PharmaExpert
PharmaExpert is an analyses tool to study the relationships between biological activities, drug-drug interactions and multiple targeting of chemical compounds and selects compounds that have a pre-defined biological activity. It helps answer a question like “How to select the most promising compounds among those known to interact with the selected protein?”
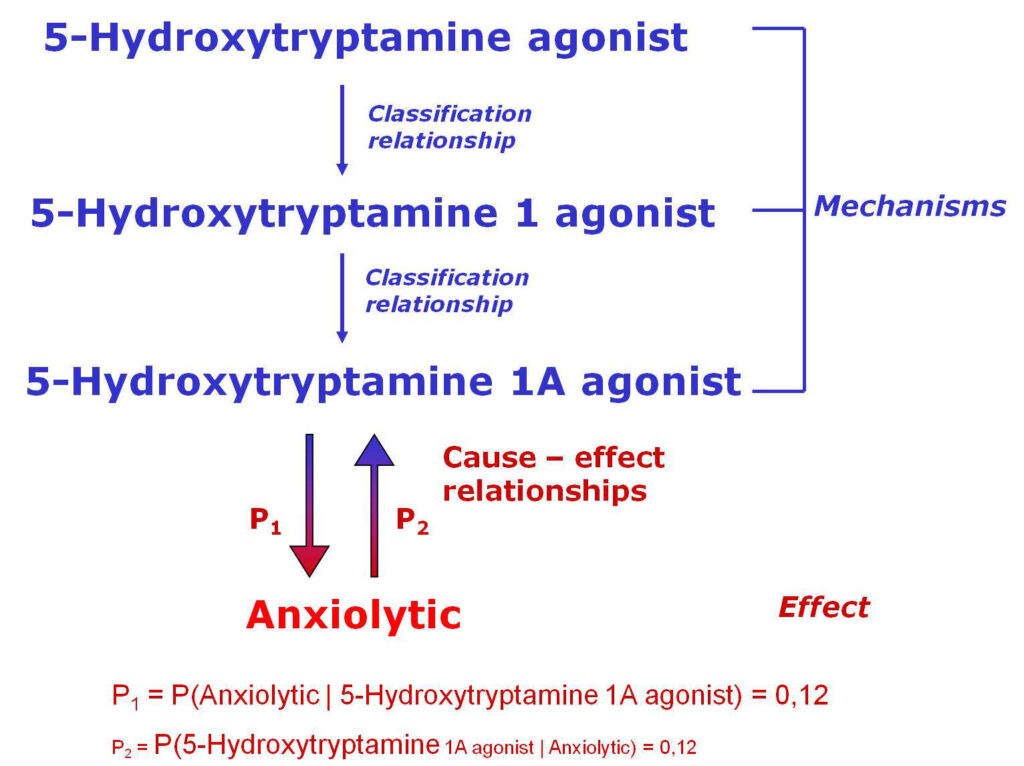
Example of classification and cause–effect relationships between mechanism of action (5-HT1A agonist) and predicted pharmacological effect (Anxiolytic).
PharmaExpert software
PharmaExpert is an expert system taking into account the known relationships between pharmacotherapeutic effects and mechanisms of action of biologically active substances.
Fields of application: Analysis of the cause-effect relationships between the biological activities, estimation of possible positive and negative pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions, selection of compounds with the needed activity spectra predicted by PASS, identification of compounds with multiple mechanisms of particular pharmacological action.
PharmaExpert is designed to visualize and to analyze the prediction results of PASS and GUSAR software.
Key features of PharmaExpert
PharmaExpert comprises several analysis tools:Retrieval and interpretation of the PASS prediction results
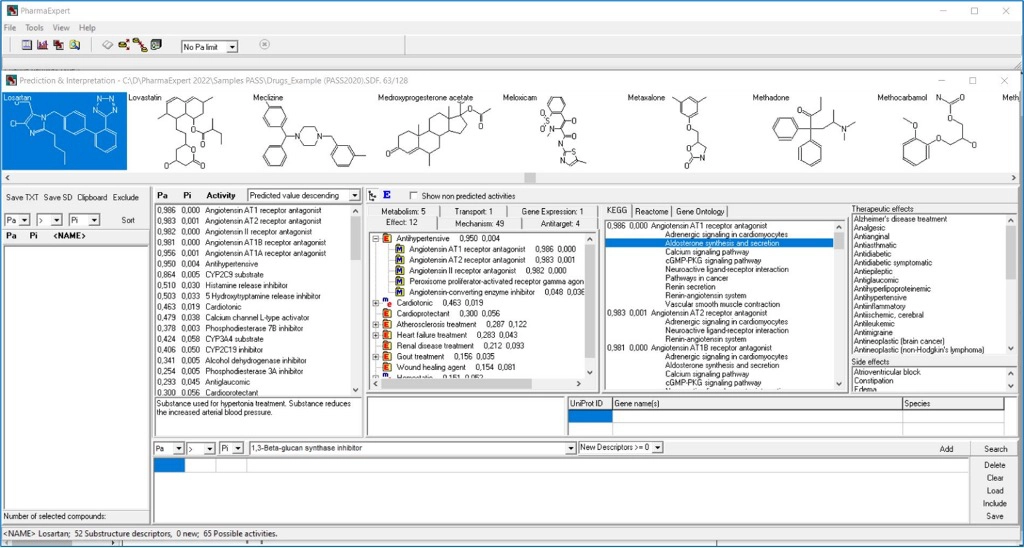
Search for multitargeted ligands

Drug-drug interaction analysis
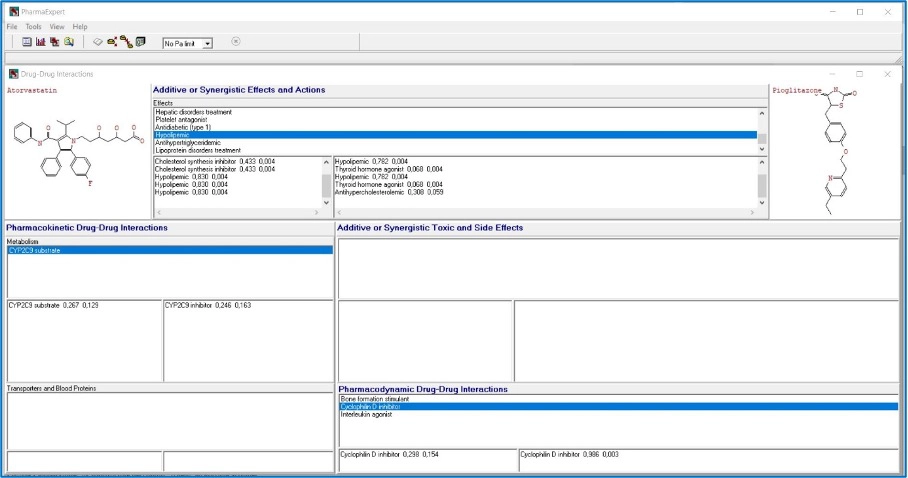
Biological activities
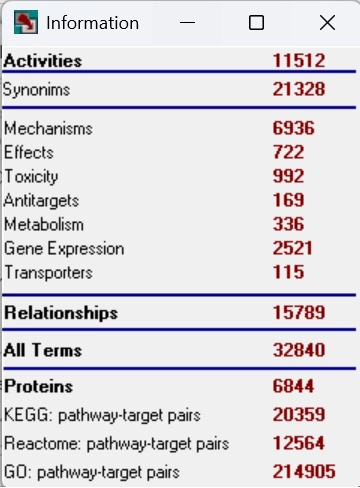
PharmaExpert 2024 contains a knowledgebase with over 15 thousands of known interactions between biological activities, as well as the relationships between proteins, signalling/regulatory pathways (KEGG or Reactome), Gene Ontology biological processes and therapeutic and adverse effects:
All biological activities are divided onto seven types:
Automatic search is provided for compounds acting on any of the mechanisms of action (or simultaneously on several mechanisms of action, up to ten) associated with the therapeutic effect or signalling/regulatory pathway (KEGG or Reactome) and biological process of Gene Ontology. Analysis of possible drug-drug interactions is performed simultaneously for all seven types of biological activity.
User-friendly interface, fast download speed and analysis of the prediction results of PASS and GUSAR
PharmaExpert results can be exported in SD or TXT file.
Benefits of PASS + PharmaExpert
Recent application of PASS and PharmaExpert
Bocharova OA, Ionov NS, Kazeev IV, Shevchenko VE, Bocharov EV, Karpova RV, Sheychenko OP, Aksyonov AA, Chulkova SV, Kucheryanu VG, Revishchin AV, Pavlova GV, Kosorukov VS, Filimonov DA, Lagunin AA, Matveev VB, Pyatigorskaya NV, Stilidi IS, Poroikov VV.
Computer-aided Evaluation of Polyvalent Medications’ Pharmacological Potential. Multiphytoadaptogen as a Case Study.
Mol Inform. 2023 Jan;42(1):e2200176.
How to cite PharmaExpert:
Lagunin AA, Goel RK, Gawande DY, Pahwa P, Gloriozova TA, Dmitriev AV, Ivanov SM, Rudik AV, Konova VI, Pogodin PV, Druzhilovsky DS, Poroikov VV.
Chemo- and bioinformatics resources for in silico drug discovery from medicinal plants beyond their traditional use: a critical review.
Nat Prod Rep. 2014 Nov;31(11):1585–611.
