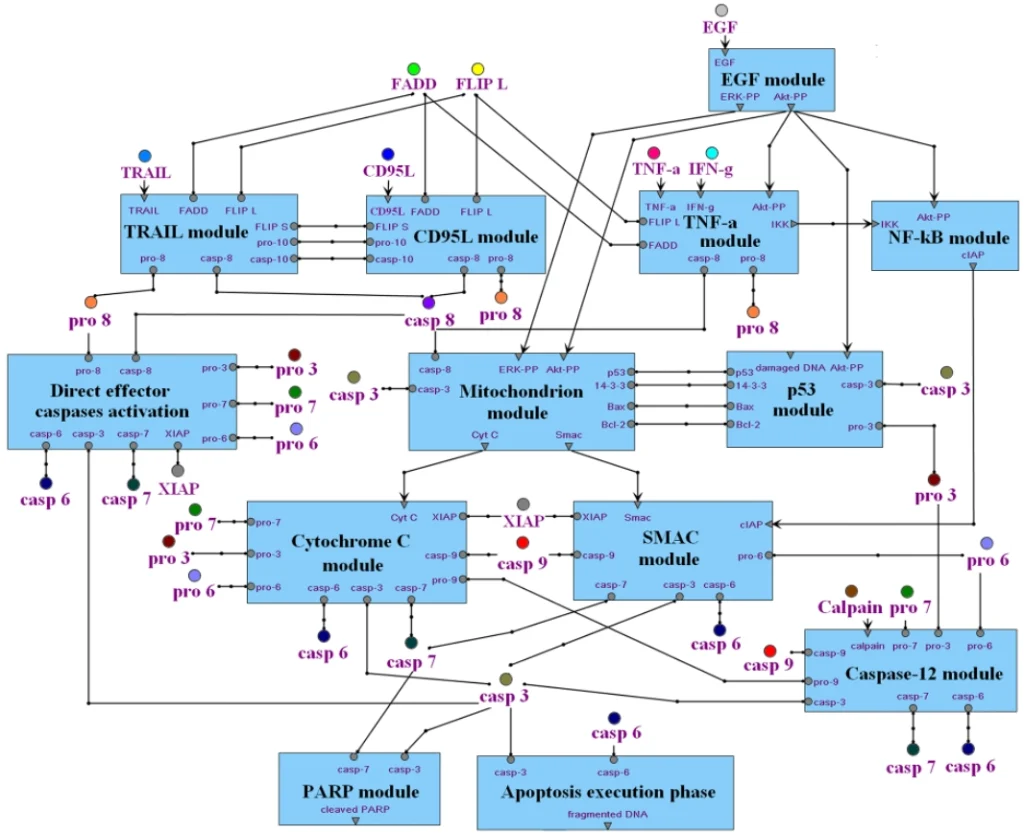
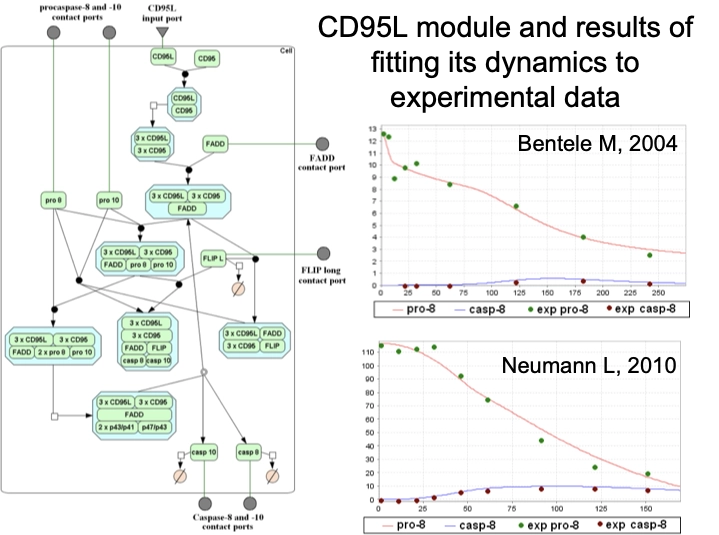
Individual reactions are documented with all experimental details, in a strictly mechanistic way that includes all reaction partners and the taxonomic origin of each molecule as reported in the published experiment (“molecular evidence level”). All evidence for a certain pathway step is accumulated to provide a more comprehensive and complete picture (“pathway step level”). On top, a semantic view is provided, which focuses on the key components only and omits mechanistic details as well as small abundant molecules (“semantic projection”). Complete networks and pathways are built from molecules and their reactions.
To consider the heterogeneity of information given in the original publications, TRANSPATH transparently but precisely differentiates protein molecules according to:
their relatedness within one genome
Information can be specifically retrieved regarding:
(a) specific individual proteins,
(b) all products of a certain gene (isoforms),
(c) different family relation levels (e.g., paralogs);
their relatedness between different genomes (orthology)
their association and modification status
(a) protein complexes are specified with their exact composition;
(b) post-translational modifications are given with their exact positions in the protein.
Pathways:
TRANSPATH® database collects and systematize canonical signal transduction and metabolic pathways. Currently it collects over 1500 various pathways.
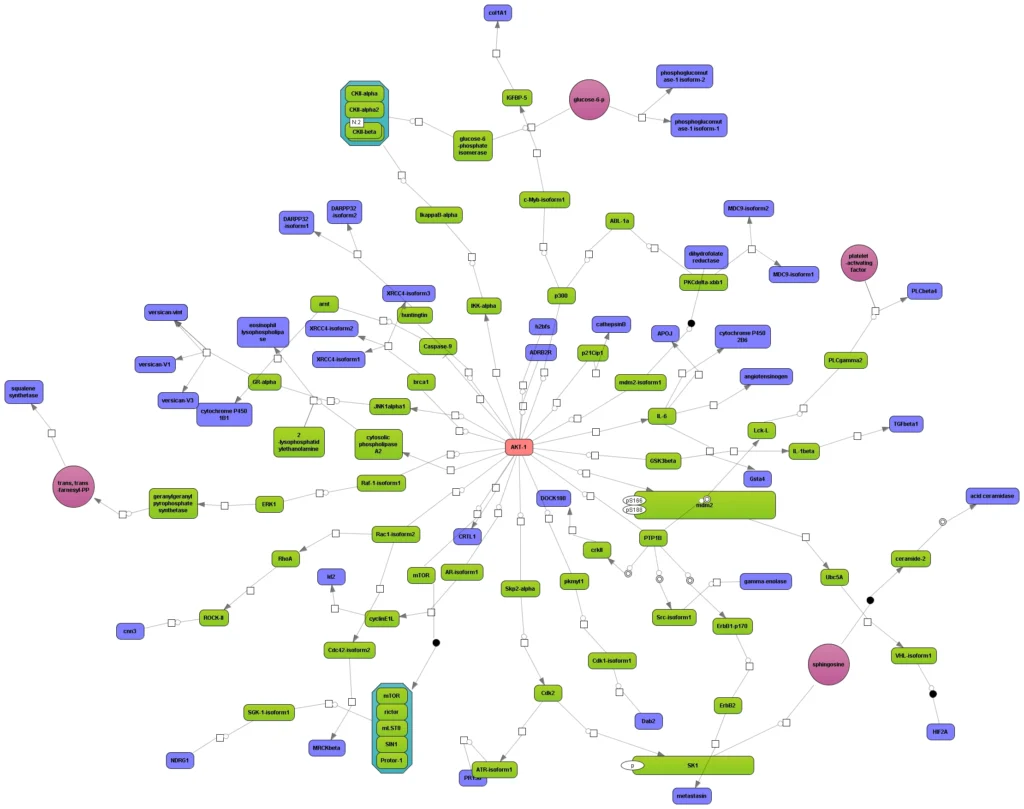
Reaction network:
TRANSPATH® database is one of the most comprehensive repositories of signal transduction reactions in mammalian cells. It collects over 1,200,000 experimentally proven reactions of phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, translocation and other types of reactions involved in signal transduction. These reactions build a highly connected regulatory reference network which is used for analysis and reconstruction of molecular mechanisms of diseases, identification of master-regulators and drug targets.
Tools
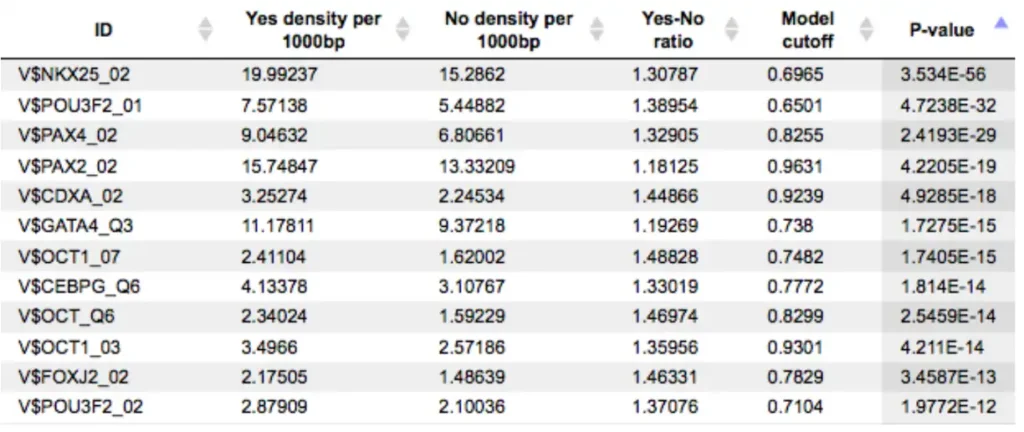
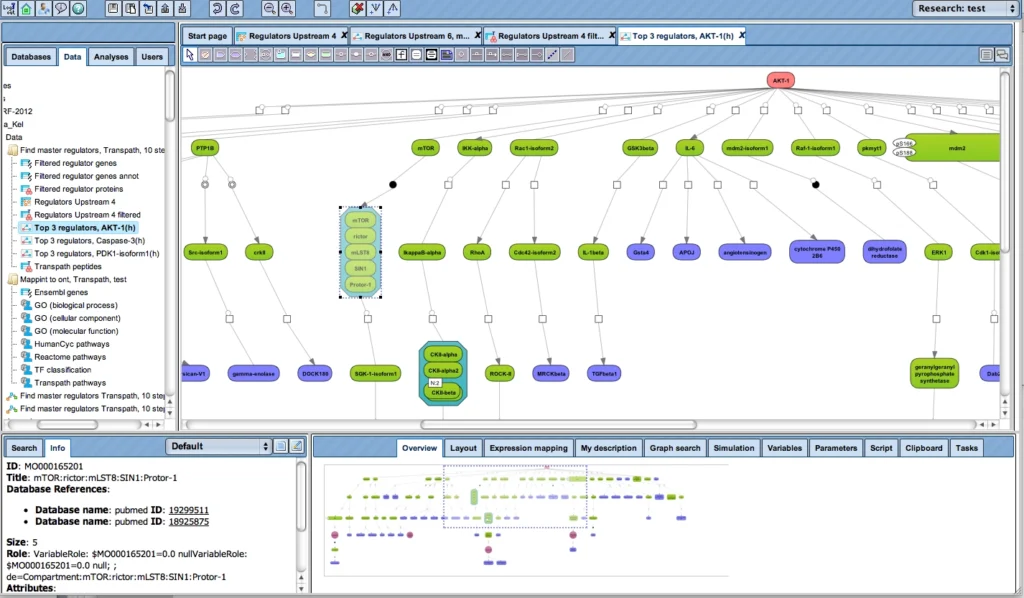
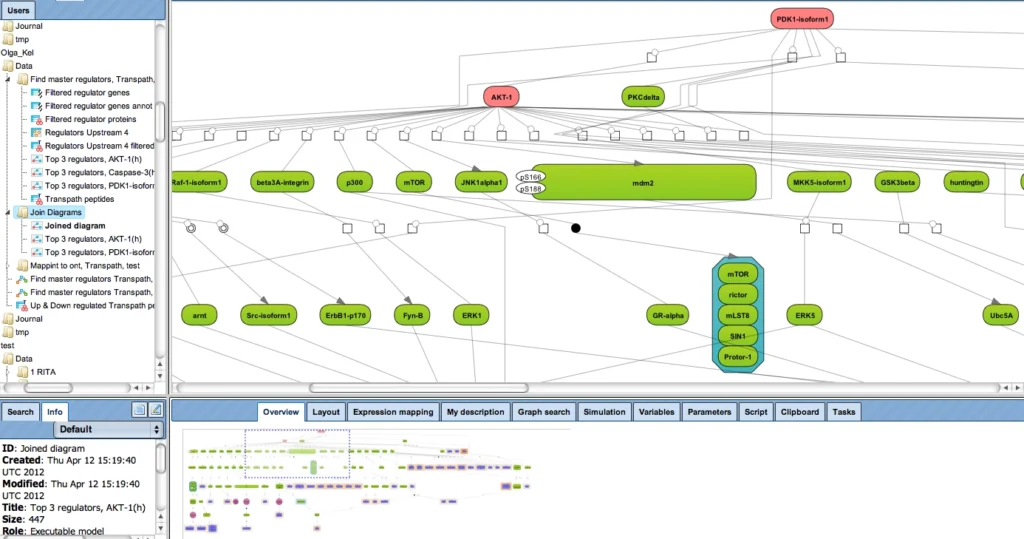
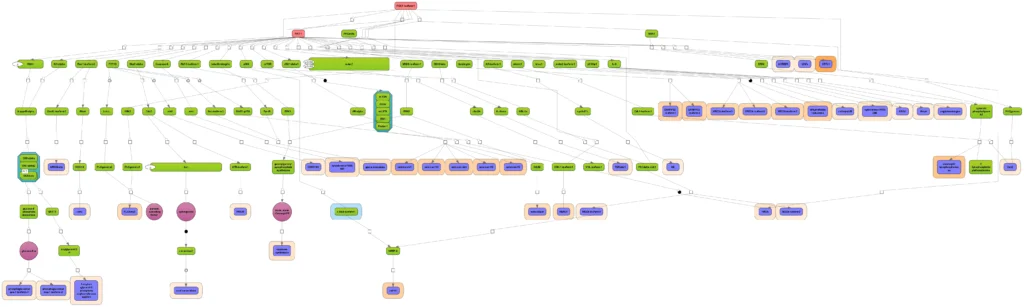
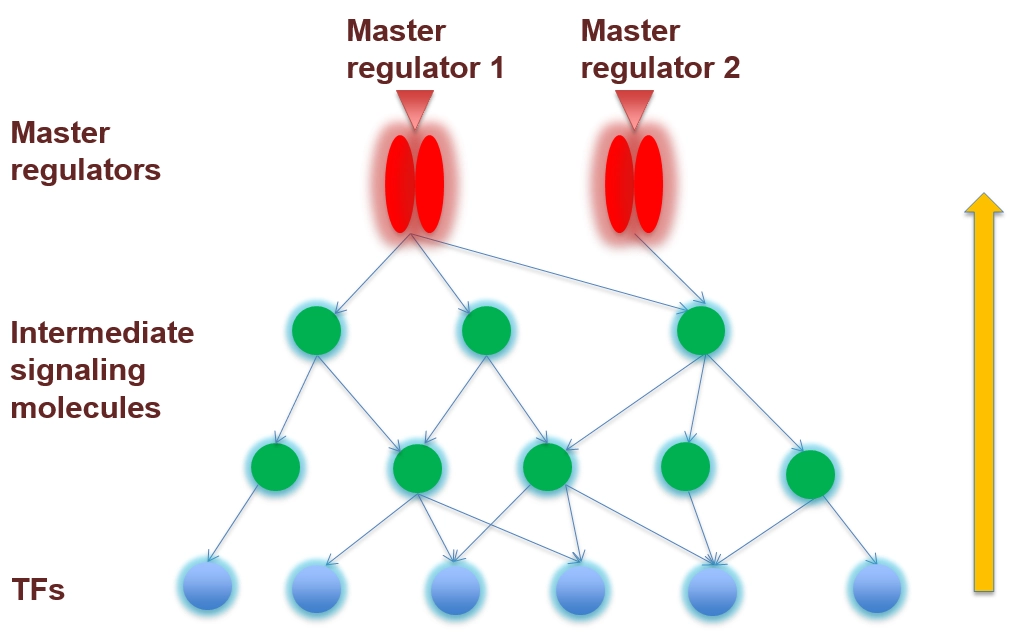
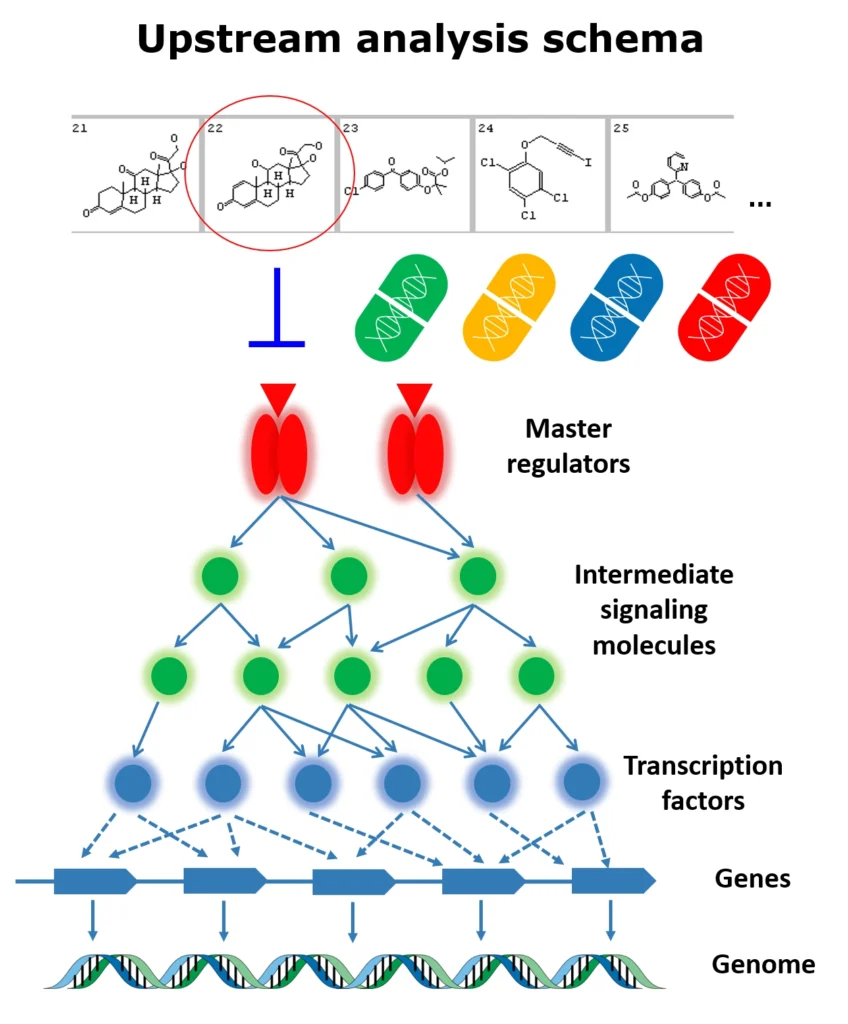
(incl. all tools of TRANSFAC BASIC)The collected signal transduction networks can be used by the included tools for pathway analysis, particularly, in connection with TF-DNA binding motifs, this allows upstream analysis as integrated promoter-network analysis, whereby the TFs of in step 1 predicted TFBSs are used as starting point for finding master regulators in step 2 converging upstream of the transcription factors.
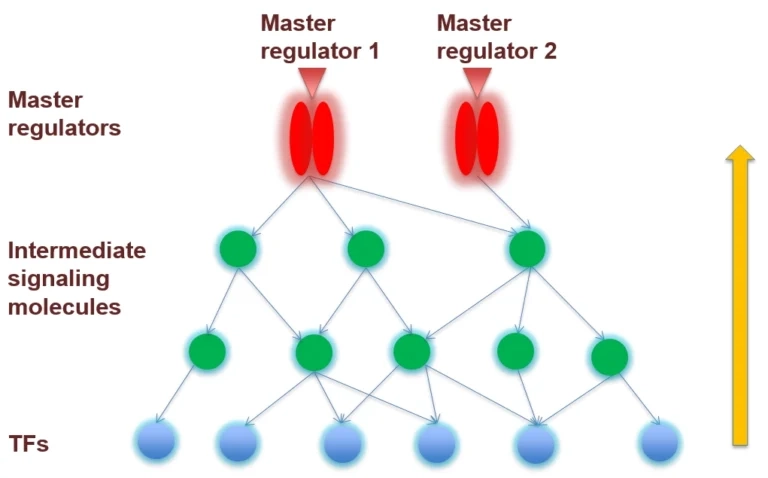
Pathways analysis
What is Pathway Analysis?
Most commonly, it is of interest to know which signaling or metabolic pathways are activated under certain experimental conditions.
A slightly different question may be to find out which pathways were used to express a certain observed phenotype.
Both types of problems can be conveniently addressed with our tools provided by TRANSFAC PATHWAYS package.
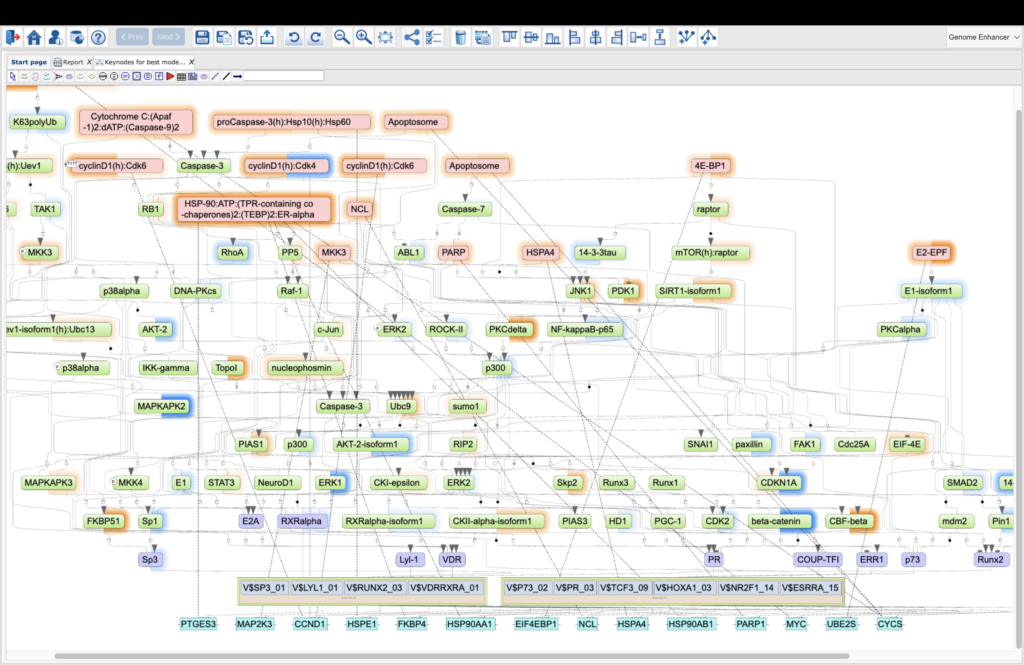
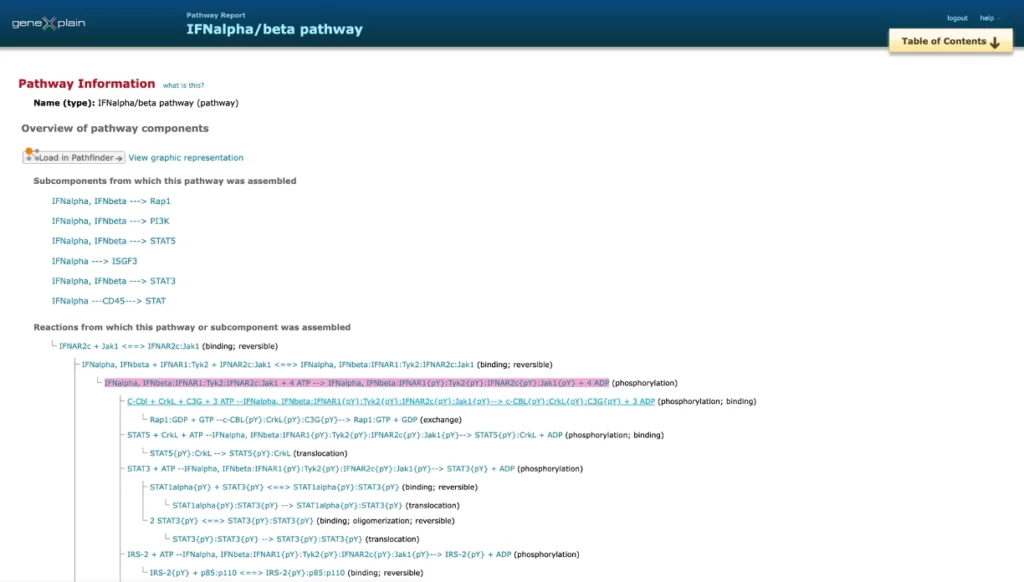
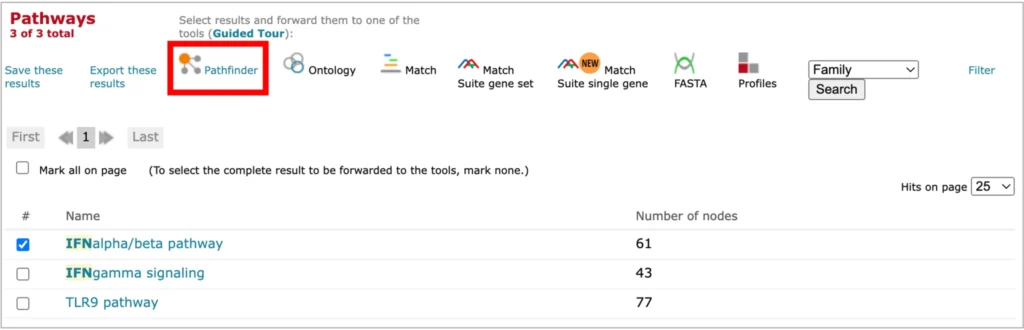
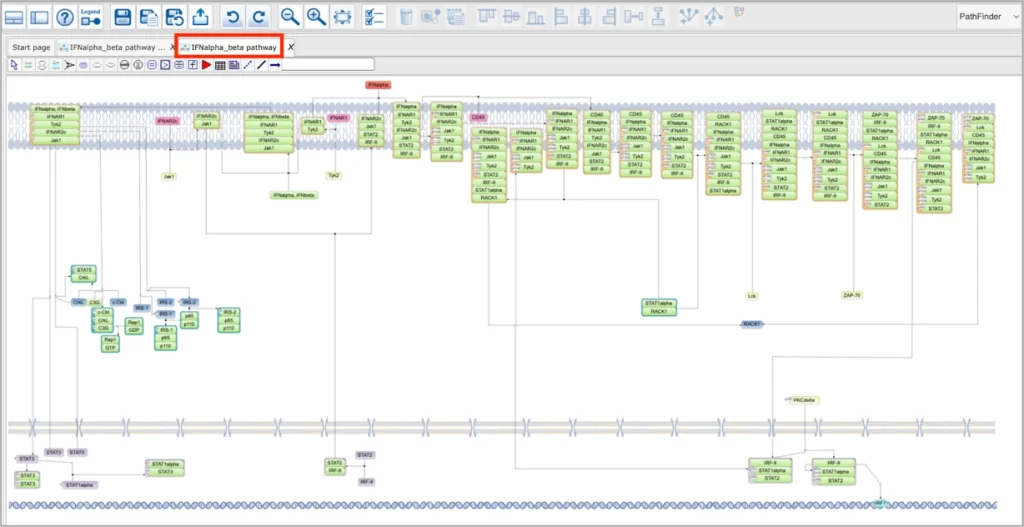
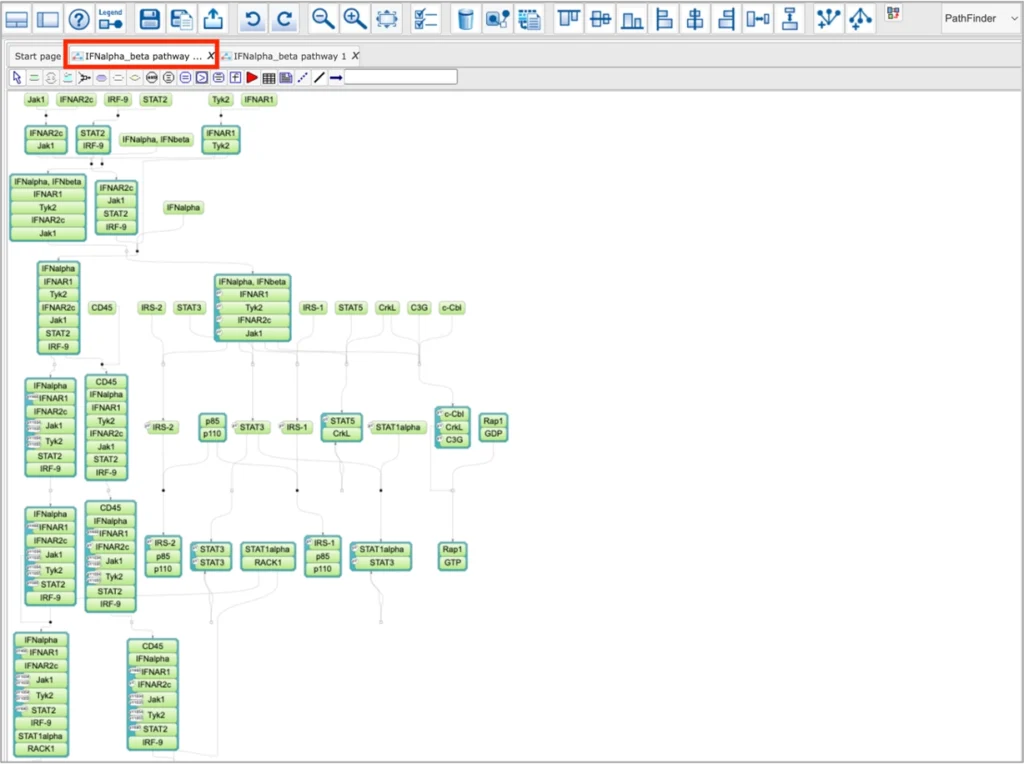
SBGN viewer:
- PathFinder is the web browser tool for visualization of signaling and metabolic pathways using (System Biology Graphic Notation) SBGN standard.
Upstream analysis:
The TRANSFAC PATHWAYS package uniquely combines promoter analysis with pathway analysis, enabling the identification of master regulators in gene regulatory networks. No other tool on the market provides such an integrated capability.
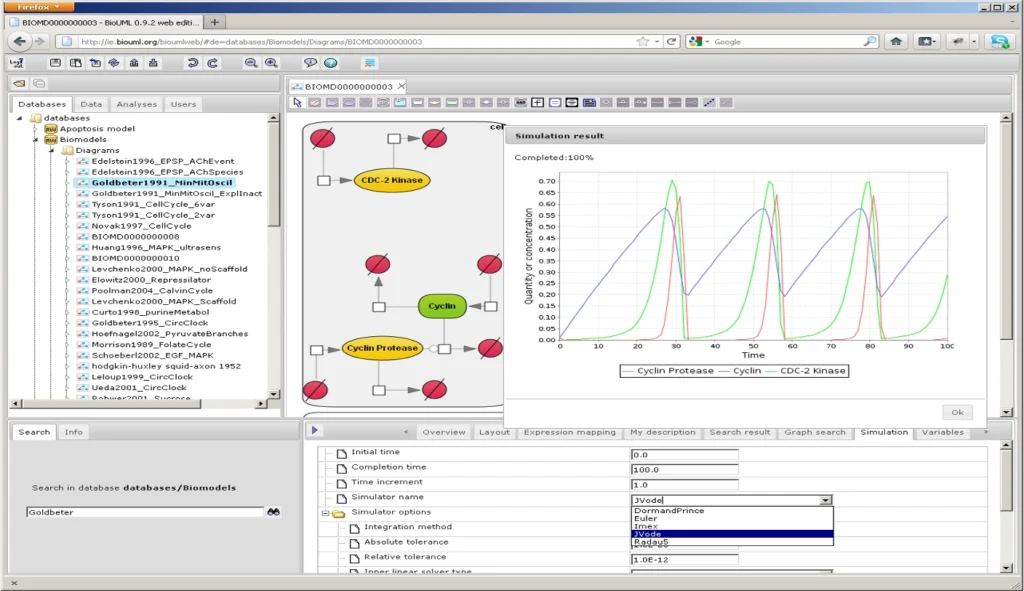
ODE modeling:
The TRANSFAC PATHWAYS package includes geneXplain platform modeling tools on the basis of BioUML simulation environment, which is according to the independent study (Maggioli F., Mancini T., Tronci E. SBML2Modelica: Integrating biochemical models within open-standard simulation ecosystems. Bioinformatics, 2019, doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz860) shown as
TRANSFAC DISEASES
Identify drug targets and disease biomarkers
Introduction
TRANSFAC DISEASES comprises all data of TRANSFAC BASIC and TRANSFAC PATHWAYS plus The Human Proteome Survey Database (HumanPSD) which is a catalog of proteins and their complexes from human cells, plus their orthologs from mouse and rat sources.
Its main focus is on the association of human proteins with diseases as well as on their potential use as biomarkers.
TRANSFAC DISEASES allows to apply the full potential of the included gene regulation and disease data and tools. Particularly, TRANSFAC DISEASES includes Genome Enhancer – a fully automated pipeline for patient omics data analysis, which identifies prospective drug targets and corresponding treatments by reconstructing the molecular mechanism of the studied pathology.
Database content
(incl. all content of TRANSFAC BASIC and of TRANSFAC PATHWAYS)HumanPSD reports detailed information about the role of human proteins as biomarkers in diseases. Information can be retrieved on the molecular functions, biological roles, localization, and modifications of proteins, expression patterns across cells, tissues, organs, and tumors, consequences of gene mutations in mice, and the physical and regulatory interactions between proteins and genes.
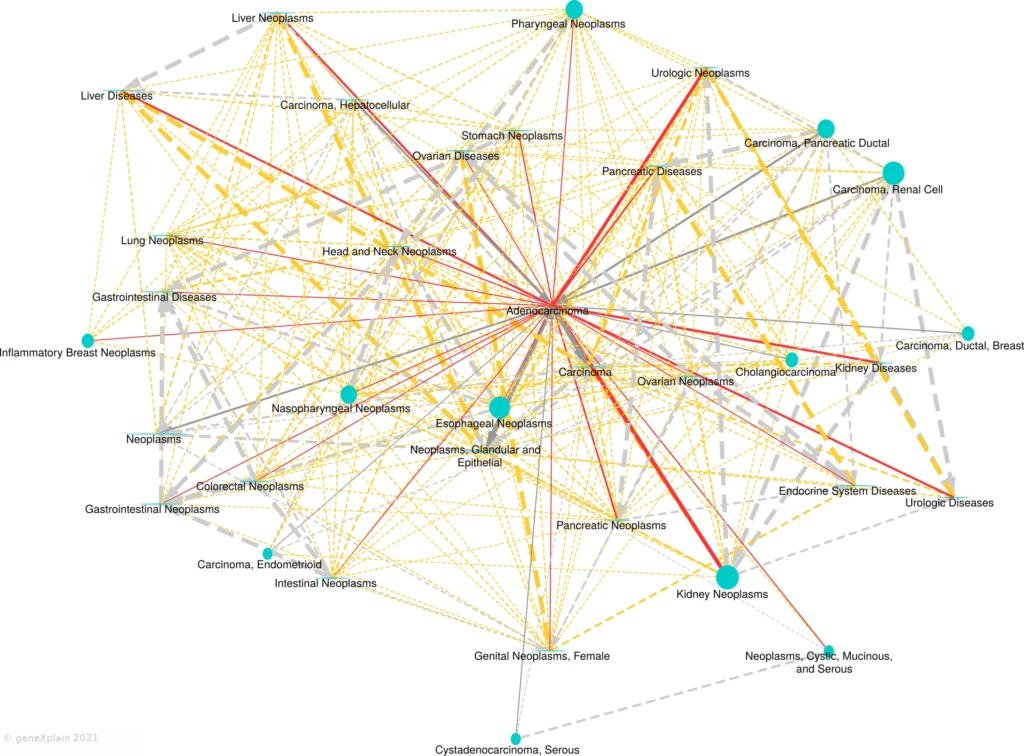
Disease similarity by common biomarkers
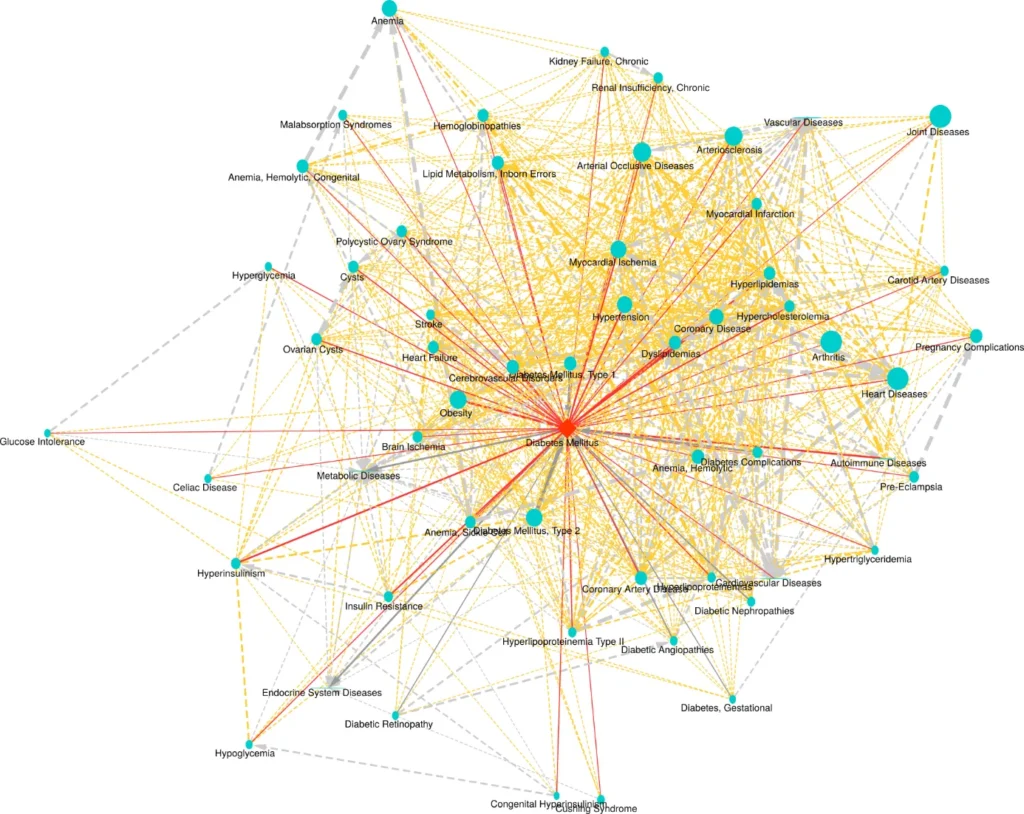
Biomarkers:
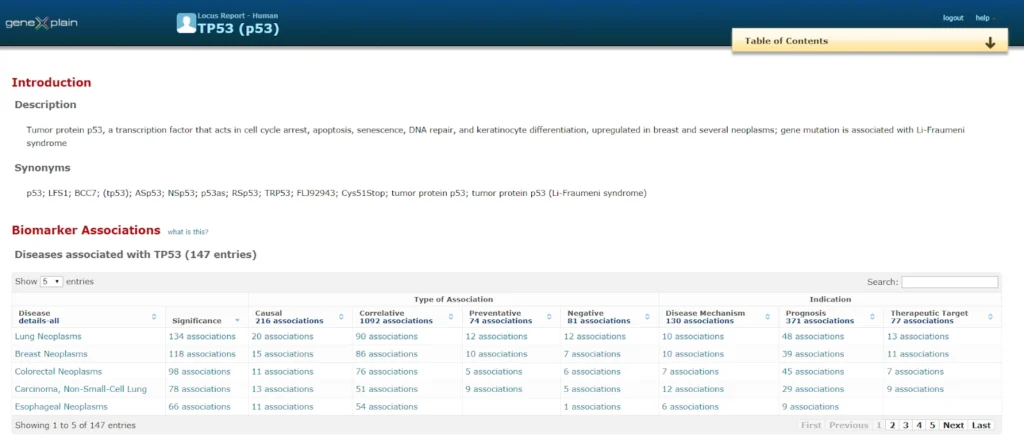
HumanPSD reports over 140,000 gene-to-disease biomarker associations (causal, correlative, preventive, negative, prognostic).
Disease mechanism:
HumanPSD reports description of disease molecular mechanisms for over 3,900 human diseases.
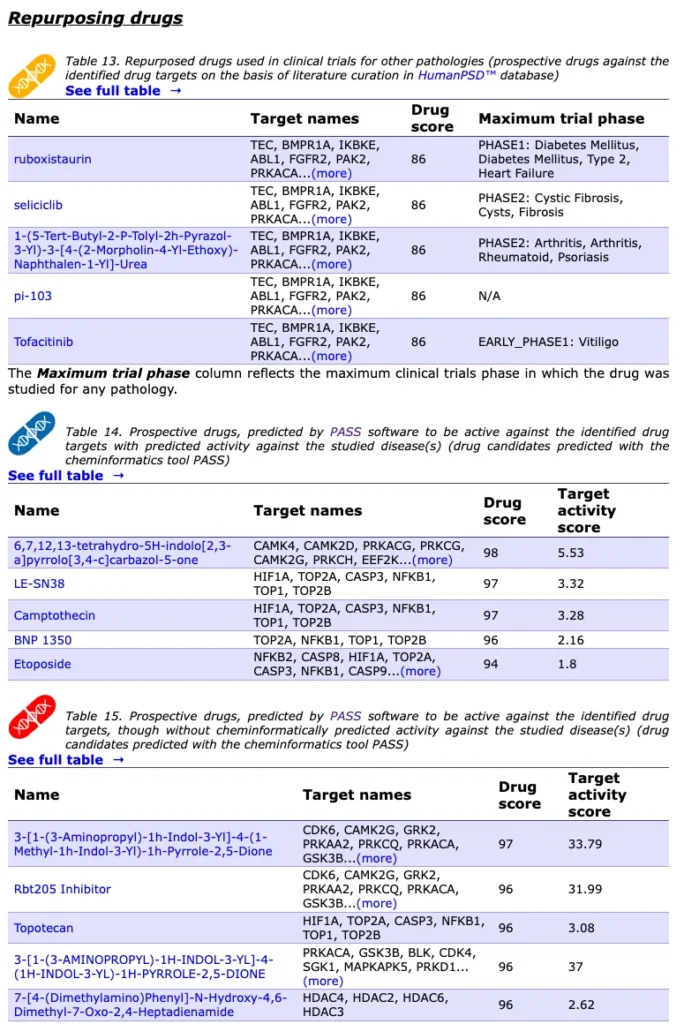
Drugs and targets
HumanPSD reports over 55,000 drug targets and associated with them over 10,000 drugs.
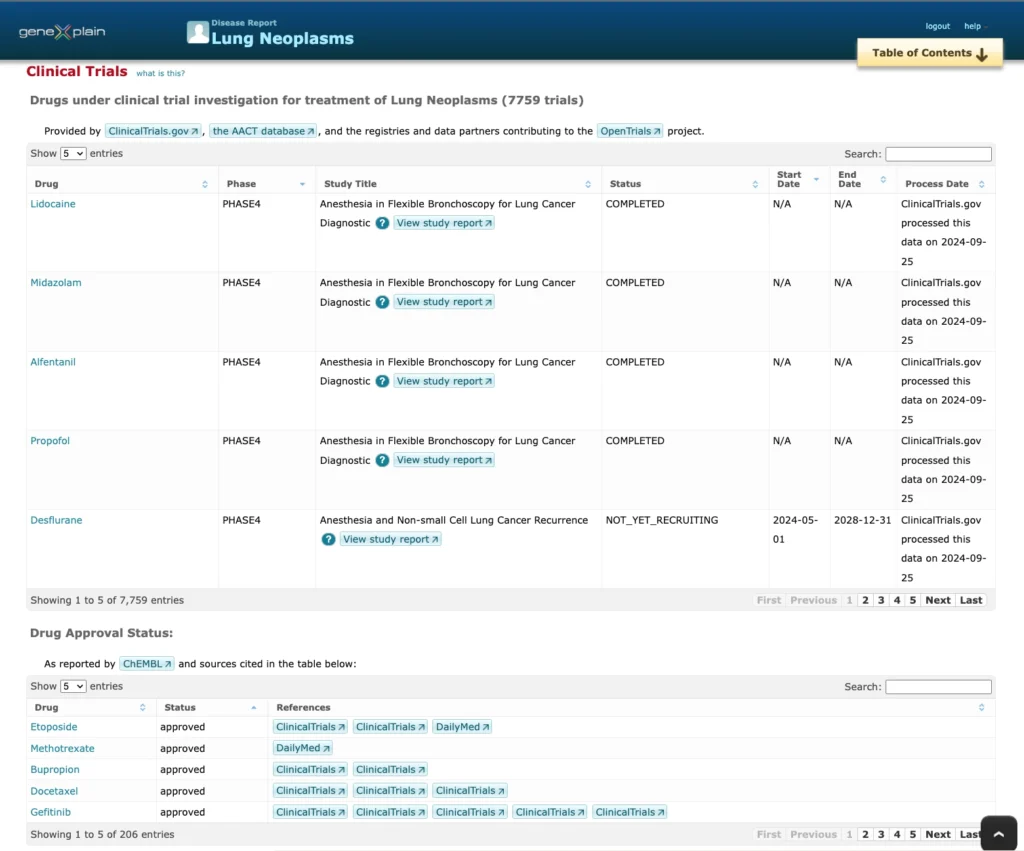
Clinical trials:
HumanPSD reports over 1,100,00 clinical trial – disease connections extracted from ClinicalTrials.gov and AACT databases, and also from the registries and data partners contributions to the OpenTrials project.
Tools
(incl. all tools of TRANSFAC BASIC and of TRANSFAC PATHWAYS)Genome Enhancer

Welcome to the new era of Precision Medicine!
In addition to other TRANSFAC-, TRANSPATH- and HumanPSD-based tools, TRANSFAC DISEASES includes the AI driven Genome Enhancer, a fully automated pipeline for patient omics data analysis, which identifies prospective drug targets and corresponding treatments by reconstructing the molecular mechanism of the studied pathology.
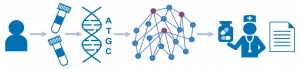
Genome Enhancer provides a powerful synergism between the automatic pipeline for multi-omics data processing and the comprehensive bioinformatics toolbox of the geneXplain® platform integrated with the TRANSFAC, TRANSPATH, and HumanPSD databases.
Genome Enhancer offers:

Multi-omics analysis
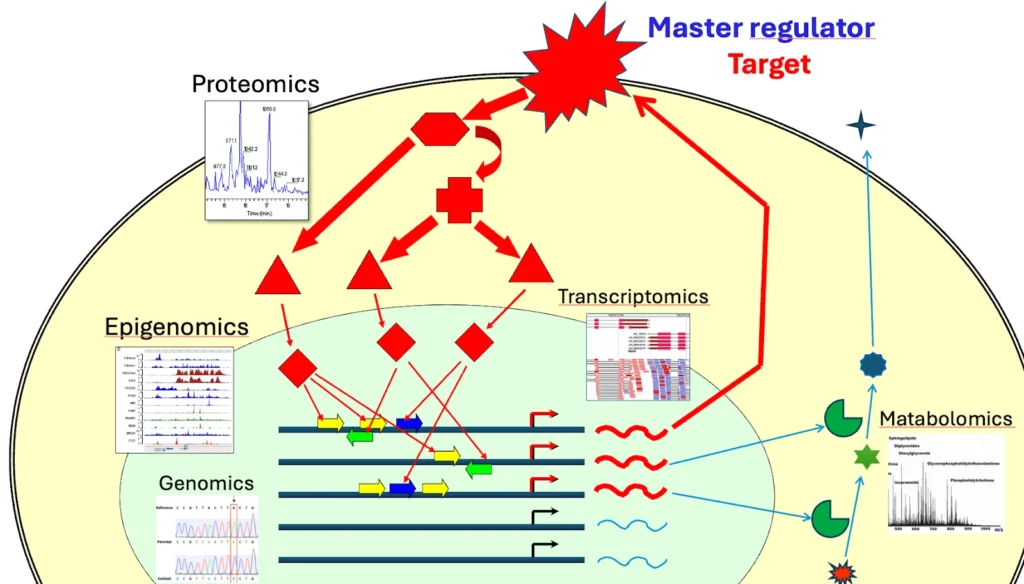
Use genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, proteomics, and epigenomics data in one analysis run and receive an integrated report

Personalized medicine
Running the analysis on omics data of a certain patient, you will identify personalized prospective drug targets and corresponding treatments

Scientific base
Integration of promoter and enhancer analysis with pathway reconstruction gives unrivaled disease molecular mechanism modeling accuracy
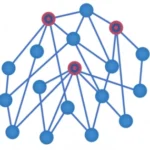
Drug target identification
Genome Enhancer reconstructs a complex network of signal transduction pathways that are activated in the pathology and identifies their key regulators
Genome Enhancer Algorithm
Genome Enhancer uses Upstream Analysis, an integrated promoter and pathway analysis, to identify potential drug targets of the studied pathology.
Disease mechanism:
Genome Enhancer applies AI algorithms such as Genetic Algorithm and complex graph analysis algorithms to discover disease molecular mechanisms and
Multi-omics integration:
Genome Enhancer provides flexible integration of all five “-omics” data types: Transcriptomics, Genomics, Epigenomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics.
Drug repurposing:
Genome Enhancer can screen for existing FDA-approved drugs that interact with the disease-specific targets,
Detailed report:
Genome Enhancer delivers a comprehensive and detailed report that includes all the essential elements for publication-ready research.
TRANSFAC DOWNLOAD
Download TRANSFAC and do whatever you like
Introduction
TRANSFAC flat file download (including the databases TRANSCompel® and TRANSProTM) contains eukaryotic transcription factors (and miRNAs), their experimentally determined genomic binding sites and consensus DNA-binding motifs (PWMs), as well as data on combinatorial gene regulation and factor-factor interaction. Promoters, enhancers and silencers annotated with transcription factor ChIP-Seq, DNase hyper-sensitivity and histone methylated intervals from the ENCODE project and from other sources complement the manually curated binding site data.
Key features
- Intended for Bioinformaticians
- No installation is needed – just download and unzip archives
- Data files are provided in DAT and JSON formats
- Promoters are provided in the DAT and GTF formats
- Direct data access without user interface: data extraction is possible via Perl scripts or other programs written by the user
- Java-based tools for TFBS search (Match Library) are accessible via a command line
- For use with customer tools and incorporation into user-specific pipelines
What you will get
- Based on the positional weight matrices (PWMs) transcription factor binding sites can be predicted in regulatory regions.
- In the TRANSFAC® flat file download, the tools of the MatchTM Library can be used on command line or the PWMs can be used with tools of the user.
How to cite
How to cite TRANSFAC:
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M, Hornischer K, Voss N, Stegmaier P, Lewicki-Potapov B, Saxel H, Kel AE, Wingender E. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(90001):D108-D110. Link
How to cite Match:
Kel AE, Gössling E, Reuter I, Cheremushkin E, Kel-Margoulis OV, Wingender E. MATCH: A tool for searching transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(13):3576-3579. Link
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M, Hornischer K, Voss N,Stegmaier P, Lewicki-Potapov B, Saxel H, Kel AE, Wingender E. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(90001):D108-D110. Link
How to cite MATCH Suite:
Waleev T, Shtokalo D, Konovalova T, Voss N, Cheremushkin E, Stegmaier P, Kel-Margoulis O, Wingender E, Kel A. Composite Module Analyst: identification of transcription factor binding site combinations using genetic algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Web Server issue):W541-5. Link
Kel AE, Gössling E, Reuter I, Cheremushkin E, Kel-Margoulis OV, Wingender E. MATCH: A tool for searching transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(13):3576-3579. Link
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M, Hornischer K, Voss N,Stegmaier P, Lewicki-Potapov B, Saxel H, Kel AE, Wingender E. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(90001):D108-D110. Link
How to cite TRANSPATH:
Krull M, Pistor S, Voss N, Kel A, Reuter I, Kronenberg D, Michael H, Schwarzer K, Potapov A, Choi C, Kel-Margoulis O, Wingender E. TRANSPATH: an information resource for storing and visualizing signaling pathways and their pathological aberrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(90001):D546-D551. Link
Boyarskikh U, Pintus S, Mandrik N, Stelmashenko D, Kiselev I, Evshin I, Sharipov R, Stegmaier P, Kolpakov F, Filipenko M, Kel A. Computational master-regulator search reveals mTOR and PI3K pathways responsible for low sensitivity of NCI-H292 and A427 lung cancer cell lines to cytotoxic action of p53 activator Nutlin-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2018;11(1):12. Link
Michael H, Hogan J, Kel A, Kel-Margoulis O, Schacherer F, Voss N, Wingender E. Building a knowledge base for systems pathology. Brief Bioinform. 2008 Nov;9(6):518-31. Link
How to cite HumanPSD:
Michael H, Hogan J, Kel A, Kel-Margoulis O, Schacherer F, Voss N, Wingender E. Building a knowledge base for systems pathology. Brief Bioinform. 2008 Nov;9(6):518-31. Link
Hodges PE, Carrico PM, Hogan JD, O’Neill KE, Owen JJ, Mangan M, Davis BP, Brooks JE, Garrels JI. Annotating the human proteome: the Human Proteome Survey Database (HumanPSD) and an in-depth target database for G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR-PD) from Incyte Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):137-41. Link
How to cite geneXplain platform:
Kel, A., Boyarskikh, U., Stegmaier, P., Leskov, L.S., Sokolov, A.V., Yevshin, I., Mandrik, N., Stelmashenko, D., Koschmann, J., Kel-Margoulis, O. and Krull, M. Walking pathways with positive feedback loops reveal DNA methylation biomarkers of colorectal cancer. BMC bioinformatics. Cambridge (UK): RSC Publishing. 2019;20(Suppl 4):119:1-20. Link
Boyarskikh U, Pintus S, Mandrik N, Stelmashenko D, Kiselev I, Evshin I, Sharipov R, Stegmaier P, Kolpakov F, Filipenko M, Kel A. Computational master-regulator search reveals mTOR and PI3K pathways responsible for low sensitivity of NCI-H292 and A427 lung cancer cell lines to cytotoxic action of p53 activator Nutlin-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2018;11(1):12. Link
Koschmann J, Bhar A, Stegmaier P, Kel AE, Wingender E. “Upstream Analysis”: An Integrated Promoter-Pathway Analysis Approach to Causal Interpretation of Microarray Data. Microarrays (Basel). 2015;4(2):270-86. Link
Kel A, Voss N, Jauregui R, Kel-Margoulis O, Wingender E. Beyond microarrays: Finding key transcription factors controlling signal transduction pathways. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;7(S2), S13. Link
How to cite Genome Enhancer:
Kel, A., Boyarskikh, U., Stegmaier, P., Leskov, L.S., Sokolov, A.V., Yevshin, I., Mandrik, N., Stelmashenko, D., Koschmann, J., Kel-Margoulis, O. and Krull, M. Walking pathways with positive feedback loops reveal DNA methylation biomarkers of colorectal cancer. BMC bioinformatics. Cambridge (UK): RSC Publishing. 2019;20(Suppl 4):119:1-20. Link
Boyarskikh U, Pintus S, Mandrik N, Stelmashenko D, Kiselev I, Evshin I, Sharipov R, Stegmaier P, Kolpakov F, Filipenko M, Kel A. Computational master-regulator search reveals mTOR and PI3K pathways responsible for low sensitivity of NCI-H292 and A427 lung cancer cell lines to cytotoxic action of p53 activator Nutlin-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2018;11(1):12. Link
YOUR BENEFITS USING TRANSFAC 2.0
MOTIFS AND PREDICTION OF TF-BINDING SITES
Use the most comprehensive library of known eukaryotic transcription factor binding motifs
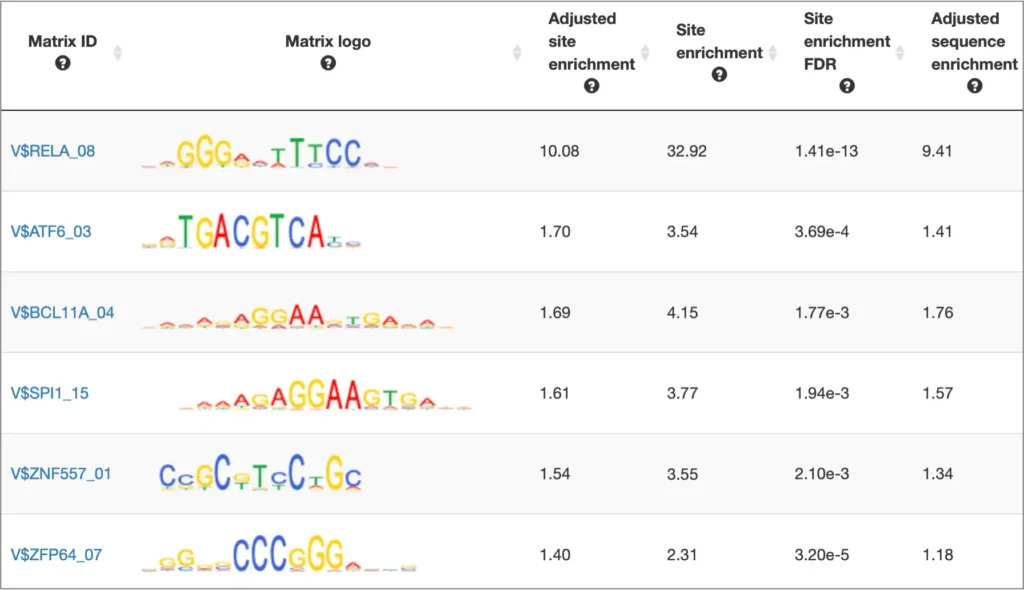
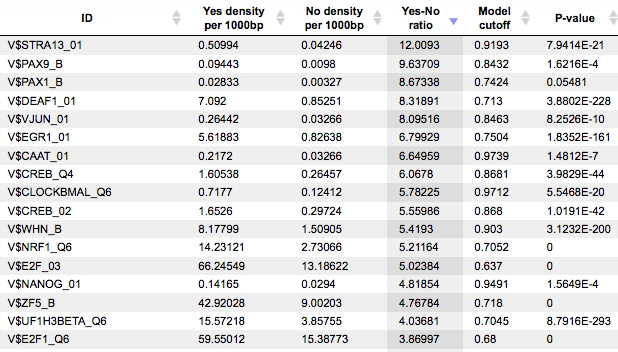
TRANSFAC systematically collects all available TF-binding motifs in the form of Positional Weight Matrices (PWMs) from scientific literature and repositories, as well as PWMs constructed by the TRANSFAC team on the basis of experimentally verified TF binding sites. Currently TRANSFAC provides more than 10,000 PWMs for various eukaryotic taxonomic groups. Our goal is to provide the most comprehensive resource of TF binding motifs for researchers world-wide
Identify common motifs in a set of target DNA sequences
Determine common motifs and compare these de-novo motifs to known transcription factor DNA binding site consensus sequences present in the TRANSFAC database
Detect genomic variants affecting TF-binding sites
Analyze mutations from your NGS data in regulatory regions for their potential negative or positive effect on transcription factor binding
Predict TF-binding sites in eukaryotic DNA sequences
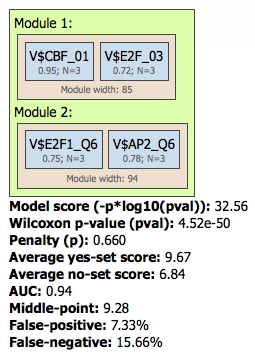
Our tools predict transcription factor (TF) binding sites and composite regulatory regions using Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
The unrivaled resource for studying promoters and enhancers
Due to its comprehensive data on transcription factors and their binding sites, tools for motif analysis, support for cross-species comparisons and functional annotations, TRANSFAC is an indispensable resource for studying promoters and enhancers
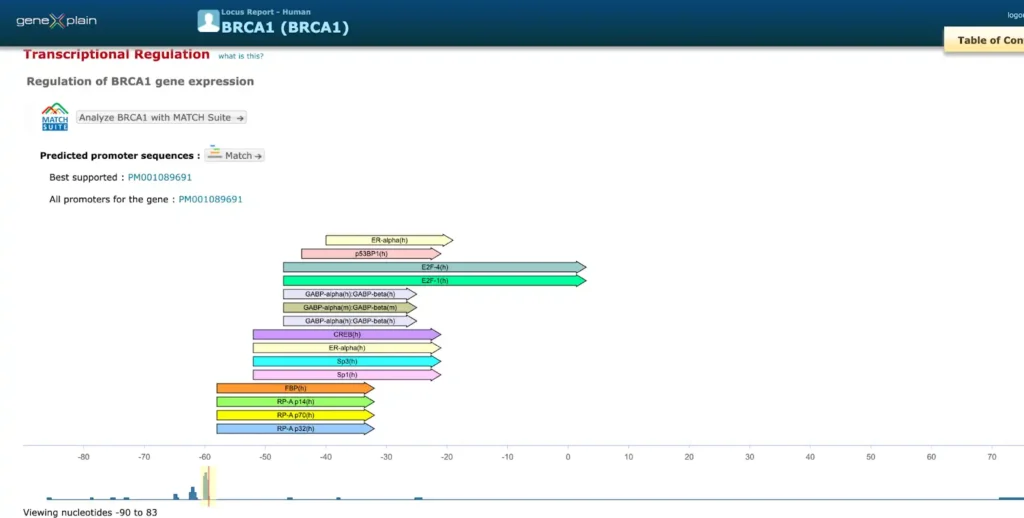
Find known transcriptional regulators for your gene(s) of interest
Search for factor-gene interactions in TRANSFAC, the largest collection of published experimentally proven transcription factor binding sites
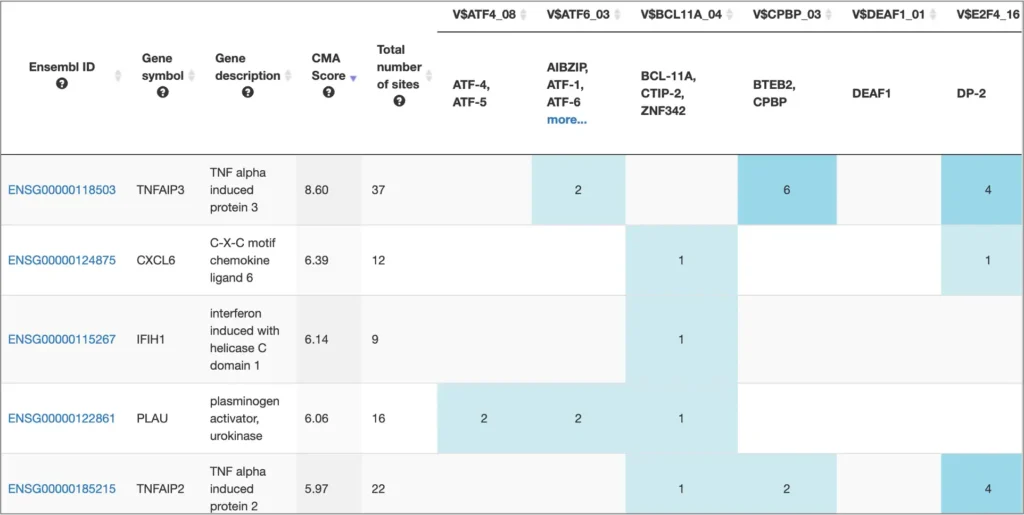
Explore factor-factor interactions and composite elements
Complement the unparalleled collection of factor-gene interactions with factor-factor interactions and synergistic and antagonistic composite elements
Predict target genes
Find target genes for a transcription factor of interest by studying from single gene promoters to whole genomes
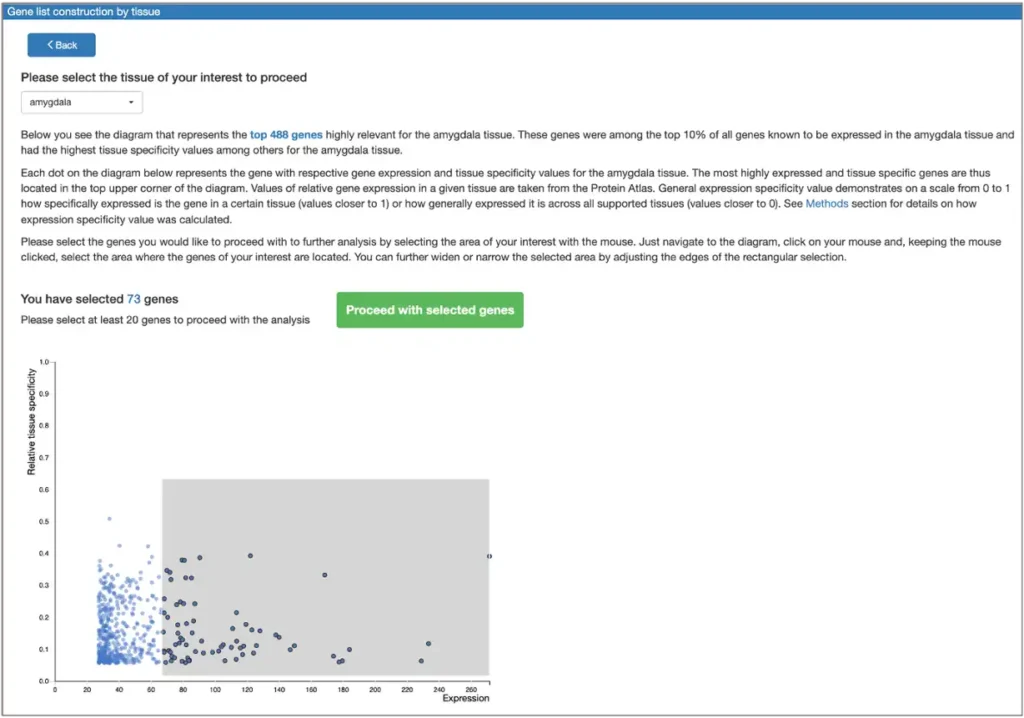
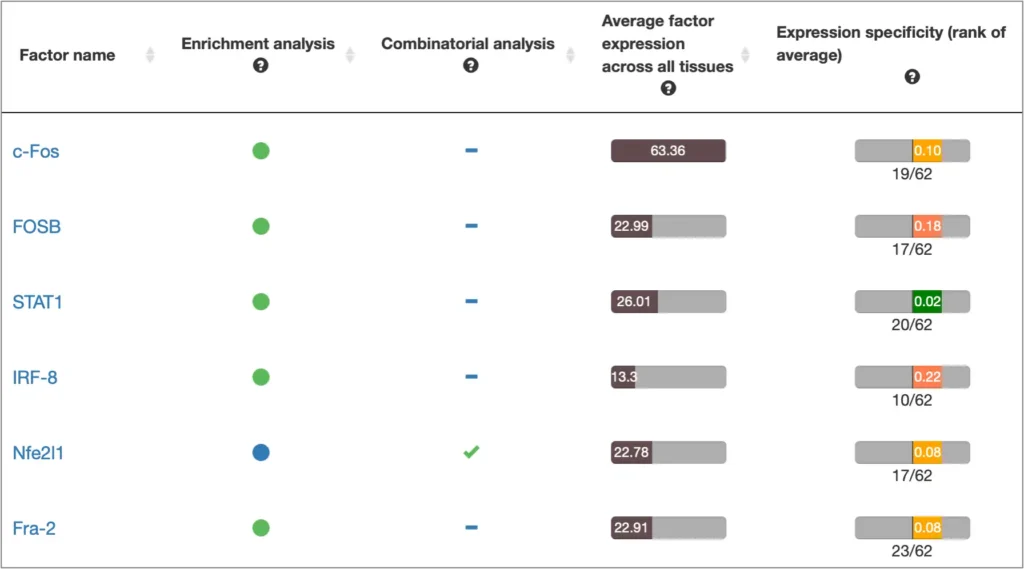
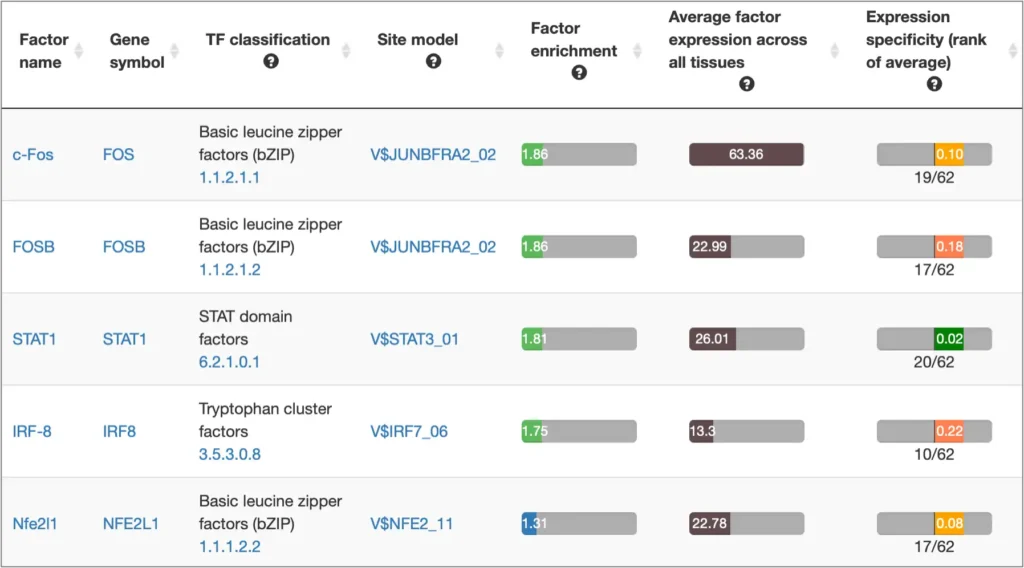
Analyze genes for tissue- and GO-specific transcription factors
Select tissue- / cell type- / induction-specific transcription factors for genes from human and model organisms
PATHWAYS AND MASTER REGULATORS
Identify pathways up- and down-stream of a gene (set)
Explore activation patterns of genes in tissues and cells of your interest and build complex interaction networks based on individual reactions with experimental details, protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and post-translational modifications (PTMs) in TRANSFAC PATHWAYS
Apply integrated network analysis and visualization
Profit from the combined approach towards causative gene regulation studies. Explore activation patterns of genes in tissues and cells of your interest and build complex interaction networks with identified master regulators
Map gene sets on pathways
Draw insights on biological function of your gene set by mapping them on pathways
Customize regulatory and metabolic networks
Build networks based on more than one million reactions extracted from original scientific literature and evaluated by experts.
MULTI-OMICS
Easily process and integrate all your omics data with TRANSFAC PATHWAYS / DISEASES
Preprocess, functionally explore, and unite various omics data (genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, proteomics and epigenomics) in a fully automized pipeline and get a combined and integrated report
Find common functional properties in a set of (co-regulated) genes
Map your data on various ontologies and identify overrepresented functional assignments in your gene set
Compare and functionally align your data
Observe how your omics data sets (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, epigenomics or metabolomics) correlate between each other
Utilize upstream analysis
Benefit from our unique upstream analysis approach combining promoter and pathway analysis to identify transcription factors and upstream master regulators (as potential drug targets) which can explain expression changes of your DEGs (or other changes in gene or protein signatures)
BIOMARKERS, DRUGS AND COMPOUNDS
Discover disease molecular mechanisms
Make use of the vast amount of gene-disease and gene-drug assignments and identify novel biomarkers and drug targets
Reconstruct disease molecular mechanism
Understand the drug’s mechanism of action (MoA) based on the collected omics data
Trace back the activated pathways
Detect disease master regulators, responsible for governing the pathology development processes, and therapeutic targets
PRECISION MEDICINE
Employ personalized medicine with TRANSFAC DISEASES
With our fully automated pipeline for patient’s multi-omics data analysis TRANSFAC DISEASES generates a comprehensive report about the personalized drug targets identified for a certain patient, or a group of patients, and the potentially effective drugs. Application examples include cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, diabetes, metabolic diseases and hypertension
Develop a personalized therapy
Identify individual drug targets and corresponding treatments based on the pathology molecular mechanism reconstructed on omics data collected from a particular patient
Repurpose drugs
Explore how known drug targets can be activated in various pathologies. Check out the possible off-label usage of treatments and identify prospective drug combinations for better patient outcomes
Find new drug candidates
Identify novel drug targets and find prospective drug-like compounds potentially acting on them by using integrated promoter, pathway and cheminformatics analysis
GENERAL
Inbuilt workflows
Make use of over 200 pre-compiled workflows
Customizable pipelines
Construct your own dedicated analysis pipeline with visual programming
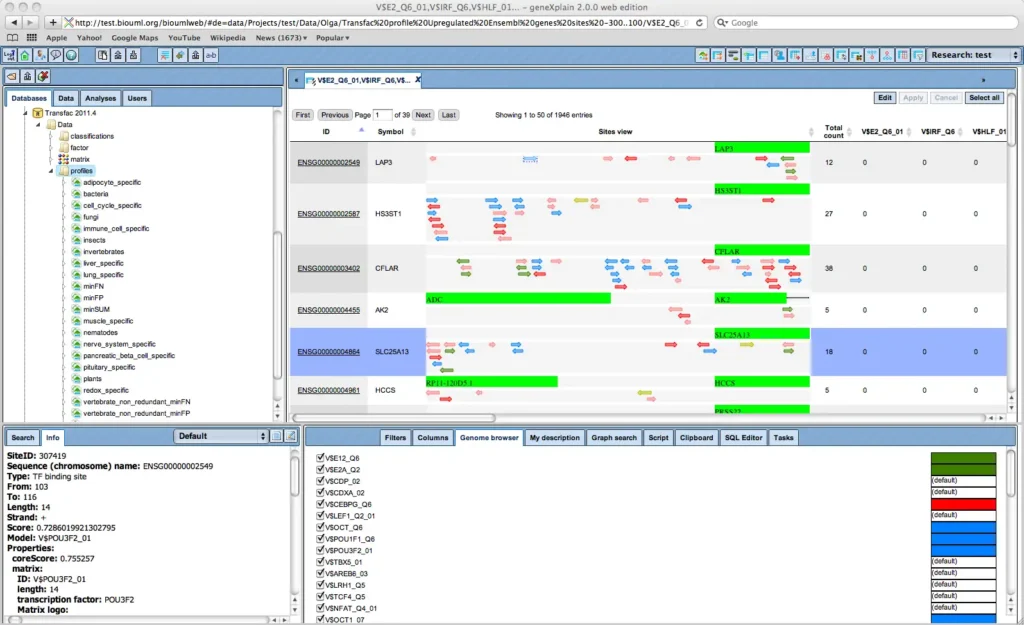
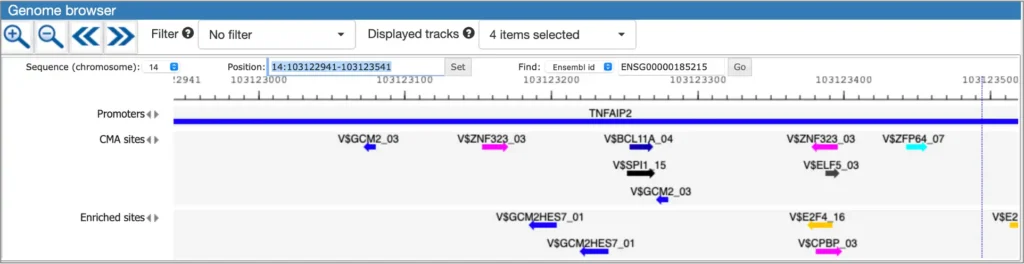
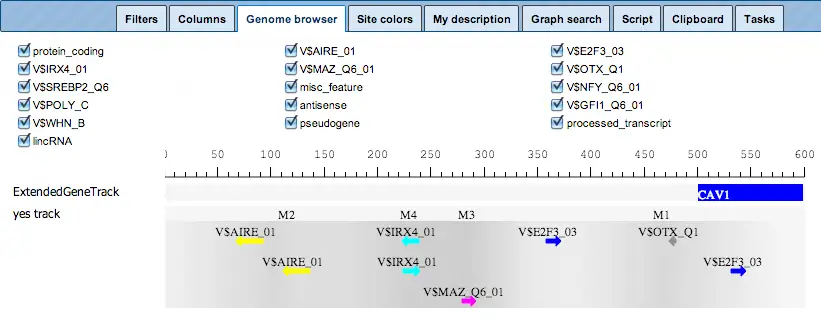
Integrated Genome Browser
Get your result in tabular format as well as in the integrated genome browser
Application Programming Interface (API)
Use Java-based API, R-based API or Jupiter notebook
Pathway/Network visualization
Visualize canonical pathways and analysis-dependent networks
Comprehensive analysis reports
Profit from automatically generated analysis reports including network visualizations, functional annotation diagrams and more
WHAT MAKES TRANSFAC 2.0 DIFFERENT FROM OTHER TOOLS?
- Most comprehensive database on gene regulation
TRANSFAC stands as the pioneering and most comprehensive database on eukaryotic transcription factors (TFs), their genomic binding sites (TFBS), and DNA binding profiles (PWMs).
- 35 years of curation and maintenance
Once established over 35 years ago, TRANSFAC has been diligently maintained and manually curated ever since.
- The biggest collection of experimentally proven functional TF binding sites
TRANSFAC 2.0 contains the biggest collection of experimentally proven TF binding sites that regulate expression of genes in genomes of eukaryotic organisms curated from original publications and documented with detailed information about tissue, cell types, TF source and quality of experimental evidence.
- The largest library of Positional Weight Matrices (PWMs)
TRANSFAC 2.0 contains over 10,000 DNA binding patterns in the format of positional weight matrices (PWMs) for animals, plants and fungi. PWMs are built based on experimentally proven TF binding sites, curated from original scientific publications and integrated from other databases.
- Signal transduction network of more than 1,200,000 reactions
TFs are connected to a network of more than 1,200,000 of signal transduction and metabolic reactions extracted from original scientific literature and evaluated by experts. Over 1500 canonical pathways are described based on these reactions.
- Unique algorithm to find master-regulators
Master-regulators are discovered by the “upstream analysis” that uniquely integrates promoter and network analysis using graph search and genetic algorithms.
- Biggest collection of more than 140,000 disease biomarkers
Manually curated collection of more than 140,000 gene to disease associations as correlative, causal and disease mechanisms biomarkers and drug targets.
- Reconstruction of disease molecular mechanisms based on the upstream analysis
Combining upstream analysis approach and disease and pathway information allows to reconstruct disease mechanisms and find novel drug targets.
- Over 300 powerful tools and pipelines to study gene regulation
TRANSFAC 2.0 provides a platform of multiple web tools and ready pipelines for analysis of NGS, RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, CUT&RUN and other types of genomics, transcriptomics, epigenomics, proteomics and metabolomics data. No cumbersome installation or special bioinformatics skills are needed.
- Robust AI algorithms for promoter and enhancer analysis
Integration of powerful tools for scanning genomes for TF binding sites and for discovering site enrichment and site combinatorial modules using AI, such as genetic algorithms, and machine learning.
- Automatic multi-omics discovery pipeline “Genome Enhancer”
Genome Enhancer provides a fully automated pipeline, including report, for patient omics data analysis, which identifies prospective drug targets and corresponding treatments by reconstructing the molecular mechanism of the studied pathology.
TRANSFAC versus JASPAR
|
Feature |
TRANSFAC |
JASPAR |
|---|---|---|
|
Database statistics |
Factors – 48,258 DNA Sites – 50,892 Factor-DNA Site Links – 68,900 Genes – 102,973 Matrices – 10,706 References – 45,130 |
– No DNA Sites -2,000 profiles (Matrices) in JASPAR core (2024 release) |
|
Database statistics (miRNA) |
miRNAs – 1,772 mRNA Sites- 67,703 miRNA-mRNA Site Links – 74,553 |
No miRNA data |
|
Database statistics |
Distinct transcription factors in Chip-seq experiment : 1,171 TF-TG associations : 15,639,406 ChIP TFBS : 95,867,624 |
No Chip-seq data. |
|
Data Depth |
Genome annotation of experimentally validated TF binding sites Genome annotation of enhancers, genome conserved regions. |
Limited to binding motifs |
|
Data Quality |
Combines public and proprietary datasets, enhancing dataset completeness. |
Restricted only to open-access data. |
|
Data Integration |
Links TF binding site data with additional omics data, including epigenetic modifications and expression profiles. Supports multi-layered analyses that combine DNA-protein interactions and gene expression. |
Focuses on TF motifs and provides limited integration with other datasets. |
|
Integrated Pathway Analysis |
Supports integrated promoter and pathway analysis allowing to identify Master Regulators of the studied processes, which in their turn can serve as prospective disease mechanism-based biomarkers and drug targets |
Limited exclusively to promoter analysis with no further pathway analysis extensions supported |
|
Additional tools |
Offers tools like MATCH™ for TFBS prediction and analysis., Click and Run pipelines integrating TRANSFAC for identifying enriched binding sites, composite modules, combinatorial analysis |
No own tools. Linked to third-party tools for motif scanning and sequence analysis |
|
AI-based extensions |
Includes AI and ML based methods for prediction of TFBS combinations, including construction of composite modules based on a genetic |
Limited to standard approached towards motif scanning and sequence analysis |
|
Clinical Relevance |
Annotated for disease-related transcription factors and binding sites. In addition to biomarker info, includes annotations for drug-disease-clinical trials relations |
Minimal disease annotations |
|
Species |
Includes data on multiple species of vertebrates, nematodes, yeast, insects, plants. TRANSFAC is integrated with geneXplain platform and provides flexibility to integrate new custom genomes and identify transcription factor binding sites |
Includes TF binding motifs for six organism classes. Integration of new custom genomes is not provided |
|
Customer Support |
Regular updates, Prompt customer support with technical assistance by experts in the industry |
Open-source platform, assistance through documentation |
|
Accessibility |
Flexible, affordable and customized packages available to access total TRANSFAC functionality |
Freely accessible for academic and non-commercial research |
Selection of articles reporting about TRANSFAC applications:
Novikova S., Tolstova T., Kurbatov L., Farafonova T., Tikhonova O., Soloveva N., Rusanov A., Zgoda V. (2024) Systems Biology for Drug Target Discovery in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25(9), 4618 Link
Ivanov, S. M., Tarasova, O. A., & Poroikov, V. V. (2023). Transcriptome-based analysis of human peripheral blood reveals regulators of immune response in different viral infections. Frontiers in immunology, 14, 1199482. Link
Menck, K., Heinrichs, S., Wlochowitz, D., Sitte, M., Noeding, H., Janshoff, A., Treiber, H., Ruhwedel, T., Schatlo, B., von der Brelie, C., Wiemann, S., Pukrop, T., Beißbarth, T., Binder, C., & Bleckmann, A. (2021). WNT11/ROR2 signaling is associated with tumor invasion and poor survival in breast cancer. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 40(1), 395. Link
Andreev-Andrievskiy, A. A., Zinovkin, R. A., Mashkin, M. A., Frolova, O. Y., Kazaishvili, Y. G., Scherbakova, V. S., Rudoy, B. A., & Nesterenko, V. G. (2021). Gene Expression Pattern of Peyer’s Patch Lymphocytes Exposed to Kagocel Suggests Pattern-Recognition Receptors Mediate Its Action. Frontiers in pharmacology, 12, 679511. Link
Ivanov, S., Filimonov, D., & Tarasova, O. (2021) A computational analysis of transcriptional profiles from CD8(+) T lymphocytes reveals potential mechanisms of HIV/AIDS control and progression. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 19, 2447–2459. Link
Li, X., Shi, J., & Li, L. M. (2025) The human intelligence evolved from proximal cis-regulatory saltations. Quantitative Biology 13(2) Link
Raj Murthi, S., Petry, A., Shashikadze, B., Stöckl, J. B., Schmid, M., Santamaria, G., Klingel, K., Kračun, D., Chen, X., Bauer, S., Schmitt, J. P., Flenkenthaler, F., Gorham, J., Toepfer, C. N., Potěšil, D., Hruška, P., Zdráhal, Z., Mayer, Z., Klop, M., Lehmann, L., … Wolf, C. M. (2025). Contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha to pathogenesis of sarcomeric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Scientific reports, 15(1), 2132. Link
Cihan, M., Schmauck, G., Sprang, M., & Andrade-Navarro, M. A. (2025). Unveiling cell-type-specific microRNA networks through alternative polyadenylation in glioblastoma. BMC biology, 23(1), 15. Link
Jian, Y., Xu, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, X. (2025). Histone modification-based functional characterization and genetic association of polymorphisms in LRRC6 and MTMR10 within CRC susceptibility regions 8q24 and 15q13.3. Gene, 943, 149286. Link
Ferreira Dos Santos, T. C., Silva, E. N., Frezarim, G. B., Salatta, B. M., Baldi, F., Simielli Fonseca, L. F., De Albuquerque, L. G., Magalhães Muniz, M. M., & Dos Santos Silva, D. B. (2025). Cis-eQTL analysis reveals genes involved in biological processes of the immune system in Nelore cattle. Gene, 937, 149138. Link
Hosseinpouri, A., Sadegh, K., Zarei-Behjani, Z., Dehghan, Z., & Karbalaei, R. (2025). Identification of critical genes and drug repurposing targets in entorhinal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurogenetics, 26(1), 27. Link
Woelk, J., Hornsteiner, F., Aschauer-Wallner, S., Stoitzner, P., Baier, G., & Hermann-Kleiter, N. (2025). Regulation of NK cell development, maturation, and antitumor responses by the nuclear receptor NR2F6. Cell death & disease, 16(1), 77. Link
Batool, F., Shireen, H., Malik, M. F., Abrar, M., & Abbasi, A. A. (2025). The combinatorial binding syntax of transcription factors in forebrain-specific enhancers. Biology open, 14(2), BIO061751. Link
Liang, Y., Yao, X., Han, J., Wang, J., Zhang, X., Zhao, D., Jiang, C., Geng, L., Lv, S., Liu, Z., & Mu, Y. (2024). Establishment of a CRISPR-Based Lentiviral Activation Library for Transcription Factor Screening in Porcine Cells. Animals : an open access journal from MDPI, 15(1), 19. Link
Dong, J. P., Xu, Y. C., Jiang, Y. N., Jiang, R. Z., Ma, L., Li, X. Z., Zeng, W. H., & Lin, Y. (2024). Identification of transcriptional signature change and critical transcription factors involved during the differentiation of mouse trophoblast stem cell into maternal blood vessel associated trophoblast giant cell. Cellular signalling, 123, 111359. Link
Mandić, K., Milutin Gašperov, N., Božinović, K., Dediol, E., Krasić, J., Sinčić, N., Grce, M., Sabol, I., & Barešić, A. (2024). Integrative analysis in head and neck cancer reveals distinct role of miRNome and methylome as tumour epigenetic drivers. Scientific reports, 14(1), 9062. Link
Syed, R., Rengasamy, P., Rajagopalan, S., Deiuliis, J. A., & Maiseyeu, A. (2024). MicroRNA 223 Enhances ABCA1 Protein Stability and Supports Efflux in Cholesterol-Burdened Macrophages. Cell Link
Nadeem, H., Jamal, S. B., Basheer, A., Bakhtiar, S. M., Faheem, M., Aziz, T., Nabi, G., Al-Harbi, M., & Raza, R. Z. (2024). Genetic Insights into Facial Variation and Craniofacial Development: Unraveling the Interplay of Genes, Expression Patterns, and Evolutionary Significance. Molecular biotechnology, 10.1007/s12033-024-01349-6. Advance online publication. Link
Zhou, Z., Lv, Y., Li, L., Yuan, X., Zhou, X., & Li, J. (2024). FoxO1 Mediated by H3K27me3 Inhibits Porcine Follicular Development by Regulating the Transcription of CYP1A1. Animals : an open access journal from MDPI, 14(23), 3514. Link
Zhou, L., Yang, Y., Qiao, Q., Mi, Y., Gan, Y., Zheng, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, M., & Zhou, Y. (2024). AKT1-Mediated NOTCH1 phosphorylation promotes gastric cancer progression via targeted regulation of IRS-1 transcription. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology, 151(1), 15. Link
Zhou L., Yang Y., Ye Y., Qiao Q., Mi Y., Liu H., Zheng Y., Wang Y., Liu M., Zhou Y. (2024). Notch1 signaling pathway promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via modulating CDH5. Aging (Albany NY). 16(16):11893–11903. Link
Li F., Wang J., Li M., Zhang X., Tang Y., Song X., Zhang Y., Pei L., Liu J., Zhang C., Li X., Xu Y., Zhang Y. (2024). Identifying cell type-specific transcription factor-mediated activity immune modules reveal implications for immunotherapy and molecular classification of pan-cancer. Brief Bioinform. 25(5):bbae368. Link
Lleshi E., Milne-Clark T., Yu H.L., Martin H.W., Hanson R., Lach R., Rossi S.H., Riediger A.L., Görtz M., Sültmann H., Flewitt A., Lynch A.G., Gnanapragasam V.J., Massie C.E., Dev H.S. (2024). Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA. iScience. 27(7):110330. Link
Ceroni F., Cicekdal M.B., Holt R., Sorokina E., Chassaing N., Clokie S., Naert T., Talbot L.V., Muheisen S., Bax D.A., Kesim Y., Kivuva E.C., Vincent-Delorme C., Lienkamp S.S., Plaisancié J., De Baere E., Calvas P., Vleminckx K., Semina E.V., Ragge N.K. (2024). Deletion upstream of MAB21L2 highlights the importance of evolutionarily conserved non-coding sequences for eye development. Nat Commun. 15(1):9245. Link
De Freitas J.T., Thakur V., LaPorte K.M., Thakur V.S., Flores B., Caicedo V., Ajaegbu C.G.E., Ingrasci G., Lipman Z.M., Zhang K., Qiu H., Malek T.R., Bedogni B. (2024). Notch1 blockade by a novel, selective anti-Notch1 neutralizing antibody improves immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma by promoting an inflamed TME. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 43:295. Link
Dig B. Mahat., Nathaniel D. Tippens., Jorge D. Martin-Rufino., Sean K. Waterton., Jiayu Fu., Sarah E. Blatt & Phillip A. Sharp. (2024) Single-cell nascent RNA sequencing unveils coordinated global transcription. Nature. 631, 216–223. Link
Sung-Joon Park., Kenta Nakai. (2024) A computational approach for deciphering the interactions between proximal and distal gene regulators in GC B-cell response. NAR Genomics & Bioiformatics. Volume 6, issue 2. Link
Farrim M.I., Gomes A., Milenkovic D., Menezes R. (2024) Gene expression analysis reveals diabetes-related gene signatures. Hum Genomics 18, 16. Link
Eni-Aganga I., Lanaghan ZM., Ismail F., Korolkova O., Goodwin JS., Balasubramaniam M., Dash C., Pandhare J. (2024). KLF6 activates Sp1-mediated prolidase transcription during TGF-β1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2024 300(2):105605. Link
Hasegawa K., Tamaki M., Sakamaki Y., Wakino S. (2024) Nmnat1 Deficiency Causes Mitoribosome Excess in Diabetic Nephropathy Mediated by Transcriptional Repressor HIC1. Int J Mol Sci. 25(12):6384. Link
Abrar M., Ali S., Hussain I., Khatoon H., Batool F., Ghazanfar S., Corcoran D., Kawakami Y., Abbasi AA. (2024). Cis-regulatory control of mammalian Trps1 gene expression. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 342(2):85-100. Link
Scaramuzzo RT., Crucitta S., Del Re M., Cammalleri M., Bagnoli P., Dal Monte M., Pini A., Filippi L.. (2024) β3-adREnoceptor Analysis in CORD Blood of Neonates (β3 RECORD): Study Protocol of a Pilot Clinical Investigation. Life (Basel). 14(6):776. Link
Cene Skubic., Hana Trček., Petra Nassib., Tinkara Kreft., Andrew Walakira., Katka Pohar., Sara Petek., zadeja Režen., Alojz Ihan., Damjana Rozman. (2024) Knockouts of CYP51A1, DHCR24, or SC5D from cholesterol synthesis reveal pathways modulated by sterol intermediates. iScience, Volume 27, Issue 9, 110651. Link
Jamil M.A., Al-Rifai R., Nuesgen N., Altmüller J., Oldenburg J., El-Maarri O. (2024) The role of microRNAs in defining LSECs cellular identity and in regulating F8 gene expression. Front Genet. 15: 1302685 Link
Coatti G.C., Vaghela N., Gillurkar P., Leir S., Harris A. (2024) A promoter-dependent upstream activator augments CFTR expression in diverse epithelial cell types. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1867(2):195031 Link
Satsu H., Gondo Y., Shimanaka H., Imae M., Murakami S., Watari K., Wakabayashi S., Park S.J., Nakai K., Shimizu M. (2022) Signaling Pathway of Taurine-Induced Upregulation of TXNIP. Metabolites. 12(7),636. Link
Deepti P., Pasha A., Kumbhakar D.V., Doneti R., Heena S.K., Bhanoth S., Poleboyina P.K., Yadala R., Anapurna S.D., Pawar S.C. (2022) Overexpression of Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) predicts poor survival in HPV positive cervical cancer. Gene. 824,146381. Link
Song Q., Bian Q., Liang T., Zhang Y., Zhang K. (2021) Identification of immune-related genes and susceptible population of pulmonary tuberculosis by constructing TF-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 131,102139. LinkThompson B., Chen Y., Davidson E.A., Garcia-Milian R., Golla J.P., Apostolopoulos N., Orlicky D.J., Schey K., Thompson D.C., Vasiliou V. (2021) Impaired GSH biosynthesis disrupts eye development, lens morphogenesis and PAX6 function. Ocul Surf. 22,190-203. Link
Selection of articles reporting about TRANSPATH applications:
Novikova S., Tolstova T., Kurbatov L., Farafonova T., Tikhonova O., Soloveva N., Rusanov A., Zgoda V. (2024) Systems Biology for Drug Target Discovery in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25(9), 4618 (2024) Link
Kisakol, B., Matveeva, A., Salvucci, M., Kel, A., McDonough, E., Ginty, F., Longley, D. B., & Prehn, J. H. M. (2024). Identification of unique rectal cancer-specific subtypes. British journal of cancer, 130(11), 1809–1818. Link
Ivanov, S. M., Tarasova, O. A., & Poroikov, V. V. (2023). Transcriptome-based analysis of human peripheral blood reveals regulators of immune response in different viral infections. Frontiers in immunology, 14, 1199482. Link
Bertram, H., Wilhelmi, S., Rajavel, A., Boelhauve, M., Wittmann, M., Ramzan, F., Schmitt, A. O., & Gültas, M. (2023). Comparative Investigation of Coincident Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Underlying Avian Influenza Viruses in Chickens and Ducks. Biology, 12(7), 969. Link
Rajavel A., Klees S., Hui Y., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2022) Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism Underlying African Animal Trypanosomiasis by Means of the 1000 Bull Genomes Project Genomic Dataset. Biology (Basel). 11(5), 742. Link
Menck K., Wlochowitz D., Wachter A., Conradi L.C., Wolff A., Scheel A.H., Korf U., Wiemann S., Schildhaus H.U., Bohnenberger H., Wingender E., Pukrop T., Homayounfar K., Beißbarth T., Bleckmann A. (2022) High-Throughput Profiling of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases Reveals Intra- and Inter-Patient Heterogeneity in the EGFR and WNT Pathways Associated with Clinical Outcome. Cancers 14(9), 2084. Link
Kechin A.A., Ivanov A.A., Kel A.E., Kalmykov A.S., Oskorbin I.P., Boyarskikh U.A., Kharpov E.A., Bakharev S.Y., Oskina N.A., Samuilenkova O.V., Vikhlyanov I.V., Kushlinskii N.E., Filipenko M.L. (2022) Prediction of EVT6-NTRK3-Dependent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Using Minor Expression Profile. Bull Exp Biol Med. 173(2),252-256. Link
Myer, P. A., Kim, H., Blümel, A. M., Finnegan, E., Kel, A., Thompson, T. V., Greally, J. M., Prehn, J. H., O’Connor, D. P., Friedman, R. A., Floratos, A., & Das, S. (2022). Master Transcription Regulators and Transcription Factors Regulate Immune-Associated Differences Between Patients of African and European Ancestry With Colorectal Cancer. Gastro Hep Adv. 1(3),328-341. Link
Chereda, H., Bleckmann, A., Menck, K., Perera-Bel, J., Stegmaier, P., Auer, F., Kramer, F., Leha, A., & Beißbarth, T. (2021). Explaining decisions of graph convolutional neural networks: patient-specific molecular subnetworks responsible for metastasis prediction in breast cancer. Genome Med. 13(1),42. Link
Menck, K., Heinrichs, S., Wlochowitz, D., Sitte, M., Noeding, H., Janshoff, A., Treiber, H., Ruhwedel, T., Schatlo, B., von der Brelie, C., Wiemann, S., Pukrop, T., Beißbarth, T., Binder, C., & Bleckmann, A. (2021). WNT11/ROR2 signaling is associated with tumor invasion and poor survival in breast cancer. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 40(1), 395. Link
Kalya M., Kel A., Wlochowitz D., Wingender E., Beißbarth T. (2021) IGFBP2 Is a Potential Master Regulator Driving the Dysregulated Gene Network Responsible for Short Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Front Genet. 12, 670240. Link
Benjamin, S.J., Hawley, K.L., Vera-Licona, P., La Vake, C.J., Cervantes, J.L., Ruan, Y., Radolf, J.D., Salazar, J.C. (2021) Macrophage mediated recognition and clearance of Borrelia burgdorferi elicits MyD88-dependent and -independent phagosomal signals that contribute to phagocytosis and inflammation. BMC Immunol. 22, 32. Link
Ivanov, S., Filimonov, D., & Tarasova, O. (2021) A computational analysis of transcriptional profiles from CD8(+) T lymphocytes reveals potential mechanisms of HIV/AIDS control and progression. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 19, 2447–2459. Link
Meier, T., Timm, M., Montani, M., Wilkens, L. (2021) Gene networks and transcriptional regulators associated with liver cancer development and progression. BMC Med. Genomics 14, 41. Link
Andreev-Andrievskiy, A. A., Zinovkin, R. A., Mashkin, M. A., Frolova, O. Y., Kazaishvili, Y. G., Scherbakova, V. S., Rudoy, B. A., & Nesterenko, V. G. (2021). Gene Expression Pattern of Peyer’s Patch Lymphocytes Exposed to Kagocel Suggests Pattern-Recognition Receptors Mediate Its Action. Frontiers in pharmacology, 12, 679511. Link
Lloyd K., Papoutsopoulou S., Smith E., Stegmaier P., Bergey F., Morris L., Kittner M., England H., Spiller D., White M.H.R., Duckworth C.A., Campbell B.J., Poroikov V., Martins Dos Santos V.A.P., Kel A., Muller W., Pritchard D.M., Probert C., Burkitt M.D.; SysmedIBD Consortium. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis Model Mech. 13(11), dmm044040. Link
Ramzan, F., Klees, S., Schmitt, A. O., Cavero, D., & Gültas, M. (2020) Identification of Age-Specific and Common Key Regulatory Mechanisms Governing Eggshell Strength in Chicken Using Random Forests. Genes (Basel). 11(4), 464. Link
Ayyildiz D., Antoniali G., D’Ambrosio C., Mangiapane G., Dalla E., Scaloni A., Tell G., Piazza S. (2020) Architecture of The Human Ape1 Interactome Defines Novel Cancers Signatures. Sci Rep. 10, 28. Link
Mekonnen, Y.A., Gültas, M., Effa, K., Hanotte, O., Schmitt, A.O. (2019) Identification of Candidate Signature Genes and Key Regulators Associated With Trypanotolerance in the Sheko Breed. Front. Genet. 10, 1095. Link
Nobis, C. C., Dubeau Laramée, G., Kervezee, L., Maurice De Sousa, D., Labrecque, N., & Cermakian, N. (2019) The circadian clock of CD8 T cells modulates their early response to vaccination and the rhythmicity of related signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116(40), 20077–20086. Link
Orekhov A.N., Oishi Y., Nikiforov N.G., Zhelankin A.V., Dubrovsky L., Sobenin I.A., Kel A., Stelmashenko D., Makeev V.J., Foxx K., Jin X., Kruth H.S., Bukrinsky M. (2018) Modified LDL Particles Activate Inflammatory Pathways in Monocyte-derived Macrophages: Transcriptome Analysis. Curr Pharm Des. 24(26),3143-3151. Link
Wlochowitz, D., Haubrock, M., Arackal, J., Bleckmann, A., Wolff, A., Beißbarth, T., Wingender, E., Gültas, M. (2016) Computational Identification of Key Regulators in Two Different Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Genet. 7, 42. Link
Kural, K.C., Tandon, N., Skoblov, M., Kel-Margoulis, O.V. and Baranova, A.V. (2016) Pathways of aging: comparative analysis of gene signatures in replicative senescence and stress induced premature senescence. BMC Genomics 17(Suppl 14), 1030. Link
Malusa, F., Taranta, M., Zaki, N., Cinti, C., & Capobianco, E. (2015) Time-course gene profiling and networks in demethylated retinoblastoma cell line. Oncotarget. 6(27), 23688–23707. Link
Kutumova E.O., Kiselev I.N., Sharipov R.N., Lavrik I.N., Kolpakov F.A. (2012) A modular model of the apoptosis machinery. Adv Exp Med Biol. 736, 235-45. Link
Schuler, M., Keller, A., Backes, C., Philippar, K., Lenhof, H. P., & Bauer, P. (2011) Transcriptome analysis by GeneTrail revealed regulation of functional categories in response to alterations of iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 11, 87. Link
Ante M., Wingender E., Fuchs M. (2011) Integration of gene expression data with prior knowledge for network analysis and validation. BMC Res Notes. 4,520. Link
Chiu SC, Tsao SW, Hwang PI, Vanisree S, Chen YA, Yang NS. (2010) Differential functional genomic effects of anti-inflammatory phytocompounds on immune signaling. BMC Genomics. 11, 513. Link
Selection of articles reporting about HumanPSD applications:
Kawashima Y., Nagai H., Konno R., Ishikawa M., Nakajima D., Sato H., Nakamura R., Furuyashiki T., Ohara O. (2022) Single-Shot 10K Proteome Approach: Over 10,000 Protein Identifications by Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Single-Shot Proteomics with Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 21(6), 1418–1427. Link
Lim, J. S., Ibaseta, A., Fischer, M. M., Cancilla, B., O’Young, G., Cristea, S., Luca, V. C., Yang, D., Jahchan, N. S., Hamard, C., Antoine, M., Wislez, M., Kong, C., Cain, J., Liu, Y. W., Kapoun, A. M., Garcia, K. C., Hoey, T., Murriel, C. L., & Sage, J. (2017). Intratumoural heterogeneity generated by Notch signalling promotes small-cell lung cancer. Nature, 545(7654), 360–364. Link
Reales‐Calderón, J. A., Aguilera‐Montilla, N., Corbí, Á. L., Molero, G., & Gil, C. (2014). Proteomic characterization of human proinflammatory M1 and anti‐inflammatory M2 macrophages and their response to Candida albicans. Proteomics, 14(12), 1503-1518. Link
Martínez‐Solano, L., Nombela, C., Molero, G., & Gil, C. (2006). Differential protein expression of murine macrophages upon interaction with Candida albicans. Proteomics, 6(S1), S133-S144. Link
Selection of articles reporting about geneXplain platform applications:
Novikova S., Tolstova T., Kurbatov L., Farafonova T., Tikhonova O., Soloveva N., Rusanov A., Zgoda V. (2024) Systems Biology for Drug Target Discovery in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25(9), 4618 Link
Kisakol, B., Matveeva, A., Salvucci, M., Kel, A., McDonough, E., Ginty, F., Longley, D., Prehn, J. (2024) Identification of unique rectal cancer-specific subtypes. Br J Cancer. 130, 1809–1818. DOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02656-0. Link
Xinxin Liu., Zhihua Huang., Qiuzheng Chen., Kai Chen., Weikang Liu., Guangnian Liu., Xiangyu Chu., Dongqi Li., Yongsu Ma., Xiaodong Tian., Yinmo Yang. (2024) Hypoxia-induced epigenetic regulation of miR-485-3p promotes stemness and chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis. Cell Death Discovery. 10, 262. Link
Drake, C., Zobl W., Wehr M., Koschmann J., De Luca D., Kühne B. A. , Vrieling H. , Boei J. , Hansen T. , Escher S. E. (2023) Substantiate a read-across hypothesis by using transcriptome data—A case study on volatile diketones. Front. Toxicol. 5. Link
Rajavel A., Klees S., Hui Y., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2022) Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism Underlying African Animal Trypanosomiasis by Means of the 1000 Bull Genomes Project Genomic Dataset. Biology (Basel). 11(5), 742. Link
Menck K., Wlochowitz D., Wachter A., Conradi L.C., Wolff A., Scheel A.H., Korf U., Wiemann S., Schildhaus H.U., Bohnenberger H., Wingender E., Pukrop T., Homayounfar K., Beißbarth T., Bleckmann A. (2022) High-Throughput Profiling of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases Reveals Intra- and Inter-Patient Heterogeneity in the EGFR and WNT Pathways Associated with Clinical Outcome. Cancers 14(9), 2084. Link
Myer P.A., Kim H., Blümel A.M., Finnegan E., Kel A., Thompson T.V., Greally J.M., Prehn J.H., O’Connor D.P., Friedman R.A., Floratos A., Das S. (2022) Master Transcription Regulators and Transcription Factors Regulate Immune-Associated Differences Between Patients of African and European Ancestry With Colorectal Cancer. Gastro Hep Adv. 1(3), 328–341. Link
Kawashima Y., Nagai H., Konno R., Ishikawa M., Nakajima D., Sato H., Nakamura R., Furuyashiki T., Ohara O. (2022) Single-Shot 10K Proteome Approach: Over 10,000 Protein Identifications by Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Single-Shot Proteomics with Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 21(6), 1418–1427. Link
Klees S., Schlüter J.S., Schellhorn J., Bertram H., Kurzweg A.C., Ramzan F., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2022) Comparative Investigation of Gene Regulatory Processes Underlying Avian Influenza Viruses in Chicken and Duck. Biology (Basel). 11(2), 219. Link
Benjamin, S.J., Hawley, K.L., Vera-Licona, P., La Vake, C.J., Cervantes, J.L., Ruan, Y., Radolf, J.D., Salazar, J.C. (2021) Macrophage mediated recognition and clearance of Borrelia burgdorferi elicits MyD88-dependent and -independent phagosomal signals that contribute to phagocytosis and inflammation. BMC Immunol. 22, 32. Link
Menck K., Heinrichs S., Wlochowitz D., Sitte M., Noeding H., Janshoff A., Treiber H., Ruhwedel T., Schatlo B., von der Brelie C., Wiemann S., Pukrop T., Beißbarth T., Binder C., Bleckmann A. (2021) WNT11/ROR2 signaling is associated with tumor invasion and poor survival in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40, 395. Link
Meier, T., Timm, M., Montani, M., Wilkens, L. (2021) Gene networks and transcriptional regulators associated with liver cancer development and progression. BMC Med. Genomics 14, 41. Link
Chereda H., Bleckmann A., Menck K., Perera-Bel J., Stegmaier P., Auer F., Kramer F., Leha A., Beißbarth T. (2021) Explaining decisions of graph convolutional neural networks: patient-specific molecular subnetworks responsible for metastasis prediction in breast cancer. Genome Med. 13, 42. Link
Heinrich F., Ramzan F., Rajavel A., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2021) MIDESP: Mutual Information-Based Detection of Epistatic SNP Pairs for Qualitative and Quantitative Phenotypes. Biology (Basel). 10(9), 921. Link
Tenesaca S., Vasquez M., Alvarez M., Otano I., Fernandez-Sendin M., Di Trani C.A., Ardaiz N., Gomar C., Bella A., Aranda F., Medina-Echeverz J., Melero I., Berraondo P. (2021) Statins act as transient type I interferon inhibitors to enable the antitumor activity of modified vaccinia Ankara viral vectors. J Immunother Cancer. 9(7), e001587. Link
Vanvanhossou S.F.U., Giambra I.J., Yin T., Brügemann K., Dossa L.H., König S. (2021) First DNA Sequencing in Beninese Indigenous Cattle Breeds Captures New Milk Protein Variants. Genes (Basel). 12(11), 1702. Link
Lloyd K., Papoutsopoulou S., Smith E., Stegmaier P., Bergey F., Morris L., Kittner M., England H., Spiller D., White M.H.R., Duckworth C.A., Campbell B.J., Poroikov V., Martins Dos Santos V.A.P., Kel A., Muller W., Pritchard D.M., Probert C., Burkitt M.D.; SysmedIBD Consortium. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis Model Mech. 13(11), dmm044040. Link
Odagiu L., Boulet S., Maurice De Sousa D., Daudelin J.F., Nicolas S., Labrecque N. (2020) Early programming of CD8+ T cell response by the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117(39), 24392–24402. Link
Ayyildiz D., Antoniali G., D’Ambrosio C., Mangiapane G., Dalla E., Scaloni A., Tell G., Piazza S. (2020) Architecture of The Human Ape1 Interactome Defines Novel Cancers Signatures. Sci Rep. 10, 28. Link
Ural, B.B., Yeung, S.T., Damani-Yokota, P., Devlin, J.C., de Vries, M., Vera-Licona, P., Samji, T., Sawai, C.M., Jang, G., Perez, O.A., Pham, Q., Maher, L., Loke, P., Dittmann, M., Reizis, B., Khanna, K.M. (2020) Identification of a nerve-associated, lung-resident interstitial macrophage subset with distinct localization and immunoregulatory properties. Sci. Immunol. 5, eaax8756. Link
Leiherer A., Muendlein A., Saely C.H., Fraunberger P., Drexel H. (2019) Serotonin is elevated in risk-genotype carriers of TCF7L2 – rs7903146. Sci Rep. 9, 12863. Link
Wang B., Ran Z., Liu M., Ou Y. (2019) Prognostic Significance of Potential Immune Checkpoint Member HHLA2 in Human Tumors: A Comprehensive Analysis. Front Immunol. 10, 1573. Link
Mekonnen, Y.A., Gültas, M., Effa, K., Hanotte, O., Schmitt, A.O. (2019) Identification of Candidate Signature Genes and Key Regulators Associated With Trypanotolerance in the Sheko Breed. Front. Genet. 10, 1095. Link
Blazquez, R., Wlochowitz, D., Wolff, A., Seitz, S., Wachter, A., Perera-Bel, J., Bleckmann, A., Beißbarth, T., Salinas, G., Riemenschneider, M.J., Proescholdt, M., Evert, M., Utpatel, K., Siam, L., Schatlo, B., Balkenhol, M., Stadelmann, C., Schildhaus, H.U., Korf, U., Reinz, E., Wiemann, S., Vollmer, E., Schulz, M., Ritter, U., Hanisch, U.K., Pukrop, T. (2018) PI3K: A master regulator of brain metastasis-promoting macrophages/microglia. Glia 66, 2438-2455. Link
Orekhov, A.N., Oishi, Y., Nikiforov, N.G., Zhelankin, A.V., Dubrovsky, L., Sobenin, I.A., Kel, A., Stelmashenko, D., Makeev, V.J., Foxx, K., Jin, X., Kruth, H.S. Bukrinsky, M. (2018) Modified LDL Particles Activate Inflammatory Pathways in Monocyte-derived Macrophages: Transcriptome Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 24, 3143-3151. Link
Smetanina, M.A., Kel, A.E., Sevost’ianova, K.S., Maiborodin, I.V., Shevela, A.I., Zolotukhin, I.A., Stegmaier, P., Filipenko, M.L. (2018) DNA methylation and gene expression profiling reveal MFAP5 as a regulatory driver of extracellular matrix remodeling in varicose vein disease. Epigenomics 10, 1103-1119. Link
Kalozoumi, G., Kel-Margoulis, O., Vafiadaki, E., Greenberg, D., Bernard, H., Soreq, H., Depaulis, A., Sanoudou, D. (2018) Glial responses during epileptogenesis in Mus musculus point to potential therapeutic targets. PLoS One 13, e0201742. Link
Mandić, A.D., Bennek, E., Verdier, J., Zhang, K., Roubrocks, S., Davis, R.J., Denecke, B., Gassler, N., Streetz, K., Kel, A., Hornef, M., Cubero, F. J., Trautwein, C. and Sellge, G. (2017) c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 promotes enterocyte survival and goblet cell differentiation in the inflamed intestine. Mucosal Immunol. 10, 1211-1223. Link
Niehof, M., Hildebrandt, T., Danov, O., Arndt, K., Koschmann, J., Dahlmann, F., Hansen, T. and Sewald, K. (2017) RNA isolation from precision-cut lung slices (PCLS) from different species. BMC Res. Notes 10, 121. Link
Triska, M., Solovyev, V., Baranova, A., Kel, A., Tatarinova, T.V. (2017) Nucleotide patterns aiding in prediction of eukaryotic promoters. PLoS One 12, e0187243. Link
Pietrzyńska, M., Zembrzuska, J., Tomczak, R., Mikołajczyk, J., Rusińska-Roszak, D., Voelkel, A., Buchwald, T., Jampílek, J., Lukáč, M., Devínsky, F. (2016) Experimental and in silico investigations of organic phosphates and phosphonates sorption on polymer-ceramic monolithic materials and hydroxyapatite. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 295-303. Link
Ciribilli, Y., Singh, P., Inga, A., Borlak, J. (2016) c-Myc targeted regulators of cell metabolism in a transgenic mouse model of papillary lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7, 65514-65539. Link
Wlochowitz, D., Haubrock, M., Arackal, J., Bleckmann, A., Wolff, A., Beißbarth, T., Wingender, E., Gültas, M. (2016) Computational Identification of Key Regulators in Two Different Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Genet. 7, 42. Link
Lee, E.H., Oh, J.H., Selvaraj, S., Park, S.M., Choi, M.S., Spanel, R., Yoon, S. and Borlak, J. (2016) Immunogenomics reveal molecular circuits of diclofenac induced liver injury in mice. Oncotarget 7, 14983-15017. Link
Kural, K.C., Tandon, N., Skoblov, M., Kel-Margoulis, O.V. and Baranova, A.V. (2016) Pathways of aging: comparative analysis of gene signatures in replicative senescence and stress induced premature senescence. BMC Genomics 17(Suppl 14), 1030. Link
Borlak, J., Singh, P. and Gazzana, G. (2015) Proteome mapping of epidermal growth factor induced hepatocellular carcinomas identifies novel cell metabolism targets and mitogen activated protein kinase signalling events. BMC Genomics 16, 124. Link
Shi, Y., Nikulenkov, F., Zawacka-Pankau, J., Li, H., Gabdoulline, R., Xu, J., Eriksson, S., Hedström, E., Issaeva, N., Kel, A., Arnér, E.S., Selivanova, G. (2014) ROS-dependent activation of JNK converts p53 into an efficient inhibitor of oncogenes leading to robust apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 21, 612-623. Link
Schlereth, K., Heyl, C., Krampitz, A.M., Mernberger, M., Finkernagel, F., Scharfe, M., Jarek, M., Leich, E., Rosenwald, A., Stiewe, T. (2013) Characterization of the p53 Cistrome – DNA Binding Cooperativity Dissects p53’s Tumor Suppressor Functions. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003726.Link
Nikulenkov, F., Spinnler, C., Li, H., Tonelli, C., Shi, Y., Turunen, M., Kivioja, T., Ignatiev, I., Kel, A., Taipale, J., Selivanova, G. (2012) Insights into p53 transcriptional function via genome-wide chromatin occupancy and gene expression analysis. Cell Death Differ. 19, 1992-2002. Link
Zawacka-Pankau, J., Grinkevich, V.V., Hunten, S., Nikulenkov, F., Gluch, A., Li, H., Enge, M., Kel, A., Selivanova, G. (2011) Inhibition of glycolytic enzymes mediated by pharmacologically activated p53: targeting Warburg effect to fight cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 41600-41615. Link
Publications authored by the geneXplain team
Selection of publications authored by the geneXplain team:
Kisakol, B., Matveeva, A., Salvucci, M., Kel, A., McDonough, E., Ginty, F., Longley, D. B., & Prehn, J. H. M. (2024). Identification of unique rectal cancer-specific subtypes. British journal of cancer, 130(11), 1809–1818. Link
Kolpakov, F., Akberdin, I., Kiselev, I., Kolmykov, S., Kondrakhin, Y., Kulyashov, M., Kutumova, E., Pintus, S., Ryabova, A., Sharipov, R., Yevshin, I., Zhatchenko, S., & Kel, A. (2022). BioUML-towards a universal research platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 50(W1),W124–31. Link
Orekhov A.N., Sukhorukov V.N., Nikiforov N.G., Kubekina M.V., Sobenin I.A., Foxx K.K., Pintus S., Stegmaier P., Stelmashenko D., Kel A., Poznyak A.V., Wu W.K., Kasianov A.S., Makeev V.Y., Manabe I., Oishi Y. (2020) Signaling Pathways Potentially Responsible for Foam Cell Formation: Cholesterol Accumulation or Inflammatory Response-What is First? Int J Mol Sci. 21(8),2716. Link
Kel A., Boyarskikh U., Stegmaier P., Leskov L.S., Sokolov A.V., Yevshin I., Mandrik N., Stelmashenko D., Koschmann J., Kel-Margoulis O., Krull M., Martínez-Cardús A., Moran S., Esteller M., Kolpakov F., Filipenko M., Wingender E. (2019) Walking pathways with positive feedback loops reveal DNA methylation biomarkers of colorectal cancer. BMC Bioinformatics. 20(Suppl 4),119. Link
Boyarskikh, U., Pintus, S., Mandrik, N., Stelmashenko, D., Kiselev, I., Evshin, I., Sharipov, R., Stegmaier, P., Kolpakov, F., Filipenko, M., Kel, A. (2018) Computational master-regulator search reveals mTOR and PI3K pathways responsible for low sensitivity of NCI-H292 and A427 lung cancer cell lines to cytotoxic action of p53 activator Nutlin-3. BMC Med. Genomics 11(Suppl 1), 12. Link
Kel, A.E., Stegmaier, P., Valeev, T., Koschmann, J., Poroikov, V., Kel-Margoulis, O.V. and Wingender, E. (2016) Multi-omics “upstream analysis” of regulatory genomic regions helps identifying targets against methotrexate resistance of colon cancer. EuPA Open Proteomics 13, 1-13. Link