FOXP3: Master Regulator of Immune Tolerance and T-Cell Identity
FOXP3 (Forkhead Box P3) is a protein-coding gene crucial for immune system balance. It is a transcription factor, which belongs to the family of Forkhead (FOX)proteins with the helix-turn-helix type of DNA-binding domain. FOXP3 was initially discovered in regulatory T cells and plays a significant role in the process of regulatory T cell differentiation.
FOXP3 is a master regulator for the development of Tregs, a specialized type of immune cell that keeps the immune system in check. Tregs, guided by FOXP3, prevent the autoimmunity and help tolerate harmless substances like food antigens and gut bacteria.
It can inhibit the production of cytokines and prevent other T cells from multiplying, effectively putting the brakes on an immune response. FOXP3 can both activate and repress gene expression. It can act as a repressor to suppress genes involved in effector T cell function and can also activate genes that are important for maintaining the Treg identity and function.
Importance of Foxp3 in disease
Autoimmune diseases:
Mutations in the FOXP3 gene can cause severe immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy [1], enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome [2] in humans. his condition results in a severe and life-threatening autoimmune disease because of a lack of functional Tregs.
Cancer:
In some contexts, tumors may express FOXP3 to create a “Treg-like” activity, which allows them to suppress the immune system and hide from it, promoting immune evasion. It can either promote cancer or suppress cancer
Promote cancer:
In certain cancers, like colorectal [3] and lung cancer [4], a high level of FOXP3 is associated with a poor prognosis, as it promotes an immunosuppressive environment that helps tumors grow.
Suppress cancer:
In other cancers, such as breast [5], prostate [6], and gastric cancer [7], high Foxp3 levels are linked to a better prognosis, suggesting a tumor-suppressive role in these cases. The specific function depends on the type of cancer and its cellular context.
Pathways that promote FOXP3 expression
TGF-β signaling:
This is a major pathway for FOXP3 induction, acting in concert with other signals like IL-2 to promote the development of regulatory T cells (Tregs). [8]
Notch signaling:
Notch1 and TGFβ1 cooperatively regulates FOXP3 expression and is important for Treg maintenance. [8, 13]
Retinoic acid (RA) signaling:
This pathway, derived from vitamin A, can promote FOXP3 expression and enhance its stability. [9]
TCR signaling:
Activation via the T-cell receptor, along with co-stimulation, triggers the activation of transcription factors like NFAT and AP-1, which bind to the FOXP3 promoter and drive its expression. [10]
c-Rel enhanceosome:
This complex, which includes transcription factors like c-Rel, NFAT, and Smad3, binds to the FOXP3 promoter and enhancers, promoting its expression. [11]
Pathways that inhibit FOXP3 expression
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling:
This pathway is known to inhibit the initial induction of FOXP3. Inhibiting this pathway with drugs like Rapamycin can promote FOXP3 expression. [12]
Here please find some parts of FOXP3 Locus Report as available in TRANSFAC professional database.
Introduction
Forkhead box P3, a transcription regulator that acts in T cell activation, aberrantly expressed in anemia, arthritis, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, leukemia, Crohn disease, and breast and several cancers; gene mutation causes autoimmune polyendocrinopathy.
Gene Information
Gene symbol: FOXP3
Synonyms: (SFN); JM2; XPID; AIID; IPEX; PIDX; FOXP3; DIETER; SCURFIN; Xp11.23; X-linked; MGC141963; MGC141961; forkhead box P3; Forkhead box protein P3; Zinc finger protein JM2; X linked syndrome of polyendocrinopathy, immune dysfunction, and diarrhea; immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy and X linked inheritance.
Gene Ontology
Molecular function: DNA binding [E], histone deacetylase binding [E], protein heterodimerization activity [E], protein homodimerization activity [E]…
Biological process: cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [E], immune response [E], lymphocyte proliferation [E], negative regulation of cell proliferation [E]…
Cellular component: nucleoplasm [Y], nucleus [E]
Biomarker Associations
Diseases associated with FOXP3 (57 entries)
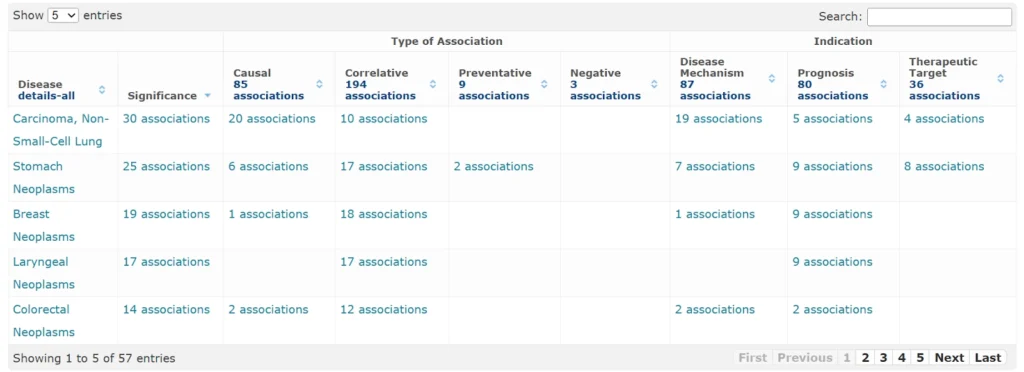
Mutant Phenotype
Mouse Foxp3 (76.3% identity to Human FOXP3) Viability effects: inviable. Affects B-lymphocytes, liver, lymphoid organs, mammary gland, serum, skin, spleen. Physiological effects include control of body size, immunity and inflammation, response to injury.
Expression
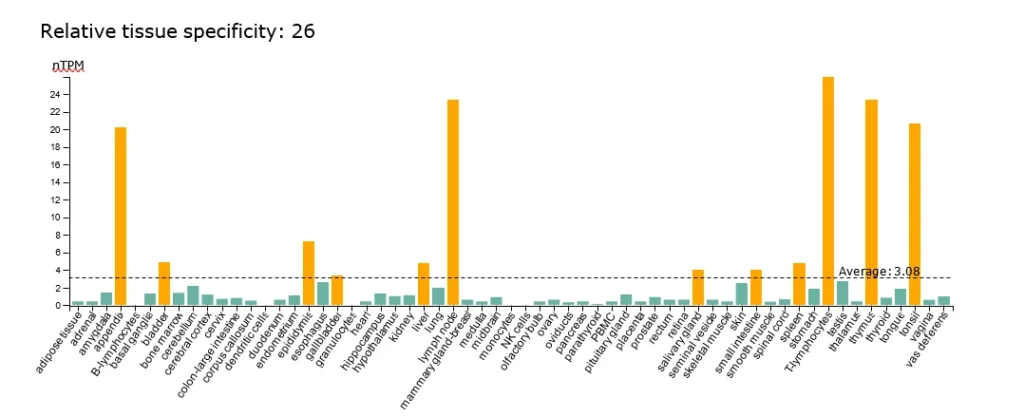
Consensus normalized transcript expression levels (Human Protein Atlas v20).
Average: 3.08 nTPM across 26 tissues including T-lymphocytes, spleen, thymus, lymph node, and others.
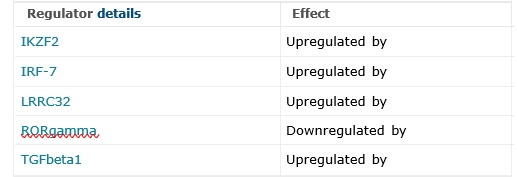
Regulation of FOXP3 Expression
Proteins, complexes, or pathways influencing FOXP3 expression (5 entries): IKZF2 (upregulated), IRF-7 (upregulated), LRRC32 (upregulated), RORgamma (downregulated), TGFbeta1 (upregulated).
Transcriptional Regulation
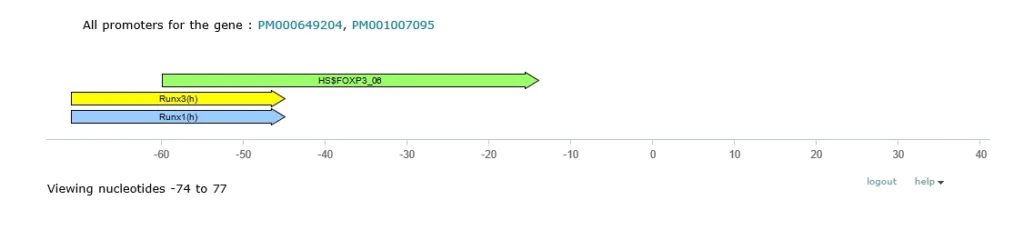
* Note: Only binding sites whose location is relative to the TSS are graphically displayed. Binding sites with an asterisk (*) are not included in the graphical display.
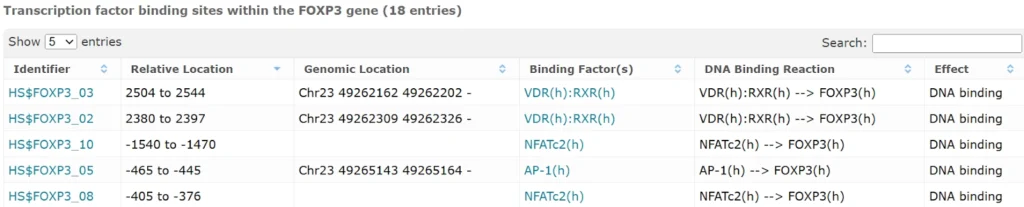
In vivo fragments within the promoter(s) of the FOXP3 gene that are bound by transcription factors (557 entries)
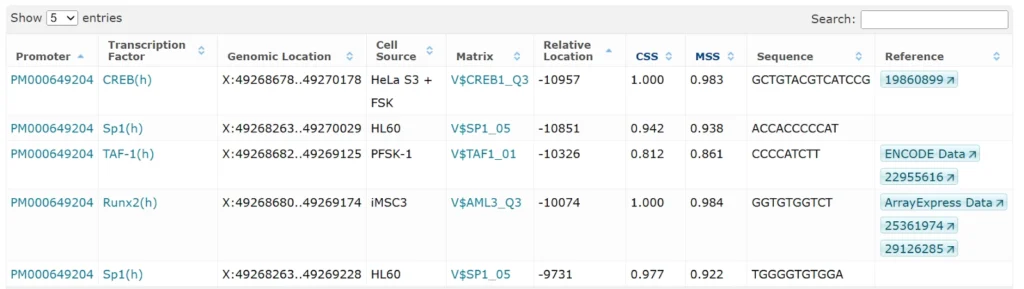
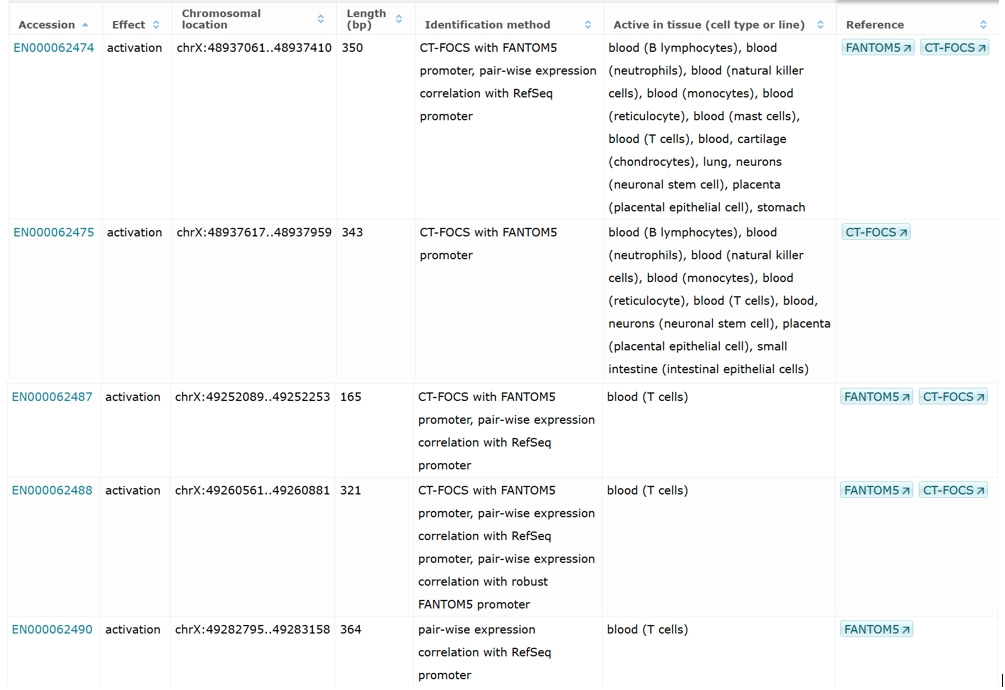
Predicted enhancers / silencers for FOXP3 regulation (6 entries)
Translational Regulation
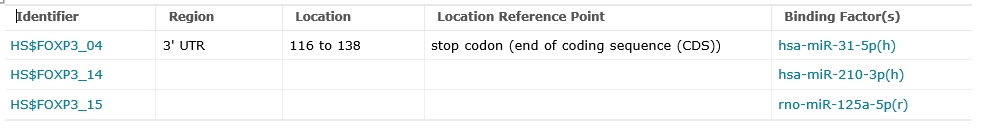
miRNA binding sites within FOXP3 mRNA (3 entries): hsa-miR-31-5p, hsa-miR-210-3p, rno-miR-125a-5p.
RNA Features
Overview of RNA sequence: 2397 nt (REFSEQ#NM_014009).
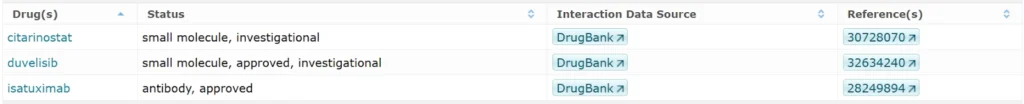
Protein & Drug Interactions
Drugs targeting FOXP3 (3 entries).
Pathways & Interactions
FoxP3 activation pathway
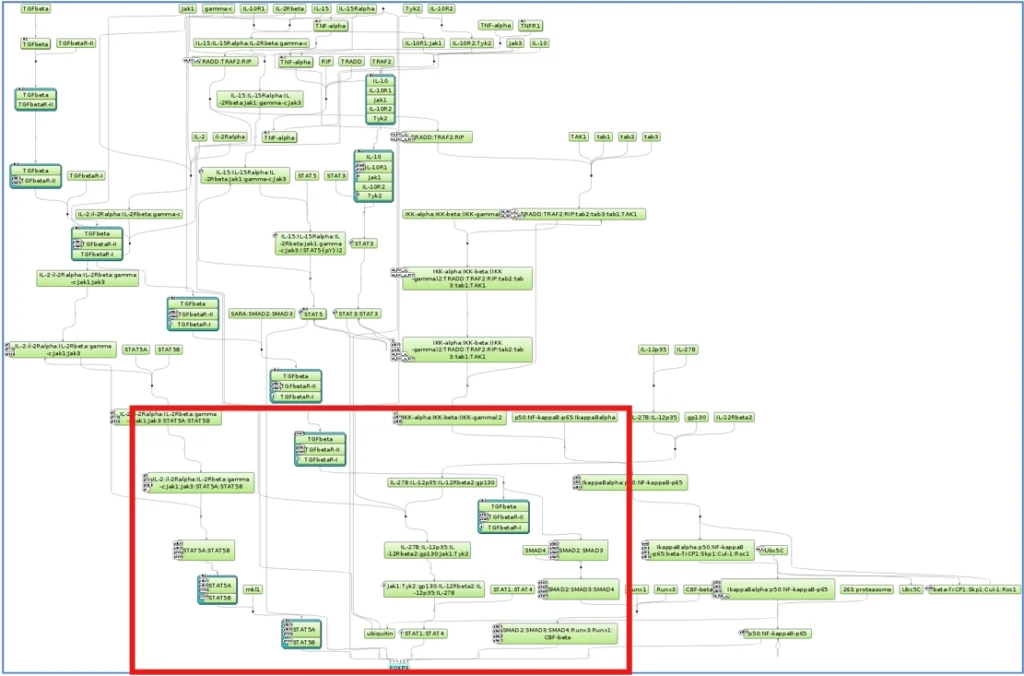
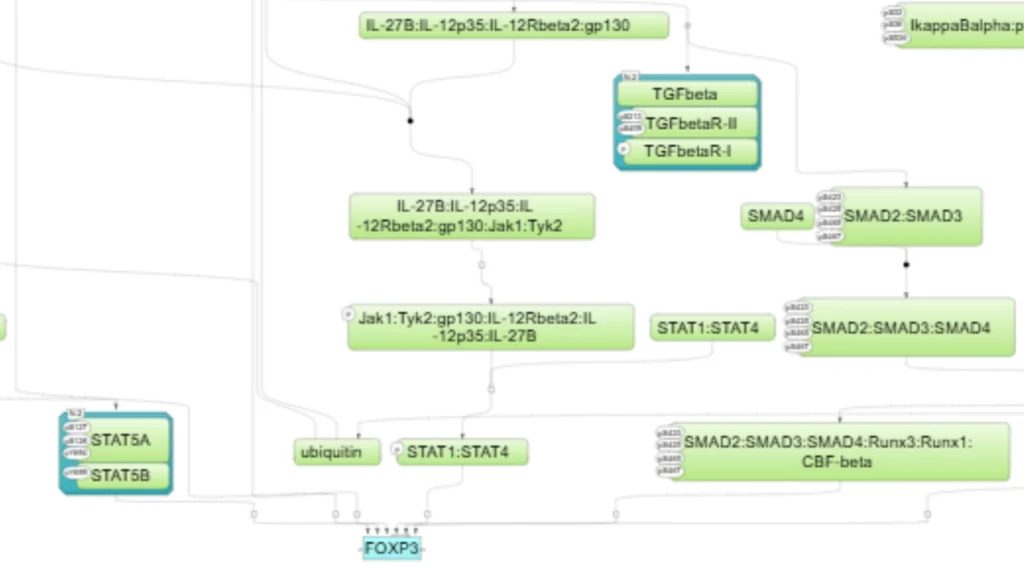
Subcomponents from which this pathway was assembled
TGFbeta—>SMAD2/3/4—>FOXP3
IL-2—>STAT5—>FOXP3
TNF-alpha–>NF-kappaB—>FOXP3
IL-10—>STAT3—>FOXP3
IL-15—>STAT5—>FOXP3
IL35(L-27B:IL-12p35)—>STAT1/STAT4—>FOXP3
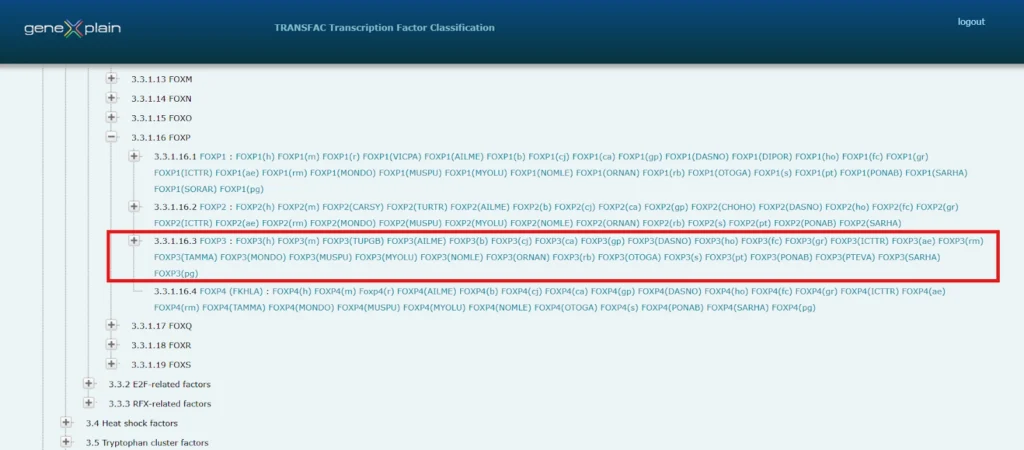
Transcription Factor Activity
Classification: Fork head/winged helix factors (3.3.1.16.3). The FOXP3 domain (~110 AA) forms a compact three α-helix structure inducing a 13° DNA bend upon binding.
Transcription factor classification:
Fork head / winged helix factors; 3.3 (Identified by homology between HNF-3A and fkh. The domain comprises approx. 110 AA. Analysis of the crystal structure has revealed a compact structure of three alpha-helices, the third alpha-helix being exposed towards the major groove of the DNA. The domain also exerts minor groove contacts. Upon binding to DNA, it induces a bend of 13 degree.
FOXP3 binding sites in gene promoters and enhancers, experimentally proven (8 entries)
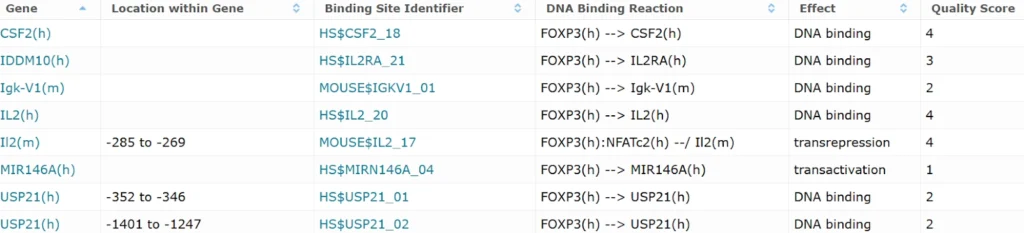
In the second table there are the T-reg specific genes with predicted Composite Module Analyst score in them.
Also we will provide a screenshot of the tool.
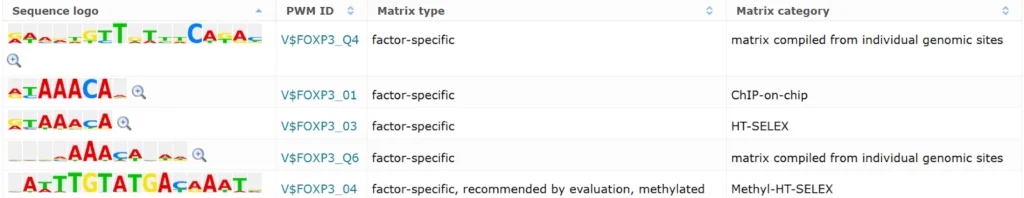
Positional weight matrices for FOXP3
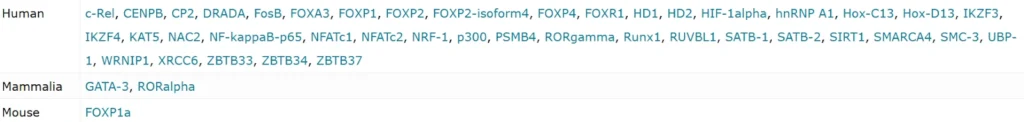
Transcription factors which interact with FOXP3
Protein Features
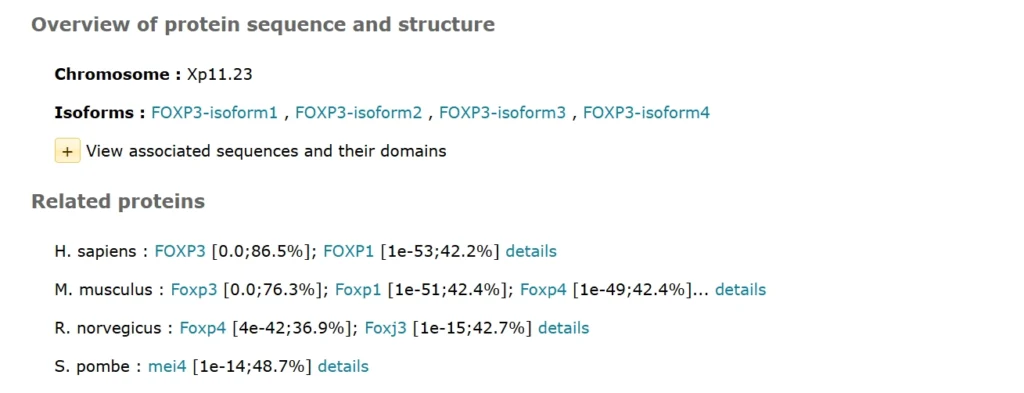

Annotations


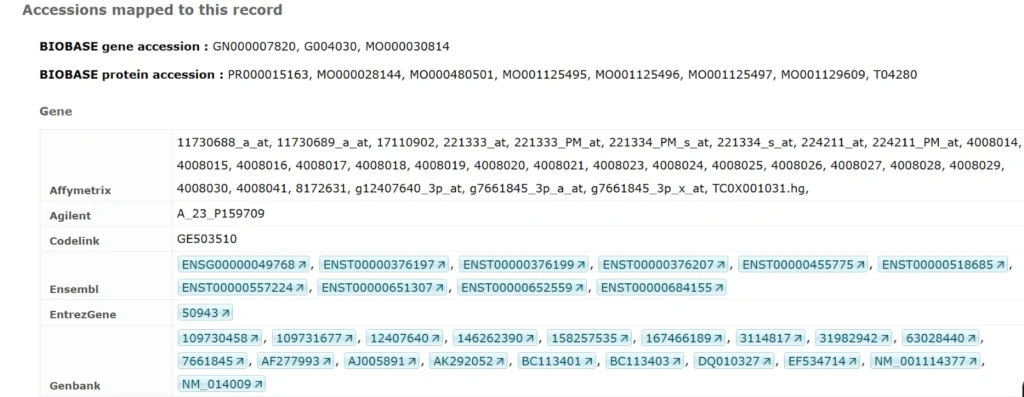
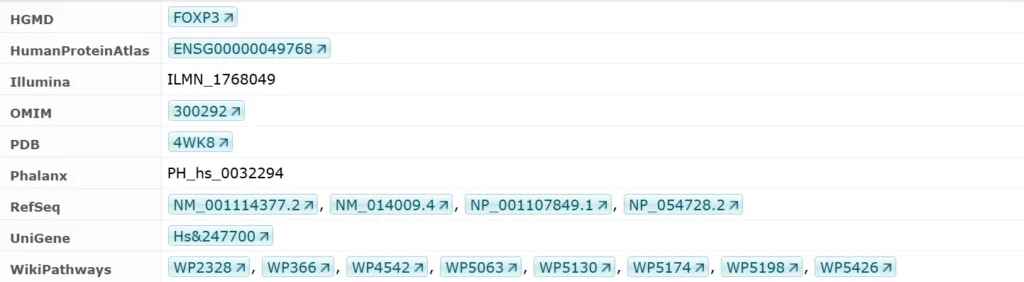
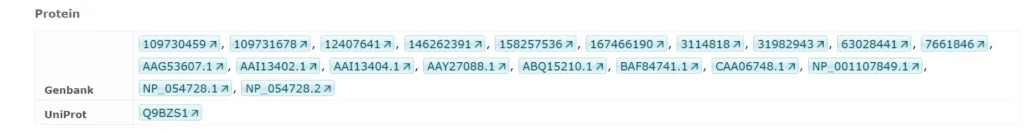
Identifiers
Composite Modules Underlying FOXP3-Driven Regulatory Programs
Composite modules represent clusters of transcription factor binding sites that act together to shape gene-specific regulatory programs. Their identification helps reveal how multiple factors cooperate or compete within promoters and enhancers to establish stable expression patterns. Using RNA-seq data from tumor-infiltrating immune cells (GSE184398), a composite-module framework highlights regulatory signatures specific to T regulatory cells, with a particular focus on FOXP3 as the central determinant of Treg identity. The analysis maps enriched TFBS clusters in promoters of up-regulated genes and outlines how these combinations contribute to lineage-specific transcriptional control.
The resulting models point to recurrent motif pairs involving FOXP3 or FOXP1 together with factors such as GATA-3, Smad-3, Snail, and Tbx2. These motif combinations reflect well-documented cooperative interactions that reinforce Treg differentiation, stability, and suppressive function. Understanding these composite modules provides a mechanistic view of how FOXP3 integrates signals from multiple regulatory pathways and how synergistic transcription-factor networks shape the unique transcriptional landscape of Tregs.
References (182 entries)
- Sperling MA, Angelousi A, Yau M. Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndromes. 2024 Jul 21. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. PMID: 25905375.
- Bacchetta R, Barzaghi F, Roncarolo MG. From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: a lesson on immune dysregulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Apr;1417(1):5-22. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13011. Epub 2016 Feb 25. PMID: 26918796.
- Sun X, Feng Z, Wang Y, Qu Y, Gai Y. Expression of Foxp3 and its prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;30(2):201-206. doi: 10.1177/0394632017710415. Epub 2017 May 31. PMID: 28560891; PMCID: PMC5806801.
- Ziółkowska-Suchanek I, Żurawek M. FOXP3: A Player of Immunogenetic Architecture in Lung Cancer. Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 15;15(4):493. doi: 10.3390/genes15040493. PMID: 38674427; PMCID: PMC11050689.
- Zhang C, Xu Y, Hao Q, Wang S, Li H, Li J, Gao Y, Li M, Li W, Xue X, Wu S, Zhang Y, Zhang W. FOXP3 suppresses breast cancer metastasis through downregulation of CD44. Int J Cancer. 2015 Sep 15;137(6):1279-90. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29482. Epub 2015 Feb 25. PMID: 25683728.
- Wang L, Liu R, Ribick M, Zheng P, Liu Y. FOXP3 as an X-linked tumor suppressor. Discov Med. 2010 Oct;10(53):322-8. PMID: 21034673; PMCID: PMC4500105.
- Chen Y, Zhao X, Zhu Y, Xu L, Wang J, Chen Z, Chen H, Rong T, Ma Y, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zheng Y, Shen L, Xie G. FKH domain-mediated nuclear FOXP3 suppresses gastric cancer malignancy via c-MYC/CDKN1A regulation, EMT inhibition, and PI3K/AKT signaling modulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Sep 24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05387-9. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40993484.
- Skarmoutsou E, Bevelacqua V, D’ Amico F, Russo A, Spandidos DA, Scalisi A, Malaponte G, Guarneri C. FOXP3 expression is modulated by TGF-β1/NOTCH1 pathway in human melanoma. Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):392-404. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3618. Epub 2018 Apr 4. PMID: 29620159; PMCID: PMC5979787.
- Elias KM, Laurence A, Davidson TS, Stephens G, Kanno Y, Shevach EM, O’Shea JJ. Retinoic acid inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood. 2008 Feb 1;111(3):1013-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-096438. Epub 2007 Oct 19. PMID: 17951529; PMCID: PMC2214761.
- Wang K, Fu W. Transcriptional regulation of Treg homeostasis and functional specification. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(21):4269-4287. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03534-7. Epub 2020 Apr 29. PMID: 32350553; PMCID: PMC7606275.
- Ruan Q, Kameswaran V, Tone Y, Li L, Liou HC, Greene MI, Tone M, Chen YH. Development of Foxp3(+) regulatory t cells is driven by the c-Rel enhanceosome. Immunity. 2009 Dec 18;31(6):932-40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.10.006. PMID: 20064450; PMCID: PMC2807990.
- Haxhinasto S, Mathis D, Benoist C. The AKT-mTOR axis regulates de novo differentiation of CD4+Foxp3+ cells. J Exp Med. 2008 Mar 17;205(3):565-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071477. Epub 2008 Feb 18. PMID: 18283119; PMCID: PMC2275380.
- Samon JB, Champhekar A, Minter LM, Telfer JC, Miele L, Fauq A, Das P, Golde TE, Osborne BA. Notch1 and TGFbeta1 cooperatively regulate Foxp3 expression and the maintenance of peripheral regulatory T cells. Blood. 2008 Sep 1;112(5):1813-21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-144980. Epub 2008 Jun 11. PMID: 18550850; PMCID: PMC2518888.
