Protein Genome Map
In the geneXplain platform, a comprehensive set of methods and workflows elucidate functional effects of genomic variants. The Protein Genome Map is a database of genomic coordinates of protein functional features derived from high quality, manual curation in Transpath® [1] as well as additional sources. With this novel resource, curated information now becomes available for functional genomics investigations such as variant effect analysis.
The database can be queried using the accompanying method “Create protein feature track”. The method extracts genomic intervals encoding protein functional features that overlap genome coordinates of interest into a platform track which can then be exported or further analyzed with a portfolio of platform tools and workflows.
The first version of the database focuses on post-translational modifications (PTMs) and contains 234192 PTM sites for 18 different modification types in 973 Drosophila, 23630 human, 5414 mouse and 39 rat protein isoforms from Transpath® and BioGRID [2, 3] as well as their genomic locations in assemblies BDGP6.54, GRCh38, GRCm39 and GRCr8. The modification types and their presentation in the database are described in the table below.
|
PTM type |
Transpath® |
BioGRID |
Human – Transpath® |
Human – BioGRID |
|
Acetylation |
165 |
146 | ||
|
Acylation |
2 |
2 | ||
|
Glycosylation |
30 |
27 | ||
|
Hydroxylation |
7 |
7 | ||
|
ISGylation (ISG15) |
3 |
3 | ||
|
Methylation |
59 |
55 | ||
|
Myristoylation |
5 |
4 | ||
|
Neddylation (Nedd8) |
2 |
1750 |
2 |
1750 |
|
Nitrosylation |
5 |
4 | ||
|
Palmitoylation |
5 |
1 | ||
|
Serine phosphorylation |
1612 |
19536 |
1373 |
19536 |
|
Sulfation |
1 |
1 | ||
|
Sumoylation (any) |
217 | |||
|
Sumoylation (SUMO1) |
119 |
84 | ||
|
Sumoylation (SUMO2) |
33 |
24 | ||
|
Sumoylation (SUMO3) |
20 |
11 | ||
|
Threonine phosphorylation |
450 |
3813 |
356 |
3813 |
|
Tyrosine phosphorylation |
315 |
520 |
257 |
520 |
|
Ubiquitination |
134 |
205666 |
109 |
191351 |
References
1. Krull M, Voss N, Choi C, Pistor S, Potapov A, Wingender E. TRANSPATH: an integrated database on signal transduction and a tool for array analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 1;31(1):97-100. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg089. PMID: 12519957; PMCID: PMC165536.
2. Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher L, Breitkreutz A, Tyers M. BioGRID: a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D535-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj109. PMID: 16381927; PMCID: PMC1347471.3. Oughtred R, Rust J, Chang C, Breitkreutz BJ, Stark C, Willems A, Boucher L, Leung G, Kolas N, Zhang F, Dolma S, Coulombe-Huntington J, Chatr-Aryamontri A, Dolinski K, Tyers M. The BioGRID database: A comprehensive biomedical resource of curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci. 2021 Jan;30(1):187-200. doi: 10.1002/pro.3978. Epub 2020 Nov 23. PMID: 33070389; PMCID: PMC7737760.
Example analysis
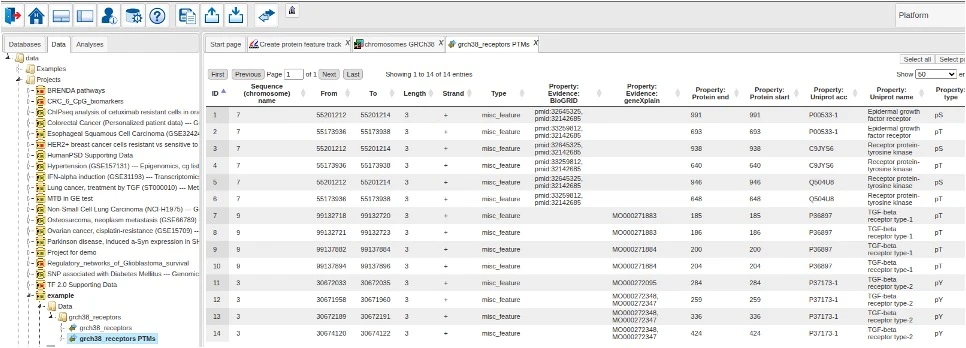
The method “Create protein feature track” extracts protein functional features encoded in genomic regions of interest from a Protein Genome Map database.To demonstrate a possible use case, we prepare a BED file with human genome regions containing the signal transduction receptor genes EGFR, TGFBR1 and TGFBR2. The contents of the BED file are shown below. We name the file grch38_receptor.bed and import it into a data folder of the platform.
grch38_receptor.bed|
chr7 |
55018819 |
55211628 |
EGFR |
1000 |
|
chr9 |
99104037 |
99154192 |
TGFBR1 |
1000 |
|
chr3 |
30606477 |
30694249 |
TGFBR2 |
1000 |
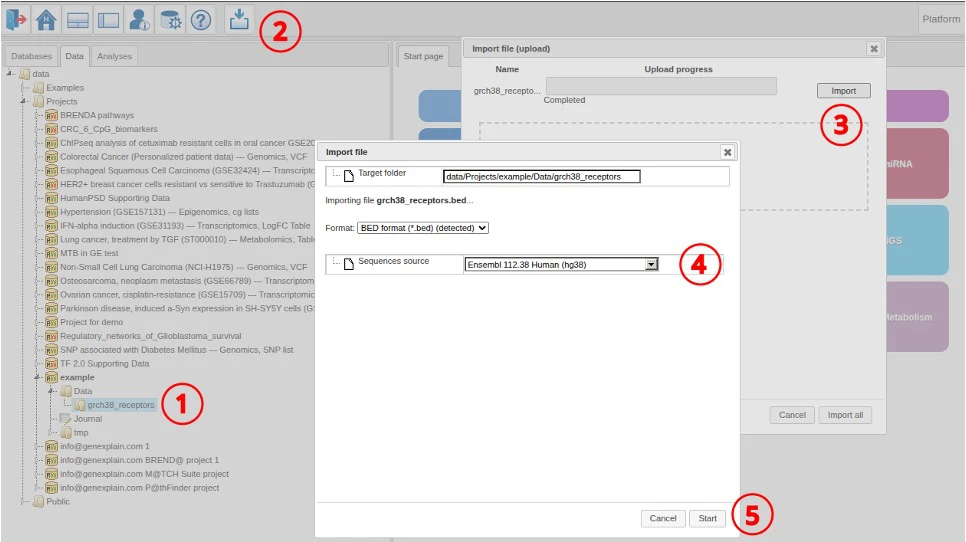
Data import
We use the following steps to import the data into the platform.
- Select target data folder
- Click the import button
- Select the file and proceed with import
- Select the reference genome (Ensembl 112.38)
- Click Start to import
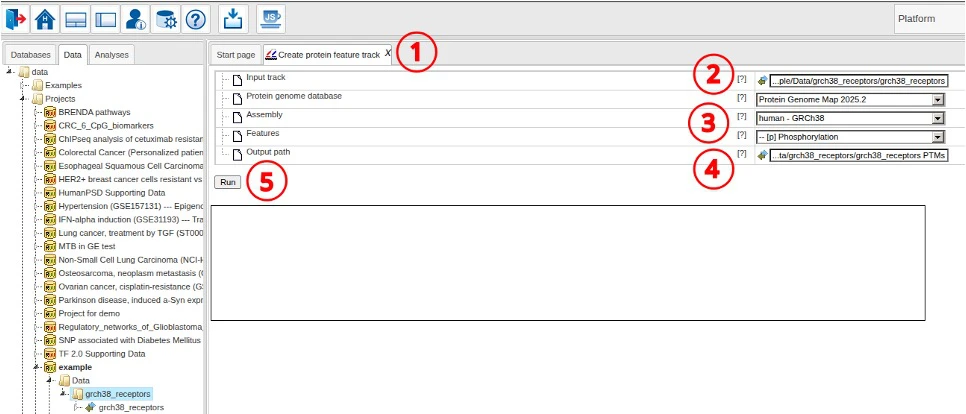
Protein feature track extraction
To create the track of protein features encoded in the receptor regions, we use the following steps.
- Open the “Create protein feature track” tool
- Select the input track
- Adjust Protein Genome Map database, the mapped genome and feature types to extract
- Adjust the output path if necessary
- Click Run to start the analysis
When analysis is finished, the resulting output track is opened in the genome viewer.
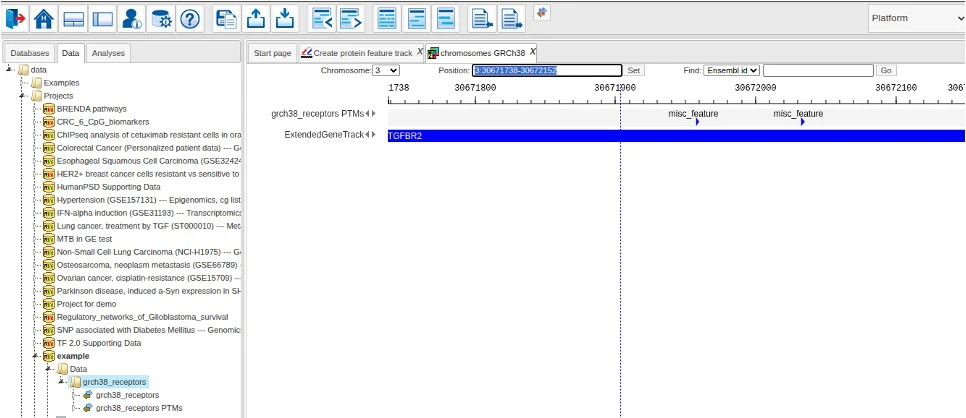
Via the context menu of the output track, one can also open the corresponding data table to inspect details of the extracted features.