geneXplain platform
The geneXplain platform is an online toolbox and workflow management system for a broad range of bioinformatic and systems biology applications.
TRANSFAC® is equipped with the best in the field, flexible online software platform that provides:
The geneXplain platform
The geneXplain platform is an online toolbox and workflow management system for a broad range of bioinformatic and systems biology applications.
The individual modules, or Bricks, are unified under a standardized interface, with a consistent look-and-feel and can flexibly be put together to comprehensive workflows. The workflow management is intuitively handled through a simple drag-and-drop system. With this system, you can edit the predefined workflows or compose your own workflows from scratch.
Own Bricks can easily be added as scripts or plug-ins and can be used in combination with pre-existing analyses.
GeneXplain GmbH provides a number of state-of-the-art bricks; some of them can be obtained free of charge, while others require licensing for small fee in order to guarantee active maintenance and dynamic adaptation to the rapidly developing know-how in this field.
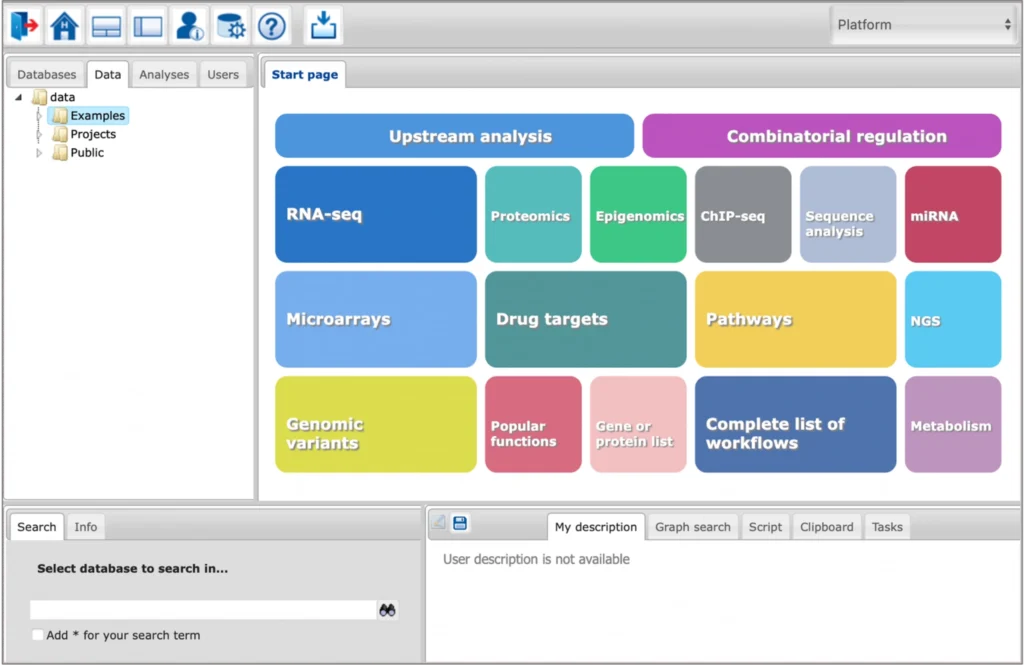
Key features
Integrated AI and ML tools for TFBS prediction
The platform provides access to advanced tools for prediction of genomic transcription factor (TF) binding sites and composite regulatory regions using such algorithms of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) as Genetic Algorithms and Sparse Logistic Regression.
Integrated databases and analysis tools
The platform provides an integrated view on several databases and analysis tools, public domain as well as commercial ones. They can be combined in a highly flexible way to design customized analyses.
Ready-made workflows for an easy start
A rapidly growing number of proven workflows facilitates a quick and easy access to the platform and its complex analysis functions. Input forms are simple and user-friendly. Workflows can be easily customized to specific needs. Experienced users can create their own workflows.
Fully integrated upstream analysis
The platform provides a fully integrated upstream analysis, which combines state-of-the-art analysis of regulatory genome regions with sophisticated pathway analyses.
Knowledge-based data analysis
The platform uses a number of renowned high-quality databases for the data analysis. TRANSFAC® and TRANSPATH® are expert-curated databases. GeneWays is generated by an NLP-based text-mining approach, providing a helpful complement for manually curated data. Well-known public-domain databases like Reactome and HumanCyc are integrated and applied as well.
JavaScript and R scripts
User-specific scripts in JavaScript and in R can be added directly into the platform, and immediately executed. They can be combined with pre-existing analyses, and can be part of the workflows.
NGS data analysis
NGS data analysis is supported by the platform. ChIP-seq data sets containing in vivo transcription factor binding sites or methylation results can be analyzed with the help of ready-made workflows. Galaxy tools are integrated, supporting RNA-seq data analysis, and many functions more.
Simulation engine inside
The platform contains a simulation engine that executes differential equation systems and visualizes the results. Parameter optimization, parameter fitting (based on expression data), and hierarchical modeling are supported.
Group project work including chat function
Share your data and results with other members of the project. Discuss what you are doing while working together on a dataset.
Videos
Here are videos about “RNA-seq preprocessing with the geneXplain platform”
Playlist about “RNA-seq data analysis from FASTQ files to master regulators with geneXplain platform”
Find below a compilation of our introductory and tutorial videos
In English Language
This video is a general introduction to the geneXplain® platform. (3:21 min)
This video is about how to convert gene identifiers from Ensembl to others in the geneXplain platform. (3:02 min)
This video is about how to annotate a gene table with the geneXplain platform. (2:57 min)
In Chinese Language
This video is a general introduction to the geneXplain® platform; it introduces you to different workflows. (1:38 min)
It shows you how to register a free platform account and to login. The audio-visual also introduces you to the look and feel of the geneXplain® platform interface. (4:11 min)
This video demonstrates how to upload raw data from an experiment to the geneXplain®platform for further analysis. (2:46 min)
In this video microarray data is used as an example to show you how to further analyze data from high-throughput experiments on the geneXplain® platform. (6:45 min)
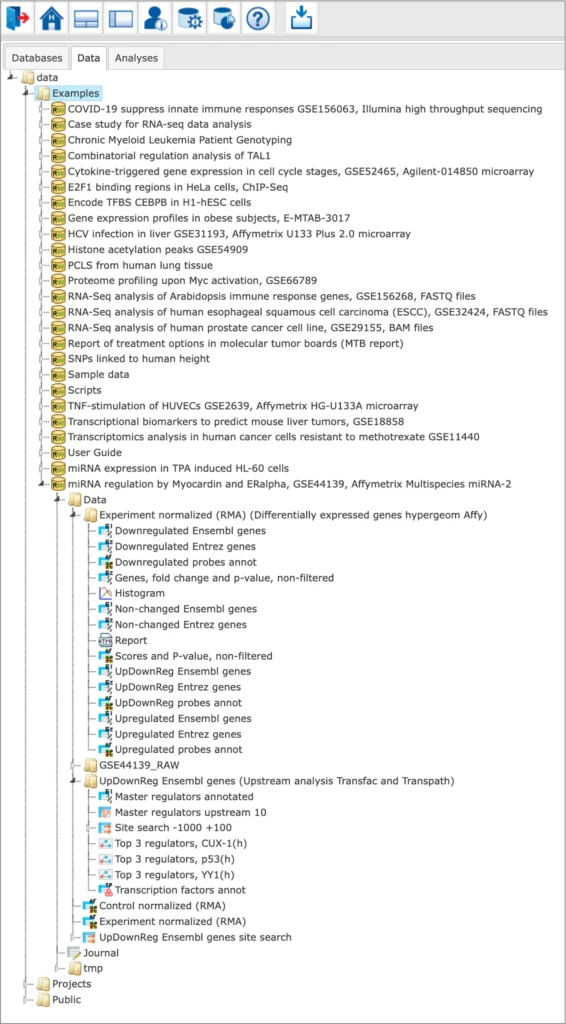
Examples
Any user of the geneXplain platform can view the free examples demonstrating the platform abilities towards processing various types of multi-omics data in different studied biological processes and pathologies.
The Examples are located in the Data tab of the geneXplain platform interface under the Examples folder:
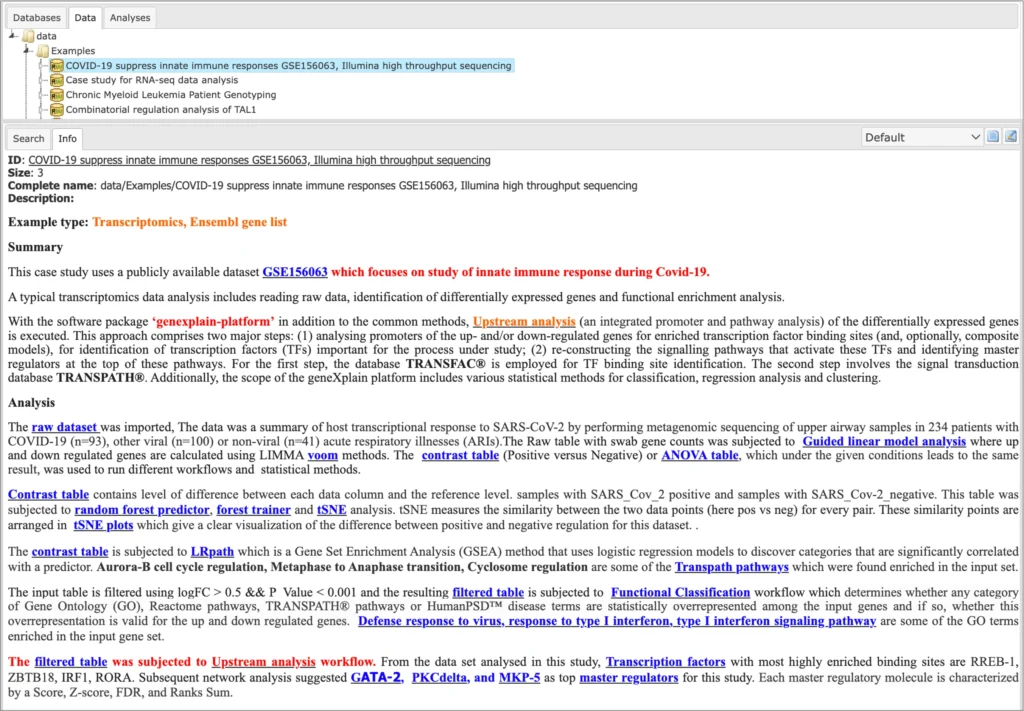
Description of each example is available in the info box upon the click on the name of the respective project:
Methods and workflows for TFBS prediction
The geneXplain platform provides TFBS prediction tools from single sequence to whole genome
In the geneXplain platform interface, you will find a great variety of methods and workflows for TFBS prediction.
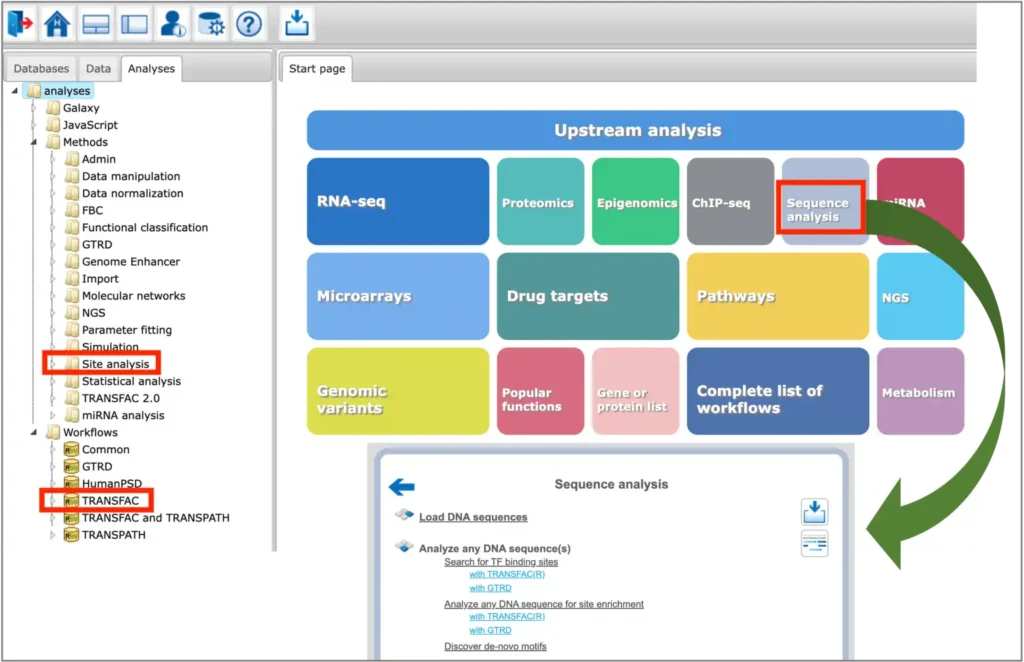
General info
The TFBS prediction tools are located in the Analyses –> Methods –> Site analysis section of the platform, as well as in the Analyses –> Workflows –> TRANSFAC section of the platform. Selected tools for sequence analysis can be found under the Sequence analysis button of the platform start page:
You can find information on the profile selection (collection of positional weight matrices – PWMs – transcription factor binding models that will be used for performing the site search) in this document or in tabular format here.
Search for TF binding sites with TRANSFAC®
The Search for TF binding sites with TRANSFAC® workflow in the geneXplain platform is designed to search for putative transcription factor binding sites, TFBS, in any input DNA sequence in EMBL, Fasta or Genbank formats. Using this workflow you can analyze DNA sequences of any species and of any genomic regions. In the analysis results of this workflow you will find a summary table and a track with found sites in the input sequences.
The summary table gives the site density per thousand bp for each matrix in the input sequence:
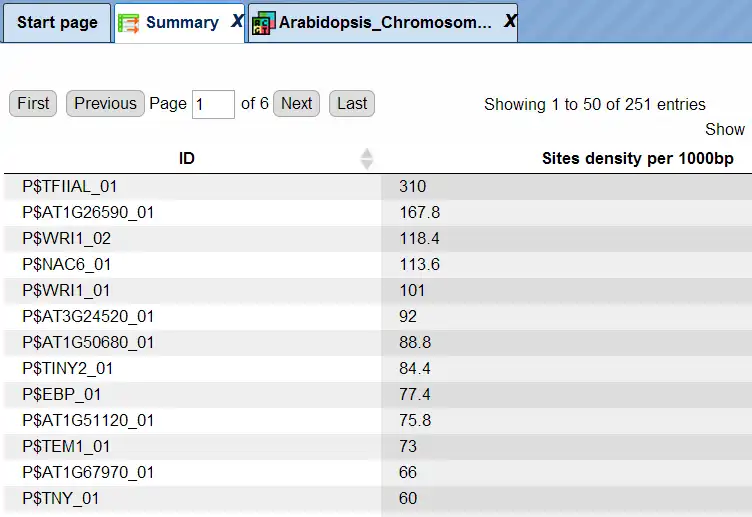
Each row summarizes the information for one site model (PWM – positional weight matrix).
For each row, the column Site density per 1000bp shows the number of matches normalized per 1000 bp length for the sequences in the input set.
The track of found sites can be visualised in genome browser:
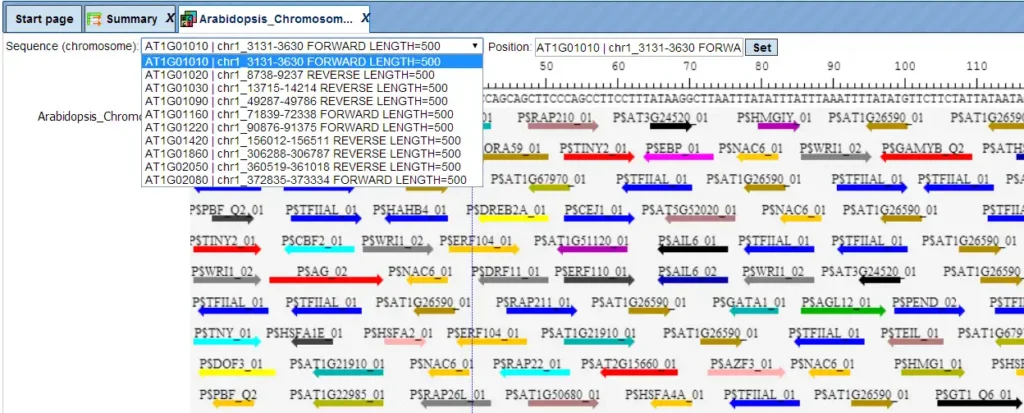
In the field Sequence (chromosome) you can find a dropdown menu. This feature helps to easily switch between visualizations of the sequences in the input set. In this particular example the input sequence set comprises ten individual promoter sequences, and each individual promoter can be visualized in the genome browser.
The same track of found sites can be opened as a table for tabular visualisation:
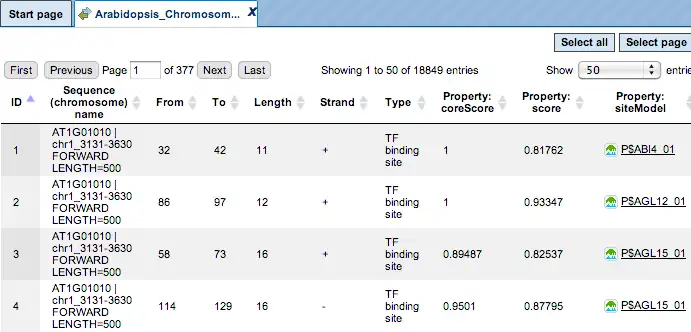
Each row of such table corresponds to one resulting TFBS and includes sequence names, site positions calculated by the algorithm and a site model (TRANSFAC® matrix). This table can be exported as a track in several different formats including intervals, bed, wig and more. DNA sequences can be exported in multi-FASTA format.
Additional visualisation options are available for selected rows of the Summary table: the Report on selected matrices button at the top menu panel of the platform will visualize the found TFBS in the input sequences. In this example, all matrices with a site density <5 were selected. The visualization results are shown below:
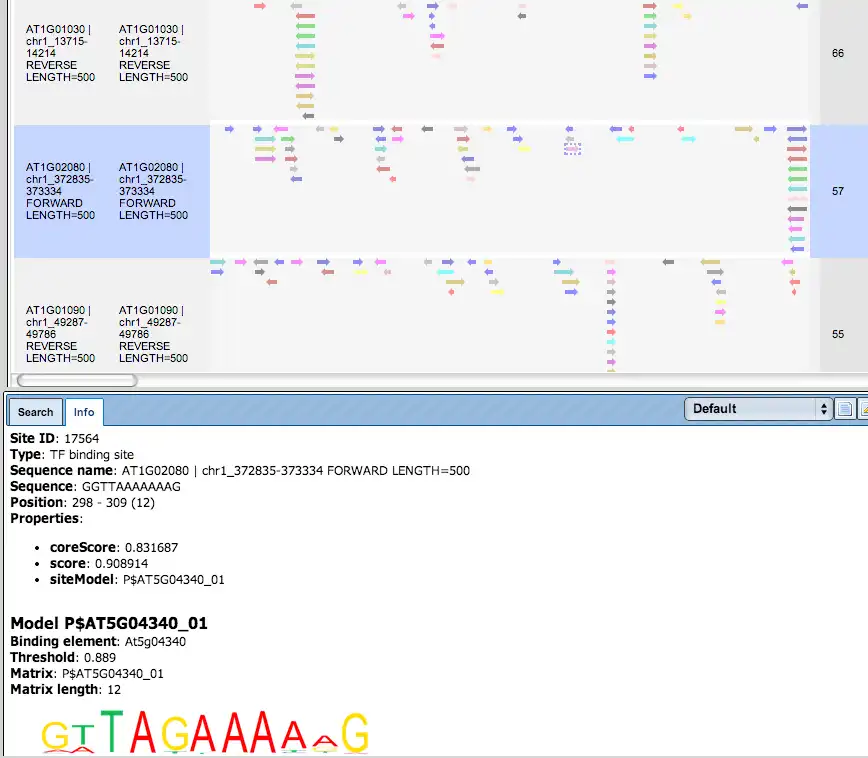
There are ten rows corresponding to the individual sequences in the input set. The column Sites view schematically represents the sequence length with mapped TFBSs. Matches for different matrices are shown in different colors. You can select individual matches by mouse click and get additional information in the Info box.
Analyze any DNA sequence for site enrichment with TRANSFAC®
The Analyze any DNA sequence for site enrichment with TRANSFAC® workflow in the geneXplain platform is designed to search for enriched TFBS in any input DNA sequence as compared to a background DNA sequence. The central part of this workflow is performed by two individual methods: Site search on track and Site search result optimization, both can be found in Analyses –> Methods –> Site analysis.
With this workflow you can analyze sequences of any species and any genomic region.
The input Yes and No sequence sets can be in EMBL, FASTA or GenBank format.
The analysis results of this workflow include several tables and tracks.
The Summary table provides the overview of the TFBS enriched in the Yes set as compared to the No set:
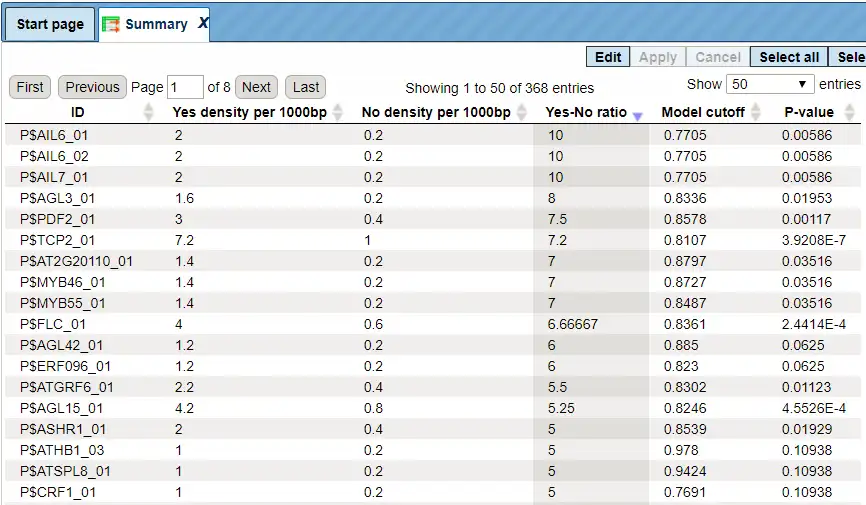
Each row summarizes the information for one site model (PWM – positional weight matri).
For each row, the columns Yes density per 1000bp and No density per 1000bp show the number of matches normalized per 1000 bp length for the sequences in the input Yes set and input No set, respectively. The Column Yes-No ratio is the ratio of the first two columns. The higher the Yes-No ratio, the higher is the enrichment of matches for the respective matrix in the Yes set. The matrix cutoff values as they are calculated by the program at the optimization step are shown in the column Model cutoff, and the last column shows the p-value of the corresponding event.
TFBSs can be further visualized in the Yes sequences by selecting one or several rows of the Summary table and clicking on the Report on selected matrices button at the top menu panel of the platform.
In this example, all matrices having a Yes-No ratio>3 were selected. The visualization results are shown below:
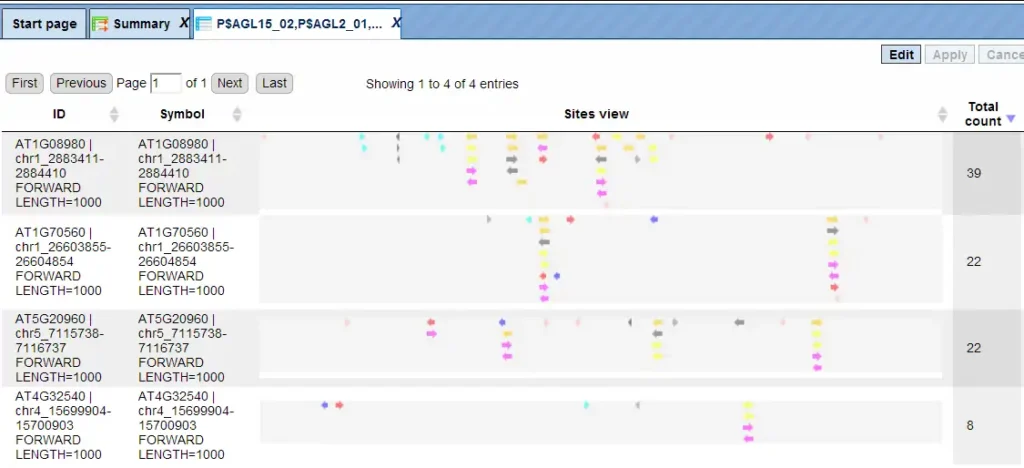
There are four rows corresponding to the individual sequences in the input Yes set. The column Sites view schematically represents the sequence length with mapped TFBSs. Matches for different matrices are shown in different colors. You can select individual matches by mouse click and get additional information in the Info box.
The track of found sites represents TFBSs that are over-represented in the Yes sequences versus the No sequences. It can be viewed in the genome browser:
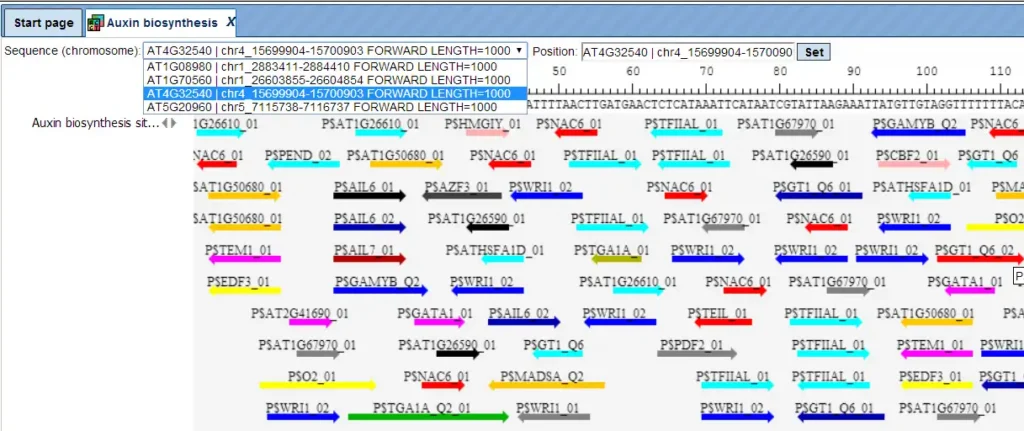
In the field Sequence (chromosome) you can find a drop down menu. This feature helps to easily switch visualization between the sequences in the input set. In this particular example the Yes sequence set comprises four individual promoter sequences, and each individual promoter can be visualized in the genome browser.
The track of found sites that are over-represented in the Yes sequences versus the No sequences can also be viewed as a table, scores of the putative TFBS are optimized by the algorithm:
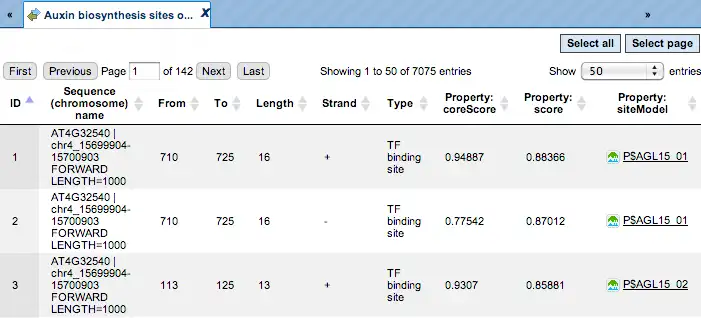
Each row of this table corresponds to one resulting TFBS, and includes its position in the Yes sequences (the columns From and To), length and strand, as well as a score calculated by the algorithm and a site model (matrix). This table can be exported as a track, in several different formats including intervals, bed, wig and more. DNA sequences can be exported in multi-FASTA format.
In case of analysis Human, Mouse or Rat data, as well as since recent release the Arabidopsis, Zebrafish, Nematoda, Fruit fly, Baker’s yeast, and Fission yeast data, additional tables will be outputted by the workflow: Transcription factors Ensembl and Transcription factors Entrez. These tables aim at showing transcription factors linked to the identified site models (matrices). These are potential candidate regulators of genes in the input Yes set. They are supposed to regulate transcription of Yes-genes via the identified enriched TFBSs.
You will find a much more detailed description of the sequence analysis workflows in the geneXplain platform in the respective chapter of the user manual.
Site search on gene set
The Site search on gene set method of the geneXplain platform provides you with an ability to search for putative TFBS in a set of genes. As input for the analysis two gene sets should be provided: Yes (e.g. differentially expressed in an experiment, test set) and No (set of background genes, control set) as well as positional range relative to the TSS and a collection of predefined weight matrices with a particular threshold (profile). The analysis can be done for Human, Mouse, Rat, Arabidopsis, Nematoda, Zebrafish, Fruit fly, Baker’s yeast, and Fission yeast genes.
The Site search on gene set analysis results contain one Summary table and six tracks: yes promoters, no promoters, yes sites, no sites, yes sites optimized, and no sites optimized.
An example of the summary table is shown below:
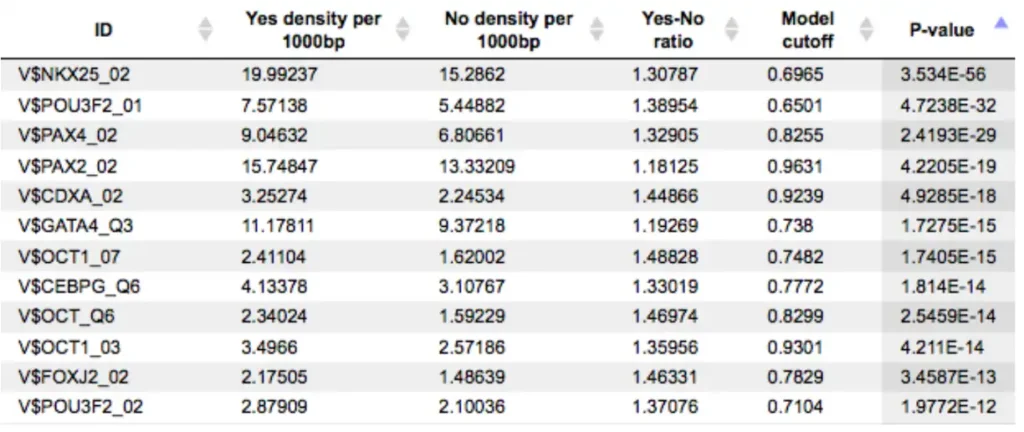
Each row summarizes the information for one PWM. For each selected matrix, the columns Yes density per 1000bp and No density per 1000bp show the number of matches normalized per 1000 bp length for the sequences in the input Yes set and input No set, respectively. The Column Yes-No ratio is the ratio of the first two columns. Only matrices with a Yes-No ratio higher than 1 are included in the summary table. The higher the Yes-No ratio, the higher is the enrichment of matches for the respective matrix in the Yes set. The matrix cutoff values as they are calculated by the program at the optimization step are shown in the column Model cutoff, and the last column shows the p-value of the corresponding event.
The Yes promoters and No promoters tracks represent promoters of the input gene sets. These tracks can be opened as tables:
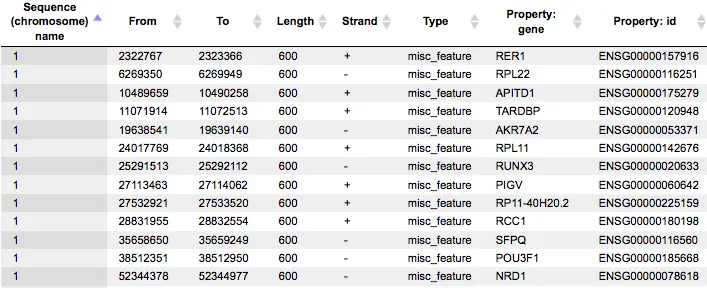
This table lists the positions of the promoter areas selected for the analysis on particular chromosomes, as shown in the columns From and To. The column Strand shows the strand on which each particular promoter is located. This track can be dragged and dropped on a particular chromosome opened in the genome browser to visualize the localizations of the promoters.
The track Yes sites optimized visualizes those putative sites that are over-represented in the promoters of the Yes set versus the No set as they are located in the promoters of the Yes set. Putative TFBS are shown as a track, scores of the putative sites are optimized by the algorithm.
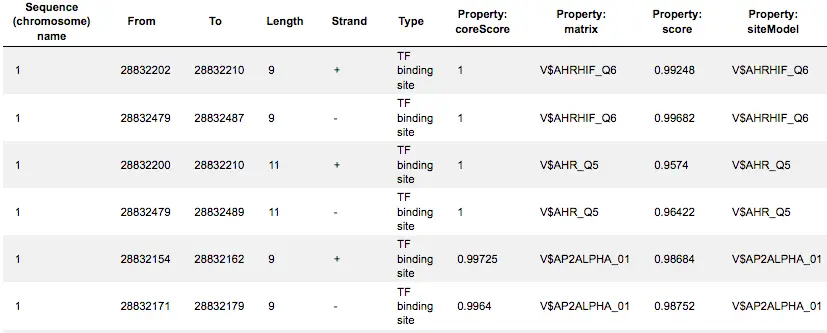
This track is a list of all putative TFBS found in one analysis, it can be opened as a table. Each row presents details for each individual match for every PWM. The columns Sequence (chromosome) name, From, To, Length and Strand show, correspondingly, genomic location of the match including chromosome number, start and end positions, strand and length of the match.
The column Type contains information about the type of the elements, in this case all matches are considered as “TF binding site”. Further columns keep information about PWM producing each match (column Property: matrix) as well as score for the whole matrix (column Property: score). The column Property: siteModel contains the identifier for the corresponding site model, which is the matrix together with a cutoff applied (and in the example shown is identical to the matrix identifier).
Yes (No) sites tracks are very similar in structure. The major difference is that these tracks include putative binding sites before the cutoff optimization, and thus they contain more sites.
Additional visualisation options of found TFBS are available for individual genes and individual matrices. Different rows of the summary table can be selected and visualized using the “report on selected matrices” button from the top menu panel of the platform:
This action will open two new files: a table and a track. The constructed track has the same structure as described above for other track files. Each row of the constructed table corresponds to one individual gene:
The column ID presents the Ensembl ID for each gene, and the gene symbol is shown in the column Symbol. The column Sites viewshows a schematic representation for each gene, where blue bars correspond to gene starts and coding regions, and TFBSs for different matrices are shown by arrows of different colors. The column Total count shows the number of TFBSs for all matrices together in the promoter of each particular gene. The next columns are named as matrices in the summary table and represent the number of TFBSs for each matrix in each particular gene.
On the picture above the table is sorted by the column Total count, and on the top we can see those genes that contain the highest total number of sites. This table can be sorted by different columns corresponding to individual matrices, and then on the top you will see those genes that contain the highest number of sites for the matrix in focus. The TFBS color schema in this table can be customized. This table can be exported in tab-separated format (txt) or comma-separated format (csv).
A much more detailed description of the Site search on gene set method can be found in the respective chapter of the geneXplain platform user guide.
Site search on track
The Site search on track method of the geneXplain platform provides you with an ability to search for putative TFBS in an input track. As input for the analysis the track for performing the site search should be provided (e.g. the track of promoter regions of studied genes), as well as the sequence source of the track and the collection of binding models (PWMs) that should be used for the TFBS search.
The result of this method is the track of found sites, which can be visualized as a table:
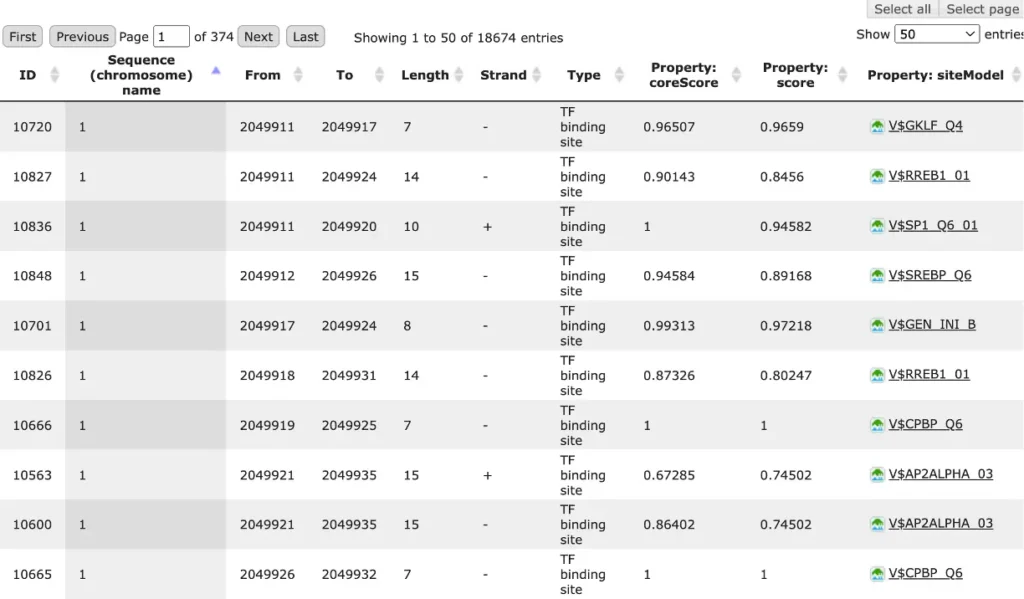
Each row of the table presents details for each individual match for every PWM.
The columns Sequence (chromosome) name, From, To, Length and Strand show, correspondingly, genomic location of the match including chromosome number, start and end positions, strand and length of the match.
The column Type contains information about the type of the elements, in this case all matches are considered as “TF binding site”.
Further columns keep information about PWM producing each match (column Property: siteModel) as well as a score of the core (column Property:coreScore) and a score for the whole matrix (column Property: score).
For details about these scores, please see Kel, Alexander E., et al. “MATCH: a tool for searching transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequences.” Nucleic acids research 31.13 (2003): 3576-3579, LINK.
geneXplain platform API
Read more about geneXplain platform API here
Articles about geneXplain platform
Selection of articles reporting about geneXplain platform applications:
Novikova S., Tolstova T., Kurbatov L., Farafonova T., Tikhonova O., Soloveva N., Rusanov A., Zgoda V. (2024) Systems Biology for Drug Target Discovery in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25(9), 4618 Link
Kisakol, B., Matveeva, A., Salvucci, M., Kel, A., McDonough, E., Ginty, F., Longley, D., Prehn, J. (2024) Identification of unique rectal cancer-specific subtypes. Br J Cancer. 130, 1809–1818. DOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02656-0. Link
Xinxin Liu., Zhihua Huang., Qiuzheng Chen., Kai Chen., Weikang Liu., Guangnian Liu., Xiangyu Chu., Dongqi Li., Yongsu Ma., Xiaodong Tian., Yinmo Yang. (2024) Hypoxia-induced epigenetic regulation of miR-485-3p promotes stemness and chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis. Cell Death Discovery. 10, 262. Link
Drake, C., Zobl W., Wehr M., Koschmann J., De Luca D., Kühne B. A. , Vrieling H. , Boei J. , Hansen T. , Escher S. E. (2023) Substantiate a read-across hypothesis by using transcriptome data—A case study on volatile diketones. Front. Toxicol. 5. Link
Rajavel A., Klees S., Hui Y., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2022) Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism Underlying African Animal Trypanosomiasis by Means of the 1000 Bull Genomes Project Genomic Dataset. Biology (Basel). 11(5), 742. Link
Menck K., Wlochowitz D., Wachter A., Conradi L.C., Wolff A., Scheel A.H., Korf U., Wiemann S., Schildhaus H.U., Bohnenberger H., Wingender E., Pukrop T., Homayounfar K., Beißbarth T., Bleckmann A. (2022) High-Throughput Profiling of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases Reveals Intra- and Inter-Patient Heterogeneity in the EGFR and WNT Pathways Associated with Clinical Outcome. Cancers 14(9), 2084. Link
Myer P.A., Kim H., Blümel A.M., Finnegan E., Kel A., Thompson T.V., Greally J.M., Prehn J.H., O’Connor D.P., Friedman R.A., Floratos A., Das S. (2022) Master Transcription Regulators and Transcription Factors Regulate Immune-Associated Differences Between Patients of African and European Ancestry With Colorectal Cancer. Gastro Hep Adv. 1(3), 328–341. Link
Kawashima Y., Nagai H., Konno R., Ishikawa M., Nakajima D., Sato H., Nakamura R., Furuyashiki T., Ohara O. (2022) Single-Shot 10K Proteome Approach: Over 10,000 Protein Identifications by Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Single-Shot Proteomics with Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 21(6), 1418–1427. Link
Klees S., Schlüter J.S., Schellhorn J., Bertram H., Kurzweg A.C., Ramzan F., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2022) Comparative Investigation of Gene Regulatory Processes Underlying Avian Influenza Viruses in Chicken and Duck. Biology (Basel). 11(2), 219. Link
Benjamin, S.J., Hawley, K.L., Vera-Licona, P., La Vake, C.J., Cervantes, J.L., Ruan, Y., Radolf, J.D., Salazar, J.C. (2021) Macrophage mediated recognition and clearance of Borrelia burgdorferi elicits MyD88-dependent and -independent phagosomal signals that contribute to phagocytosis and inflammation. BMC Immunol. 22, 32. Link
Menck K., Heinrichs S., Wlochowitz D., Sitte M., Noeding H., Janshoff A., Treiber H., Ruhwedel T., Schatlo B., von der Brelie C., Wiemann S., Pukrop T., Beißbarth T., Binder C., Bleckmann A. (2021) WNT11/ROR2 signaling is associated with tumor invasion and poor survival in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40, 395. Link
Meier, T., Timm, M., Montani, M., Wilkens, L. (2021) Gene networks and transcriptional regulators associated with liver cancer development and progression. BMC Med. Genomics 14, 41. Link
Chereda H., Bleckmann A., Menck K., Perera-Bel J., Stegmaier P., Auer F., Kramer F., Leha A., Beißbarth T. (2021) Explaining decisions of graph convolutional neural networks: patient-specific molecular subnetworks responsible for metastasis prediction in breast cancer. Genome Med. 13, 42. Link
Heinrich F., Ramzan F., Rajavel A., Schmitt A.O., Gültas M. (2021) MIDESP: Mutual Information-Based Detection of Epistatic SNP Pairs for Qualitative and Quantitative Phenotypes. Biology (Basel). 10(9), 921. Link
Tenesaca S., Vasquez M., Alvarez M., Otano I., Fernandez-Sendin M., Di Trani C.A., Ardaiz N., Gomar C., Bella A., Aranda F., Medina-Echeverz J., Melero I., Berraondo P. (2021) Statins act as transient type I interferon inhibitors to enable the antitumor activity of modified vaccinia Ankara viral vectors. J Immunother Cancer. 9(7), e001587. Link
Vanvanhossou S.F.U., Giambra I.J., Yin T., Brügemann K., Dossa L.H., König S. (2021) First DNA Sequencing in Beninese Indigenous Cattle Breeds Captures New Milk Protein Variants. Genes (Basel). 12(11), 1702. Link
Lloyd K., Papoutsopoulou S., Smith E., Stegmaier P., Bergey F., Morris L., Kittner M., England H., Spiller D., White M.H.R., Duckworth C.A., Campbell B.J., Poroikov V., Martins Dos Santos V.A.P., Kel A., Muller W., Pritchard D.M., Probert C., Burkitt M.D.; SysmedIBD Consortium. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis Model Mech. 13(11), dmm044040. Link
Odagiu L., Boulet S., Maurice De Sousa D., Daudelin J.F., Nicolas S., Labrecque N. (2020) Early programming of CD8+ T cell response by the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117(39), 24392–24402. Link
Ayyildiz D., Antoniali G., D’Ambrosio C., Mangiapane G., Dalla E., Scaloni A., Tell G., Piazza S. (2020) Architecture of The Human Ape1 Interactome Defines Novel Cancers Signatures. Sci Rep. 10, 28. Link
Ural, B.B., Yeung, S.T., Damani-Yokota, P., Devlin, J.C., de Vries, M., Vera-Licona, P., Samji, T., Sawai, C.M., Jang, G., Perez, O.A., Pham, Q., Maher, L., Loke, P., Dittmann, M., Reizis, B., Khanna, K.M. (2020) Identification of a nerve-associated, lung-resident interstitial macrophage subset with distinct localization and immunoregulatory properties. Sci. Immunol. 5, eaax8756. Link
Leiherer A., Muendlein A., Saely C.H., Fraunberger P., Drexel H. (2019) Serotonin is elevated in risk-genotype carriers of TCF7L2 – rs7903146. Sci Rep. 9, 12863. Link
Wang B., Ran Z., Liu M., Ou Y. (2019) Prognostic Significance of Potential Immune Checkpoint Member HHLA2 in Human Tumors: A Comprehensive Analysis. Front Immunol. 10, 1573. Link
Mekonnen, Y.A., Gültas, M., Effa, K., Hanotte, O., Schmitt, A.O. (2019) Identification of Candidate Signature Genes and Key Regulators Associated With Trypanotolerance in the Sheko Breed. Front. Genet. 10, 1095. Link
Blazquez, R., Wlochowitz, D., Wolff, A., Seitz, S., Wachter, A., Perera-Bel, J., Bleckmann, A., Beißbarth, T., Salinas, G., Riemenschneider, M.J., Proescholdt, M., Evert, M., Utpatel, K., Siam, L., Schatlo, B., Balkenhol, M., Stadelmann, C., Schildhaus, H.U., Korf, U., Reinz, E., Wiemann, S., Vollmer, E., Schulz, M., Ritter, U., Hanisch, U.K., Pukrop, T. (2018) PI3K: A master regulator of brain metastasis-promoting macrophages/microglia. Glia 66, 2438-2455. Link
Orekhov, A.N., Oishi, Y., Nikiforov, N.G., Zhelankin, A.V., Dubrovsky, L., Sobenin, I.A., Kel, A., Stelmashenko, D., Makeev, V.J., Foxx, K., Jin, X., Kruth, H.S. Bukrinsky, M. (2018) Modified LDL Particles Activate Inflammatory Pathways in Monocyte-derived Macrophages: Transcriptome Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 24, 3143-3151. Link
Smetanina, M.A., Kel, A.E., Sevost’ianova, K.S., Maiborodin, I.V., Shevela, A.I., Zolotukhin, I.A., Stegmaier, P., Filipenko, M.L. (2018) DNA methylation and gene expression profiling reveal MFAP5 as a regulatory driver of extracellular matrix remodeling in varicose vein disease. Epigenomics 10, 1103-1119. Link
Kalozoumi, G., Kel-Margoulis, O., Vafiadaki, E., Greenberg, D., Bernard, H., Soreq, H., Depaulis, A., Sanoudou, D. (2018) Glial responses during epileptogenesis in Mus musculus point to potential therapeutic targets. PLoS One 13, e0201742. Link
Mandić, A.D., Bennek, E., Verdier, J., Zhang, K., Roubrocks, S., Davis, R.J., Denecke, B., Gassler, N., Streetz, K., Kel, A., Hornef, M., Cubero, F. J., Trautwein, C. and Sellge, G. (2017) c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 promotes enterocyte survival and goblet cell differentiation in the inflamed intestine. Mucosal Immunol. 10, 1211-1223. Link
Niehof, M., Hildebrandt, T., Danov, O., Arndt, K., Koschmann, J., Dahlmann, F., Hansen, T. and Sewald, K. (2017) RNA isolation from precision-cut lung slices (PCLS) from different species. BMC Res. Notes 10, 121. Link
Triska, M., Solovyev, V., Baranova, A., Kel, A., Tatarinova, T.V. (2017) Nucleotide patterns aiding in prediction of eukaryotic promoters. PLoS One 12, e0187243. Link
Pietrzyńska, M., Zembrzuska, J., Tomczak, R., Mikołajczyk, J., Rusińska-Roszak, D., Voelkel, A., Buchwald, T., Jampílek, J., Lukáč, M., Devínsky, F. (2016) Experimental and in silico investigations of organic phosphates and phosphonates sorption on polymer-ceramic monolithic materials and hydroxyapatite. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 295-303. Link
Ciribilli, Y., Singh, P., Inga, A., Borlak, J. (2016) c-Myc targeted regulators of cell metabolism in a transgenic mouse model of papillary lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7, 65514-65539. Link
Wlochowitz, D., Haubrock, M., Arackal, J., Bleckmann, A., Wolff, A., Beißbarth, T., Wingender, E., Gültas, M. (2016) Computational Identification of Key Regulators in Two Different Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Genet. 7, 42. Link
Lee, E.H., Oh, J.H., Selvaraj, S., Park, S.M., Choi, M.S., Spanel, R., Yoon, S. and Borlak, J. (2016) Immunogenomics reveal molecular circuits of diclofenac induced liver injury in mice. Oncotarget 7, 14983-15017. Link
Kural, K.C., Tandon, N., Skoblov, M., Kel-Margoulis, O.V. and Baranova, A.V. (2016) Pathways of aging: comparative analysis of gene signatures in replicative senescence and stress induced premature senescence. BMC Genomics 17(Suppl 14), 1030. Link
Borlak, J., Singh, P. and Gazzana, G. (2015) Proteome mapping of epidermal growth factor induced hepatocellular carcinomas identifies novel cell metabolism targets and mitogen activated protein kinase signalling events. BMC Genomics 16, 124. Link
Shi, Y., Nikulenkov, F., Zawacka-Pankau, J., Li, H., Gabdoulline, R., Xu, J., Eriksson, S., Hedström, E., Issaeva, N., Kel, A., Arnér, E.S., Selivanova, G. (2014) ROS-dependent activation of JNK converts p53 into an efficient inhibitor of oncogenes leading to robust apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 21, 612-623. Link
Schlereth, K., Heyl, C., Krampitz, A.M., Mernberger, M., Finkernagel, F., Scharfe, M., Jarek, M., Leich, E., Rosenwald, A., Stiewe, T. (2013) Characterization of the p53 Cistrome – DNA Binding Cooperativity Dissects p53’s Tumor Suppressor Functions. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003726.Link
Nikulenkov, F., Spinnler, C., Li, H., Tonelli, C., Shi, Y., Turunen, M., Kivioja, T., Ignatiev, I., Kel, A., Taipale, J., Selivanova, G. (2012) Insights into p53 transcriptional function via genome-wide chromatin occupancy and gene expression analysis. Cell Death Differ. 19, 1992-2002. Link
Zawacka-Pankau, J., Grinkevich, V.V., Hunten, S., Nikulenkov, F., Gluch, A., Li, H., Enge, M., Kel, A., Selivanova, G. (2011) Inhibition of glycolytic enzymes mediated by pharmacologically activated p53: targeting Warburg effect to fight cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 41600-41615. Link
