Sp1, STAT3, IRF1 in colorectal cancer (CRC)
TFClass 2.3.1.1.1
TFClass 6.2.1.0.3
TFClass 3.5.3.0.1
Histone demethylase JMJD2D is known to promote colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Recently, the role of JMJD2D in cancer immune escape was studied.
JMJD2D was proven as a transcriptional co-activator for Sp1, STAT3 and IRF1 factors. Direct protein-protein interactions between JMJD2D and each of these three TFswere shown including dissections of the interacting domains.
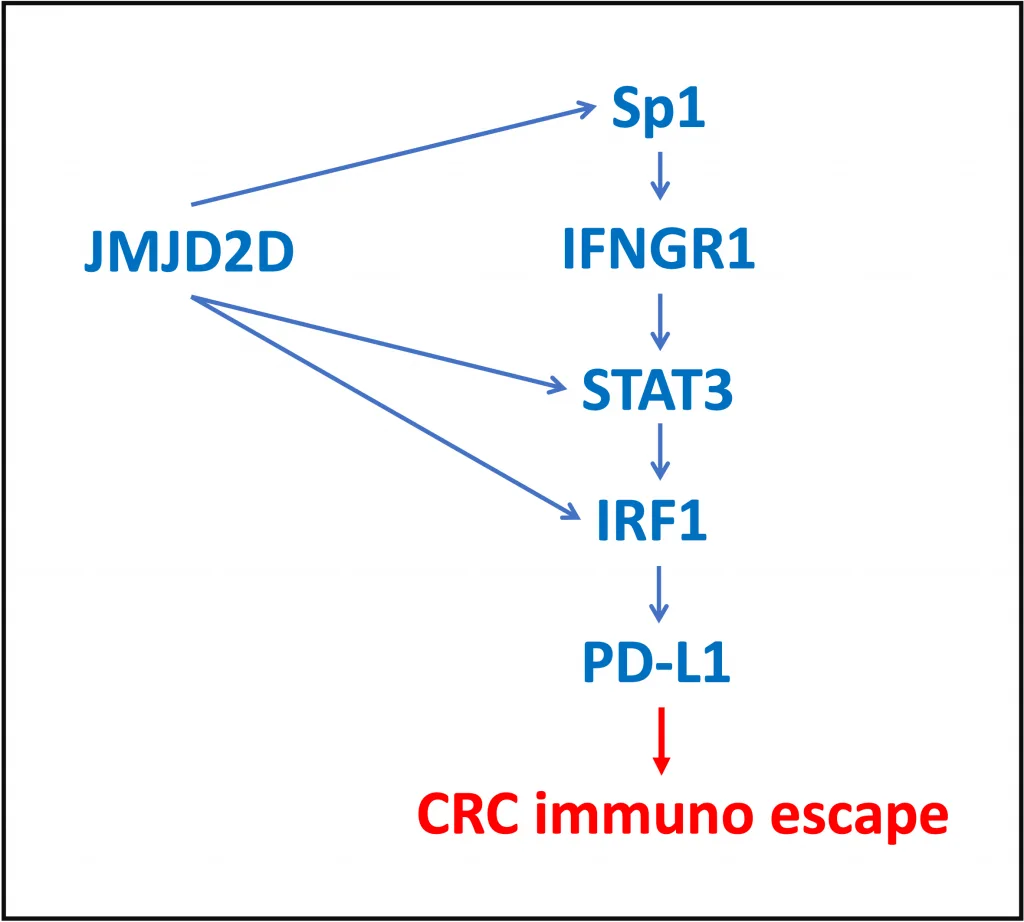
Interaction of JMJD2D with the DNA binding domain of Sp1 leads to enhanced expression of IFN-γ receptor 1 gene, IFNGR1.
The downstream TFs of the IFN-γ pathway are STAT and IRF factors, and STAT3 phosphorylation is known to be increased upon IFNGR1 activation. In this study, the authors have shown that JMJD2D is a co-activator for STAT3 and DBD of STAT3 is involved in the interactions with JMJD2D. The complex of JMJD2D and STAT3 binds to the promoter of IRF-1 gene and results in its upregulation. JMJD2D was demonstrated to interact with the central domain of IRF-1.
STAT3 and IRF1 in cooperation with co-activator JMJD2D enhance PD-L1 gene expression, which results in CRC immune escape (Chen, Q. et al., 2022. Oncogene, 41: 1421-1433).
Sp1 (SP1), together with 8 other Sp1-like factors, belongs to the big class of C2H2 zinc finger factors, especially to a family known as “Three-zinc finger Krueppel-related factors” (TFClass link).
STAT3 belongs to the class of STAT domain factors (TFClass link), which in turn belongs to a superclass of TFs known as “Immunoglobulin fold” (TFClass 6).
IRF1 belongs to a family of Interferon-regulatory factors within the class of Tryptophan cluster factors which is placed within the superclass of Helix-turn-helix domains (TFClass link).
Sp1 is known for its association with at least 20 tumor types, the top associated tumors are nasopharyngeal, breast, pancreatic, lung, liver neoplasms; glioblastoma, glioma, myeloma (HumanPSD database).
STAT3 is associated with over 70 diseases, majority of them are various tumor types (HumanPSD database).
IRF1 is associated with at least 15 tumor types, among them are stomach, ovarian, breast neoplasms, different leukemia types. Both STAT3 and IRF1 are associated with viral diseases, especially with HIV-infections and COVID-19 (HumanPSD database).
A disease similarity map for CRC can be viewed here.
Among these three TFs, Sp1 expression is the most ubiquitous; it is expressed in the majority of tissues and organs investigated at average level, except for various blood cell types where its expression level is quite low. Expression of Sp1 in normal colon, large intestine and in rectum is above its average expression (HumanPSD database, Human Protein Atlas v20).
STAT3 is characterized by the highest expression level among these three TFs, with an average expression at least 2,5 times higher than Sp1 and IRF1.
IRF1 is enriched in immune organs and cell types, with extremely high expression level in granulocytes followed by monocytes and T-lymphocytes (HumanPSD database, Human Protein Atlas v20).
STAT3 is a known direct target for over 30 different drugs, FDA-approved and investigational (HumanPSD database) and is involved in 12 different pathways in the TRANSPATH database, as shown on the screenshot below:
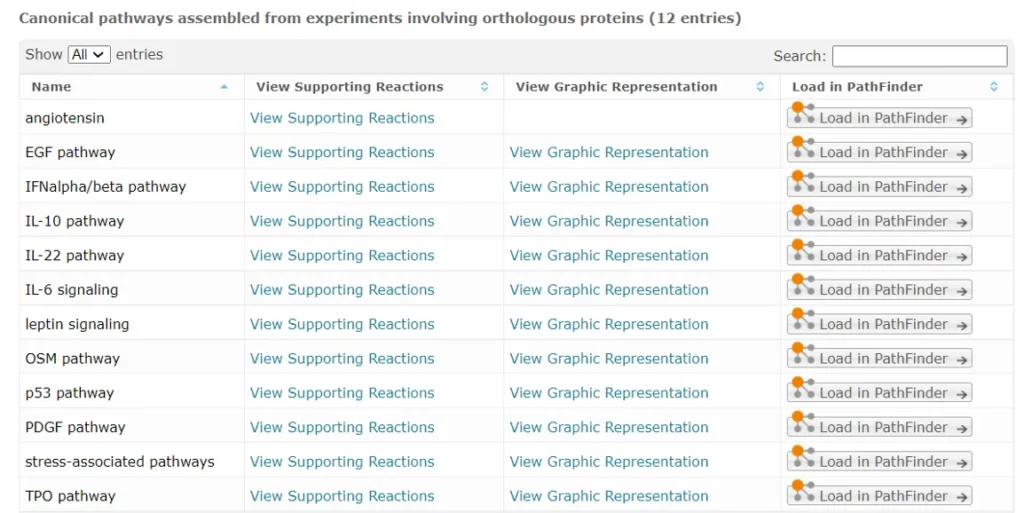
IRF1 appears in IFN-γ and TLR9 pathways (TRANSPATH database).
In TRANSFAC 2.0, there are several consensus binding matrices for each of these three TFs. Among them, there are matrices constructed from the individual genomic binding sites, collected from publications based on the SELEX experiments as well as built from the ChIP-seq experiments.
The core binding motif for Sp1 is GGGGGCGGGG; for STAT3 is TTCCRGGAA, where R can be G or A; and for IRF1 is TTTCACTTTC (TRANSFAC database: Sp1, STAT3, IRF1).
Many more details can be found in the integrated database TRANSFAC + TRANSPATH + HumanPSD, for example, in the Locus Report for human IRF1:
Open this report as a PDF file.
Chen, Q. et al., 2022. Demethylase JMJD2D induces PD-L1 expression to promote colorectal cancer immune escape by enhancing IFNGR1-STAT3-IRF1 signaling. Oncogene, 41: 1421-1433. PMID: 35027670.
This page was published and last revised on 21.11.2022
Examples of some other transcription factors in cancer can be found here.
